



Biochar is the residue left after the pyrolysis of any organic matter and is used as a soil amendment. Pyrolysis occurs when the organic matter is heated in anaerobic conditions, which is usually done in specially designed kilns. Sometimes it is also made in a conventional fire, which is extinguished before the char turns to ash. Agricultural wastes like rice husks or unfilled grains are mainly used. Biochar can have many positive effects on the soil and plants:
-It buffers the pH, and has usually a high pH due to theash content.
-Due to its porous structure, it holds water and serves as refuge for microorganisms.
-It absorbs and adsorbs nutrients, both cations and anions. They are available for the plant roots.
-It can increase the resistance of plants to diseases.
Due to all these effects, the increased yields are higher than those that can be achieved only through the nutrients contained in the Biochar itself. Biochar is and was used in many parts of the world as soil amendment, with some benefits persisting for centuries. In Cambodia it was used during the Pol Pot regime to reduce the smell of the human faeces that were used on the fields due to a lack of other fertilizers. Today research in the Biochar domain is increasing, especially since the discovery of the man-made terra preta soils in South America.
Biochar is mainly used to increase the fertility, water holding capacity and carbon content of the soil. The fact that the benefits of Biochar addition to the soil remain for several years, unlike chemical fertilizers, makes it attractive to farmers. Other purposes, like the increased resistance of plants to diseases and buffering of nutrients are also of importance.
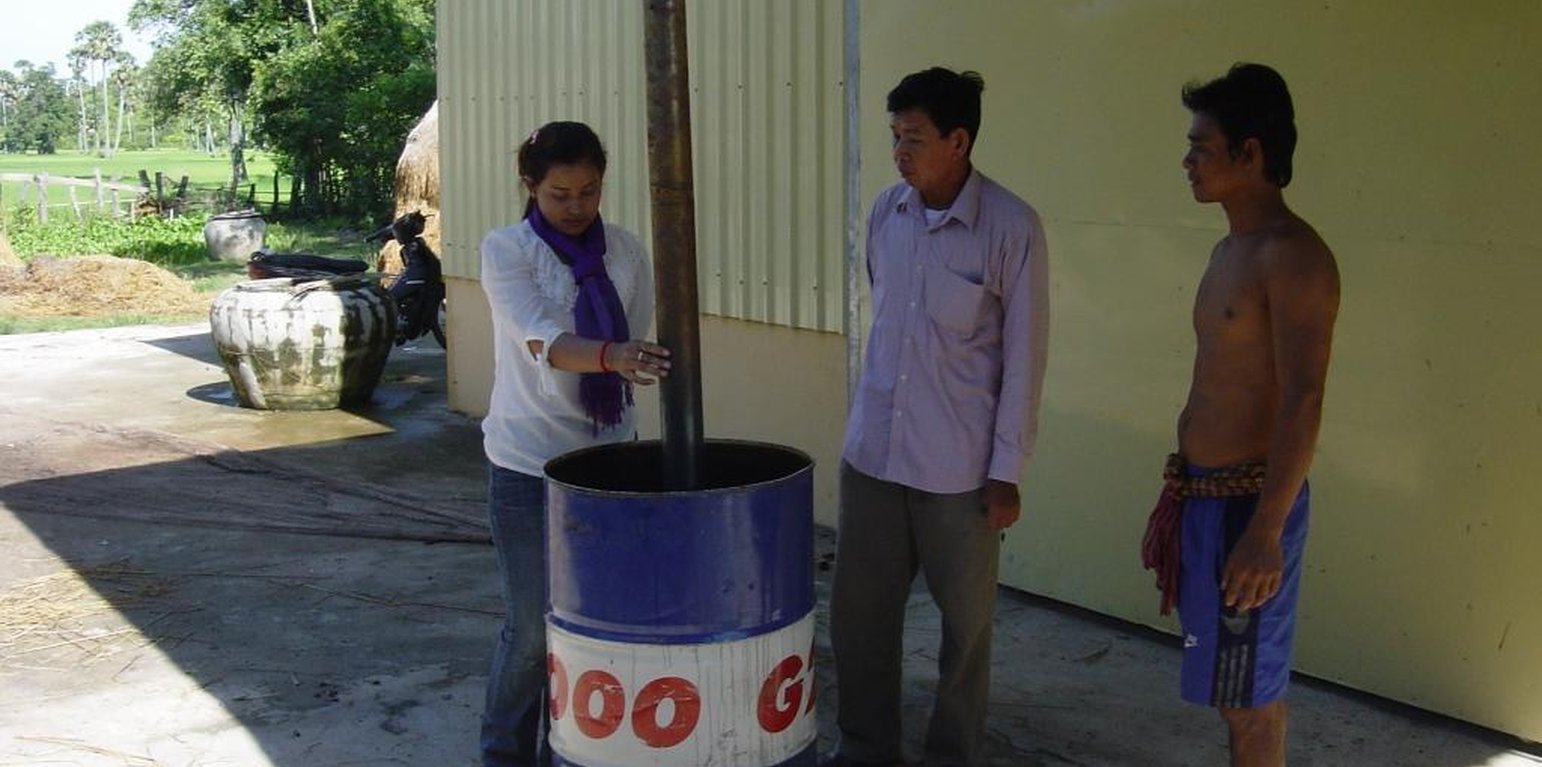
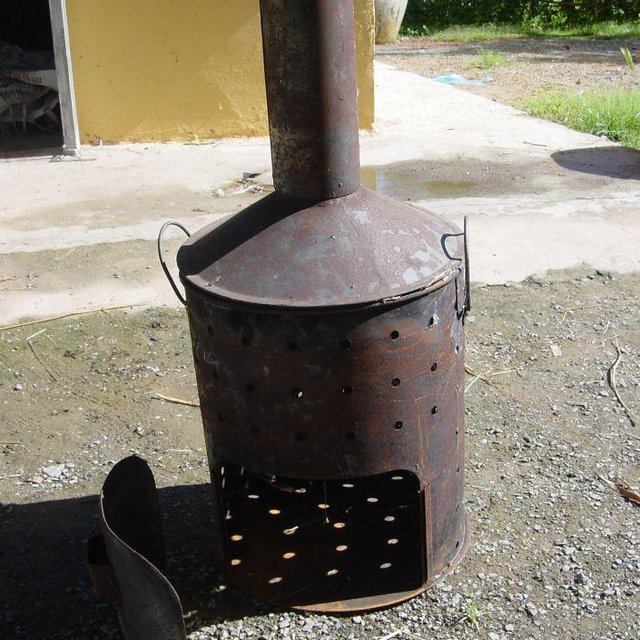
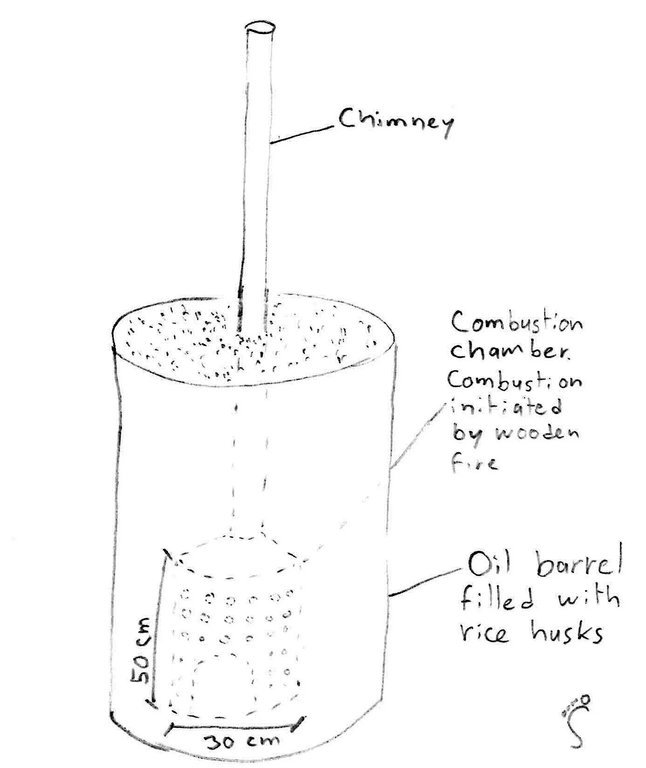
Biochar was introduced or reintroduced trough different NGOs, JICA (Japanese International Cooperation Agency) in this case study. Because of knowledge exchange between farmers, a rice husk char/ash mix, as residue from the pottery baking, was used already in 2011. In 2013 JICA borrowed a Biochar kiln to the local farmer self-help group with a training, so they could produce Biochar by themselves. The inner part of the kiln (cf. technical drawing) is filled with wood and lit. It is then put into an empty oil barrel, which is filled with rice husks. The heat pyrolyses the husks from the bottom to the top of the barrel, and the gases are burned in the inner part of the kiln and the chimney. Just before the upper part is pyrolysed, the husks are extinguished. There is a weight loss of about 50 to 60 % caused by this process. The Biochar is added to the fields after ploughing, and the fields are harrowed. In this case study, Biochar is used both in rice seed beds and in a vegetable patch. Concentrations of 0.5 kg/m2 are used in the rice seed bed, and 2.5 kg for the vegetables. Due to the little available quantities of husks, Biochar is not applied to the field yet. The use of Biochar is spreading quickly from farm to farm
The analysed area is flat (slope < 2%), with a tropical climate (dry season from November to May and wet season from June to October), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soil has a low fertility, contains little organic matter, and acidifies. The area has been deforested a long time ago, and the groundwater table is rather high (1-2 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season).
Due to climate change, farmers notice more erratic rainfall, temperature rises and more recurrent droughts. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Cattle are usually grazing on the fields after the harvest, without much control. Thus the cattle grazes too often and too much on the same spot, leading to degradation.
The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge. Several NGOs are trying to re-establish the knowledge.
ទីតាំង: Kraing Leav, Kampong Chhnang, ប្រទេសកម្ពុជា
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (approx. 0.1-1 គម2)
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖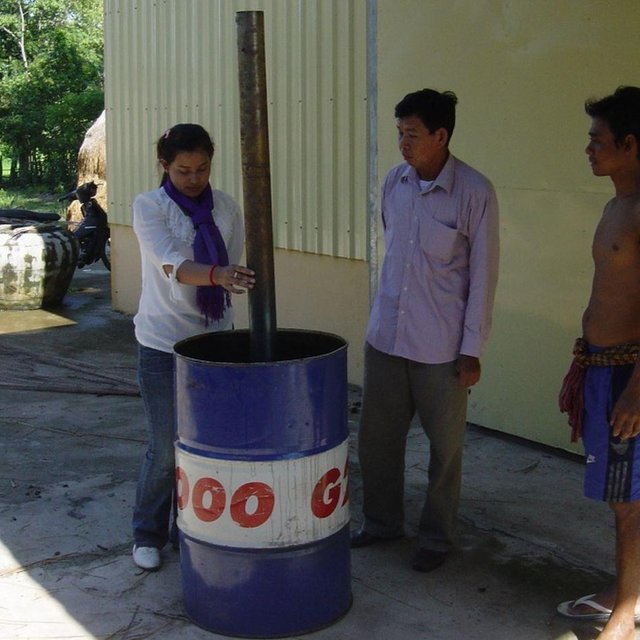





| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Riels) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Riels) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| kiln | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | ||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 50.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 0.01 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Riels) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Riels) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| labour | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| machine use | 1,0 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 100,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| rise husks | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 24.25 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 0.01 | ||||
According to the farmer, 50 to 70 % yield increase on his vegetable patches.
Rice husks become a demanded product instead of a waste. On the other hand, less pesticides are needed.
Biochar has to be made and added to the fields.
Increased production, healthier plants/less pests.
Less pesticides needed.
Increased income, less expenses on pesticides.
Plants can stand a short dry spell better if grown with Biochar.
A waste, rice husks, is returned to the soil. Biochar also adsorbs and absorbs nutrients.
The carbon from Biochar has a long half-life period in the soil .
Less pesticides needed.