Equitable Payments for Watershed Services
(ប្រទេសតង់សានី)
ការពណ៌នា
Equitable Payments for Watershed Services (EPWS) is a programme using Payments for Ecosystem Services (PES) to improve rural livelihoods.
Aims / objectives: Incentive mechanisms are used to reward upstream landowners for maintaining a beneficial land use or for adapting a particular land use practice which affects the availability and/or quality of downstream water resources. The EPWS approach has enormous potential to advance a new conservation revolution based on a compensation mechanism encouraging and financing conservation efforts as well as improving the livelihoods of the rural poor. EPWS aims to spread SLM technologies to communities, to raise awareness of the benefits of SLM and to improve land productivity. Farmer groups are formed to lead the implementation of SLM.
Methods: The approach includes supervision, support and training of farmers to ensure appropriate implementation of SLM and efficient soil erosion control. Methods include demonstration plots and farmer-to-farmer extension. Capacity building to farmers (on gender mainstreaming, good governance and relevant laws and policies) and monitoring of hydrological and livelihood status are important components of the approach. Efforts to ensure good women integration resulted in a relatively high proportion within the farmer groups (>35%). A payment mechanism has been established to compensate farmers for delivering watershed services (in form of freshwater) through implementation of SLM. Compensation payments – paid in cash and through material support – are made first to establish land use changes, and thereafter for service delivery and maintenance. They are mainly covered through international donors (DANIDA) and ‘buyers’ from the private sector, investing in watershed management.
Role of stakeholders: The EPWS team consisting of CARE International, WWF staffs and short-term workers (such as students) is always involving government staff in various activities to induce them to knowledge on EPWS in particular and the PES concept at large.
Other important information: This PES approach is very new in the country and there is little expertise within the government -which therefore needs to take deliberate efforts to groom experts through seminars and courses on PES mechanisms and its operationalisation
ទីតាំង
ទីតាំង: Morogoro, ប្រទេសតង់សានី
ចំណុចយោងភូមិសាស្ត្រនៃទីតាំងជ្រើសរើស
កាលបរិច្ឆេទចាប់ផ្តើម: មិនមាន
ឆ្នាំបញ្ចប់: មិនមាន
ប្រភេទនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
-
ក្រុមប្រពៃណី/ក្រុមជនជាតិភាគតិច
-
អ្នកផ្តួចផ្តើមក្នុងតំបន់/អ្នករុករកឃើញថ្មីៗ
-
ផ្អែកលើគម្រោង/កម្មវិធី
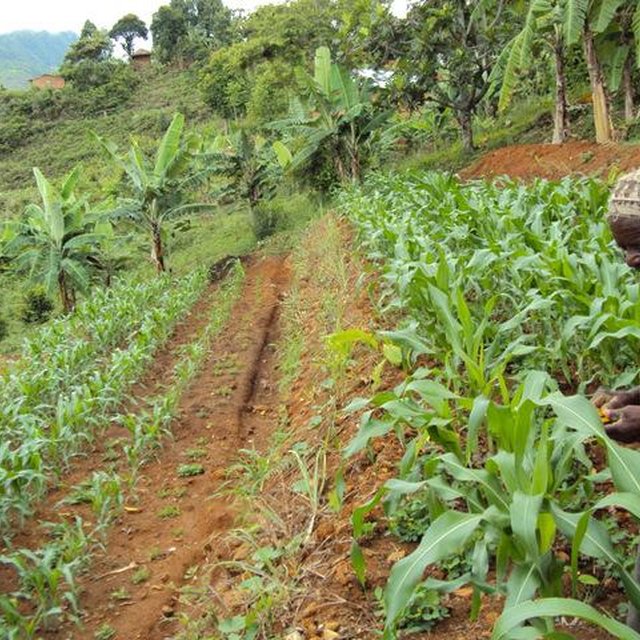

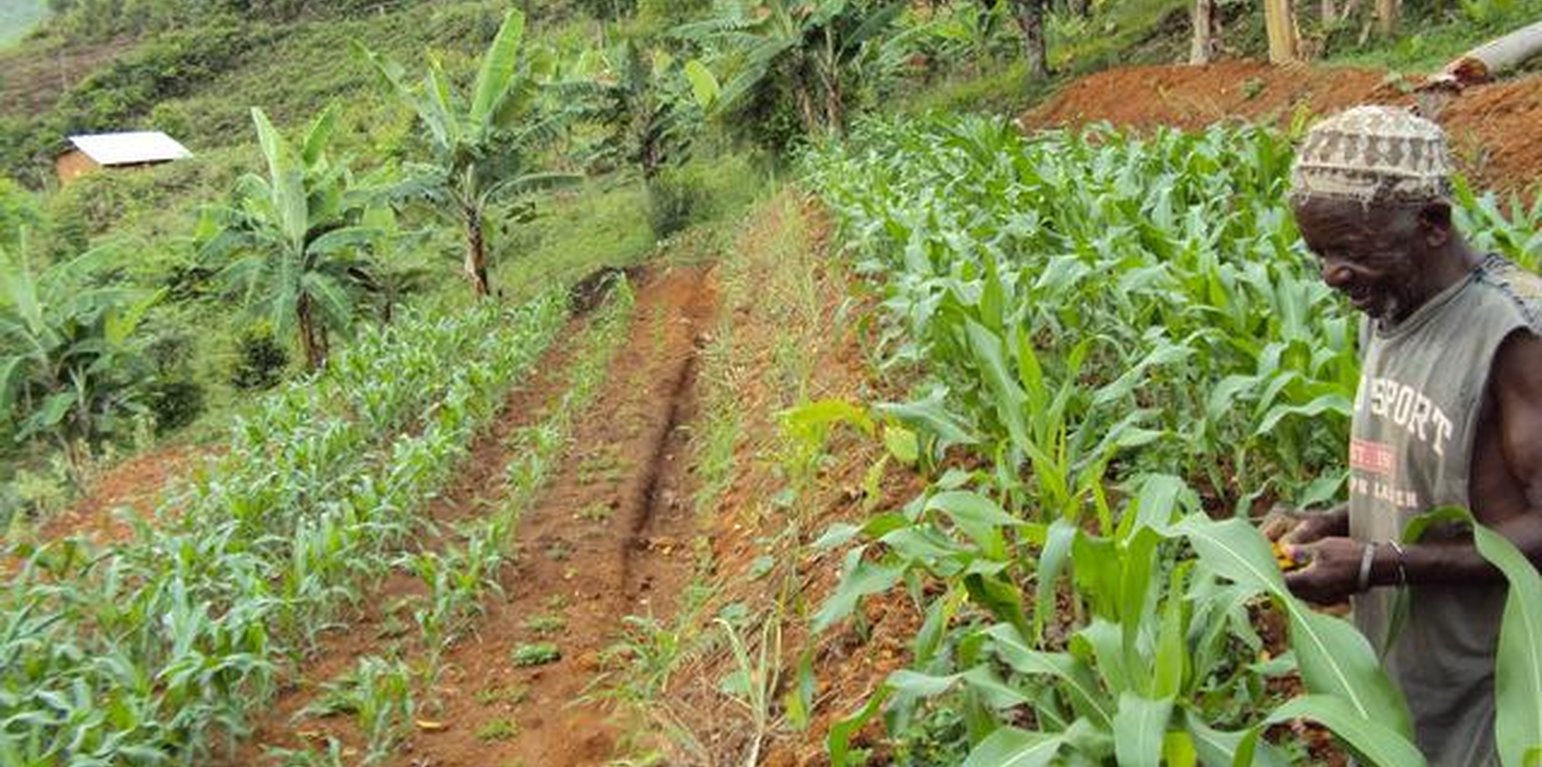
Man observing maize growth after changing his practices to Fanya juu terraces (Erasto Massoro)
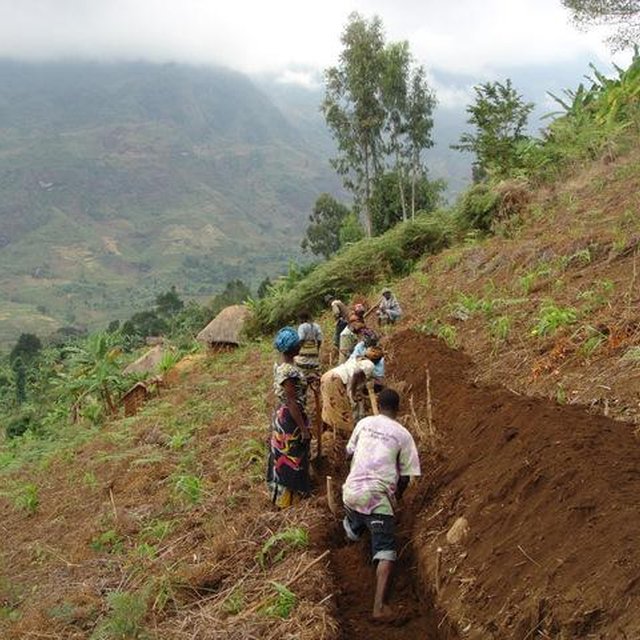

Farmers excavating Fanya juu terraces to reduce run off and improve crop production (Erasto Massoro)
គោលបំណងនៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយនិងបរិស្ថានអំណោយផល
គោលបំណងនៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Improvement of livelihoods, improvement of hydrological system)
Improve livelihoods through SLM / Improvement of hydrological system / Mechanism to ensure effectiveness, growth and sustainability of EPWS / Enhance quality of program implementation
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Land cover changes due to extensive cultivations / Deforestation and forest degradation / Soil erosion, loss of soil fertility / Low storage capacity of the Uluguru Mountains due to land cover change / Declining amount of available water in the river coming from Uluguru Mts / Increased run-off and sediment load in water system due to bare lands
លក្ខខណ្ឌអំណោយផលដល់ការអនុវត្តបចេ្ចកទេសដែលបានប្រើក្នុងវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
លក្ខខណ្ឌរាងរាំងដល់ការអនុវត្តបចេ្ចកទេសដែលបានប្រើក្នុងវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
ការចូលរួមនិងតួរនាតីរបស់ភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធដែលចូលរួម
ភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធដែលចូលរួមក្នុងវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ និងតួរនាទីរបស់គាត់
| តើមានភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធ/ភ្នាក់ងារអនុវត្តន៍ណាខ្លះដែលបានចូលរួមក្នុងវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ? |
សូមបញ្ជាក់ភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធ |
សូមពណ៌នាតួនាទីរបស់ភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធ |
| អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/សហគមន៍ |
|
Efforts to ensure good women integration resulted in a relatively high proportion within the farmer groups (>35%). |
| អ្នកឯកទេសគ្រប់គ្រងដីប្រកបដោយចីរភាព/ទីប្រឹក្សាបច្ចេកទេសកសិកម្ម |
experts on hydrology, GIS, SWC, economics, forests, etc. |
|
| អង្គការក្រៅរដ្ឋាភិបាល |
DAWASCO |
|
| វិស័យឯកជន |
Coca Cola KLtd |
|
| រដ្ឋាភិបាលថ្នាក់មូលដ្ឋាន |
Morogoro district council |
district commissioners, ward councillors |
| អង្គការអន្តរជាតិ |
DANIDA, CARE International Tanzania, WWF Tanzania |
|
ការចូលរួមពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីឬសហគមមូលដ្ឋានក្នុងតំណាក់កាលផ្សេងគ្នានៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
គ្មាន
អសកម្ម
ការគាំទ្រពីខាងក្រៅ
អន្តរកម្ម
គំនិតផ្តួចផ្តើមដោយខ្ឡួនឯង
ការចាប់ផ្តើម/ការលើកទឹកចិត្ត
ការអនុវត្តន៍
Farmers are being compensated (paid in cash) for labour and area provided for the implementation of SLM (opportunity costs). Material support through manure, seeds and working tools is given as well.
ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃ
ការសម្រេចចិត្តលើការជ្រើសរើសបច្ចេកទេស SLM
ការសម្រេចចិត្តត្រូវបានធ្វើដោយ
-
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដោយខ្លួនឯងផ្ទាល់ (គំនិតផ្តួចផ្តើមដោយខ្លួនឯង)
-
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ដោយមានការគាំទ្រពីអ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM
-
គ្រប់ភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់ដែលជាផ្នែកនៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយដោយមានការចូលរួម
-
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM បន្ទាប់ពីបានប្រឹក្សាយោបល់ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM តែឯង
-
អ្នកនយោបាយ /អ្នកដឹកនាំ
ការសម្រេចចិត្តត្រូវបានធ្វើដោយផ្អែកលើ៖
-
វាយតម្លៃទៅលើចំណេះដឹងស្តីអំពី SLM ដែលបានចងក្រងជាឯកសារបានត្រឹមត្រូវ (ផ្អែកលើភស្តុតាងជាមូលដ្ឋានដើម្បីសម្រេចចិត្ត)
-
លទ្ធផលបានពីការស្រាវជ្រាវ
-
បទពិសោធន៍ និងគំនិតផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន(ពុំមានចងក្រងជាឯកសារ)
ការគាំទ្របច្ចេកទេស ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព និងការគ្រប់គ្រងចំណេះដឹង
សកម្មភាព ឬសេវាកម្មខាងក្រោមបានប្រើជាផ្នែកនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
-
ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព/ បណ្តុះបណ្តាល
-
សេវាផ្តល់ប្រឹក្សាយោបល់
-
ការពង្រឹងសមត្ថភាពស្ថាប័ន (ការអភិរឌ្ឍន៍អង្គភាព)
-
ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃ
-
ការស្រាវជ្រាវ
ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព/ ការបណ្តុះបណ្តាល
ការបណ្តុះបណ្តាលបានផ្តល់ដល់អ្នកពាក់ព័ន្ធដូចខាងក្រោម
-
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
បុគ្គលិកចុះទីវាល/អ្នកផ្តល់ប្រឹក្សាយោបល់
ទម្រង់នៃការបណ្តុះបណ្តាល
-
អនុវត្តន៍ជាមួយការងារ
-
ពីកសិករទីកសិករ
-
ទីតាំងបង្ហាញ
-
ការប្រជុំជាសាធារណៈ
-
វគ្គបណ្តុះបណ្តាល
មុខវិទ្យាដែលបានបញ្ចូល
practical skills on SLM measures, leadership skills, governance, gender mainstreaming, policies and laws to ensure their understanding on the implementation of the EPWS project in their locality
សេវាកម្មប្រឹក្សា
សេវាកម្មប្រឹក្សាត្រូវបានផ្តល់ឱ្យ
-
នៅលើដីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
នៅមជ្ឈមណ្ឌលជាអចិន្ត្រៃ
Key elements: technical support on monitoring, provision of extension services for improved land use, situation analysis, awareness creation, capacity building on legal issues and mapping of interventions; People involved: University, foresters, hydrologists, Ministry of agriculture, land use planners
ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃ
bio-physical aspects were monitored through measurements
socio-cultural aspects were monitored through observations
economic / production aspects were monitored through observations
ការស្រាវជ្រាវ
ការស្រាវជ្រាវពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងប្រធានបទខាងក្រោម
-
សង្គមវិទ្យា
-
សេដ្ឋកិច្ច/ទីផ្សារ
-
បរិស្ថានវិទ្យា
-
បច្ចេកវិទ្យា
Research is a main part of PES as an approach to facilitate SLM adoption and has been very effective in guiding programme design; it included SLM assessment, hydrological analysis, economic analysis, social and livelihoods assessment, etc. All interventions applied were proposed by research conducted before and during implementation.
Research was carried out on-farm
ការផ្តល់ថវិកា និងការគាំទ្រសម្ភារពីខាងក្រៅ
ថវិកាប្រចាំឆ្នាំគិតជាដុល្លាអាមេរិកសម្រាប់ផ្នែក SLM
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
100,000-1,000,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: មិនមាន
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (DANIDA): 60.0%; private sector ('buyers' of ecosystem service): 9.0%; local community / land user(s) (through labour power): 31.0%
សេវាកម្ម និងការលើកទឹកចិត្តខាងក្រោមត្រូវបានផ្តល់ដល់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
ការគាំទ្រផ្នែកហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ / សម្ភារៈដែលបានផ្តល់ទៅឱ្យអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
បដិភាគសម្រាប់ធាតុចូលជាក់លាក់
-
ឥណទាន
-
ការលើកទឹកចិត្ត ឬវិធីសាស្ត្រដ៏ទៃទៀត
ការគាំទ្រថវិការ/ សម្ភារដែលបានផ្តល់ដល់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ផ្តល់ហិរញ្ញវត្ថុមួយផ្នែក
ផ្តល់ហិរញ្ញវត្ថុទាំងស្រុង
កំលាំងពលកម្មដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីគឺ
-
ដោយស្ម័គ្រចិត្ត
-
ធ្វើការងារប្តូរជាអាហារ
-
បង់ជាសាច់ប្រាក់
-
ផ្តល់ជារង្វាន់តាមរយៈការគាំទ្រជាសម្ភារៈ
ការវិភាគផលប៉ះពាល់ និងសេចក្តីសន្និដ្ឋាន
ឥទ្ធិពលនៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
ទេ
បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយជួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដើម្បីអនុវត្តន៍ និងថែទាំបច្ចេកទេស SLM?
increased production
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយនេះផ្តល់សិទ្ធិអំណាចដល់សង្គមនិងសេដ្ឋកិច្ចដែលក្រុមមិនទទួលបានផលប្រយោជន៍?
women have gained training in improving land use practices
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
Upscaling to neighbouring villages will be facilitated by the establishment of networks of farmers groups to receive training by local extension services. A steering committee, with representatives of the farmers, investors and government offices will facilitate replication in other parts of the country.
ការជំរុញទឹកចិត្តសំខាន់បំផុតនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងការអនុវត្ត SLM
-
បង្កើនផលិតកម្ម
-
បង្កើនប្រាក់ចំណេញ (សមត្ថភាព) បង្កើនអត្រាចំណេញ
-
ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
កាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ
-
កាត់បន្ថយទំហំការងារ
-
ការចំណាយ/បដិភាគ
-
ច្បាប់ និងបទបញ្ជា (ផាកពិន័យ)/ការប្រតិបត្តិ
-
កិត្តិនាម សម្ពាធសង្គម/ការផ្សាភ្ជាប់ទៅនឹងសង្គម
-
ការផ្សារភ្ជាប់ទៅនឹងចលនា/គម្រោង/ក្រុម/បណ្តាញ
-
ពង្រឹងស្មារតីផ្នែកបរិស្ថាន
-
ទម្លាប់ និងជំនឿ សីលធម៌
-
លើកកម្ពស់ចំណេះដឹង និងជំនាញ SLM
-
ការកែលម្អសោភ័ណ្ឌភាព
-
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
-
well-being and livelihoods improvement
និរន្តរភាពនៃសកម្មភាពផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីអាចបន្តដោយនិរន្តរភាពនូវអ្វីដែលបានអនុវត្តតាមរយៈការផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (ដោយមិនមានការគាំទ្រពីខាងក្រៅ)?
Participant land users can continue the activity without additional support- maintenance costs are low and the technologies will improve productivity and resilience of farming system. Upscaling to neighbouring villages will be facilitated by the establishment of networks of farmers groups to receive training by local extension services. A steering committee, with representatives of the farmers, investors and government offices will facilitate replication in other parts of the country.
សេក្តីសន្និដ្ឋាន និងមេរៀនបទពិសោធន៍
ភាពខ្លាំង: ទស្សនៈអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ភាពខ្លាំង: ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រង ឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ផ្សេងទៀត
-
PES as an additional argument for supporting property claims
-
To ensure services are delivered and payments are made and a reliable monitoring mechanism has been put in place
-
Poor people are in the centre of the objectives
-
Approach rewards land users for providing watershed services
-
PES as an incentive for conservation, helping to change land users’ vision towards improved land management
-
Once measures are applied they are simple and cheap to maintain
ចំណុចខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ : ទស្សនៈអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីវិធីដោះស្រាយ
ចំណុចខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ : ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រង ឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ផ្សេងទៀតវិធីដោះស្រាយ
-
May reduce the effectiveness of non-incentive based approaches as people will now demand rewards/payments
awareness creation is important to all players including government and local communities
-
Payments / rewards are realised before service delivery
ensure integration of PES with other approaches to ensure effectives short and long term benefits. Paying labour cost upfront while waiting for the service delivery rewards
ឯកសារយោង
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: 7 ខែ កុម្ភៈ ឆ្នាំ 2011
កែតម្រូវចុងក្រោយ: 6 ខែ កក្កដា ឆ្នាំ 2017
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ
-
Philippe Zahner (philippe.zahner@deza.admin.ch) - អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM
-
Lopa Dosteus (dosteus.lopa@co.care.org) - អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM
ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតក្នុងប្រព័ន្ធគ្រប់គ្រងទិន្នន័យរបស់វ៉ូខេត
ឯកសារនេះត្រូវបានសម្របសម្រួលដោយ
ស្ថាប័ន៖
- CARE International (CARE) - សហរដ្ឋអាមេរិក
- Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
គម្រោង






