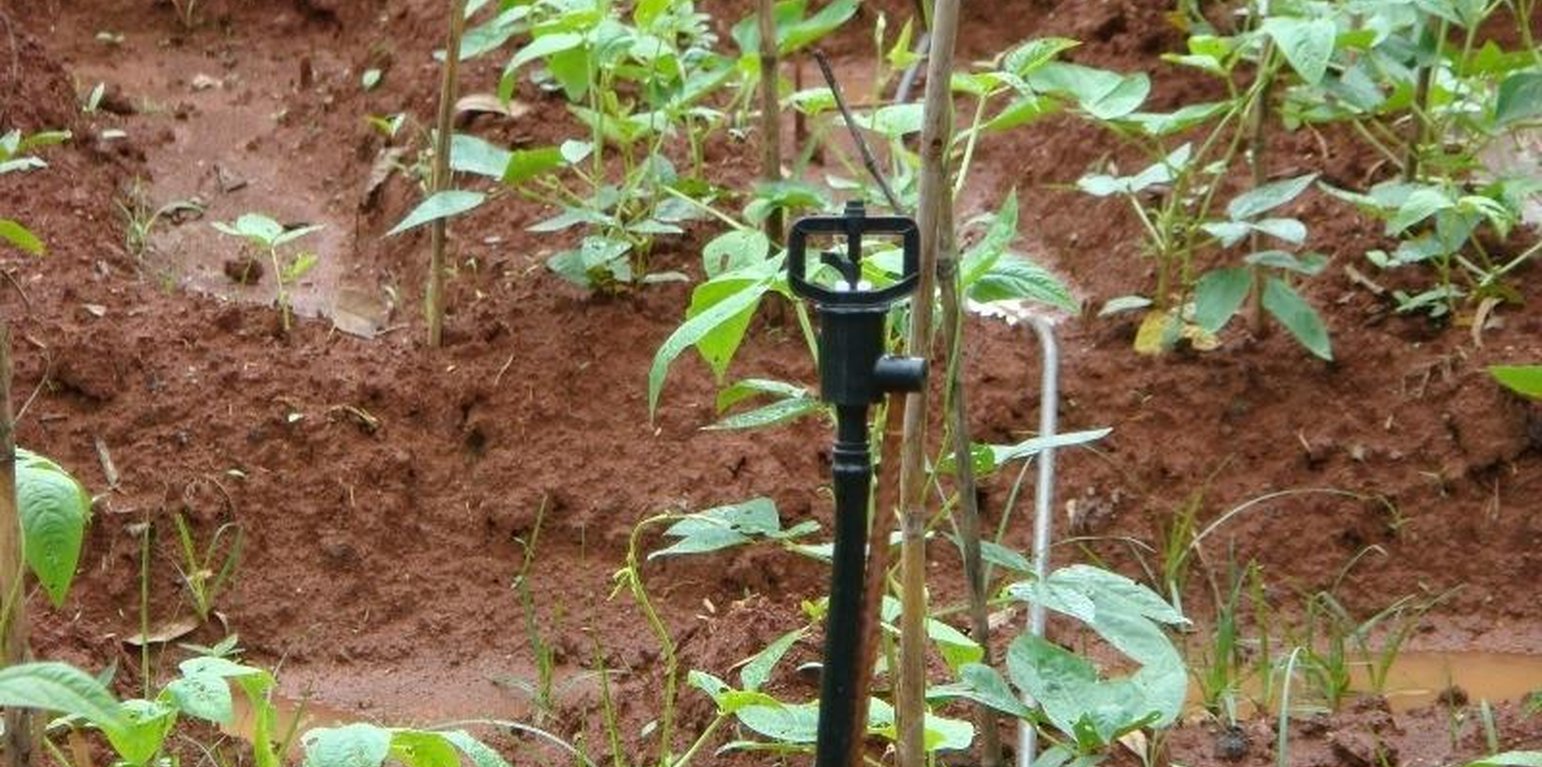
Low cost micro-sprinkler irrigation
(ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់)
Phohara sinchai - Nepali
ការពណ៌នា
An irrigation system that delivers small-sized water droplets through a rotating head allowing longer watering time with less runoff
Micro-sprinkler irrigation is an efficient and alternative method of irrigation for high value cash crops. It has been demonstrated in the Jhikhu Khola watershed (JKW) in Nepal’s middle mountains by the People and Resource Dynamics in Mountain Watersheds of the Hindu Kush-Himalayas Project (PARDYP). The NGO International Development Enterprises (IDE-Nepal) has assisted private companies to assemble and market micro-irrigation systems.
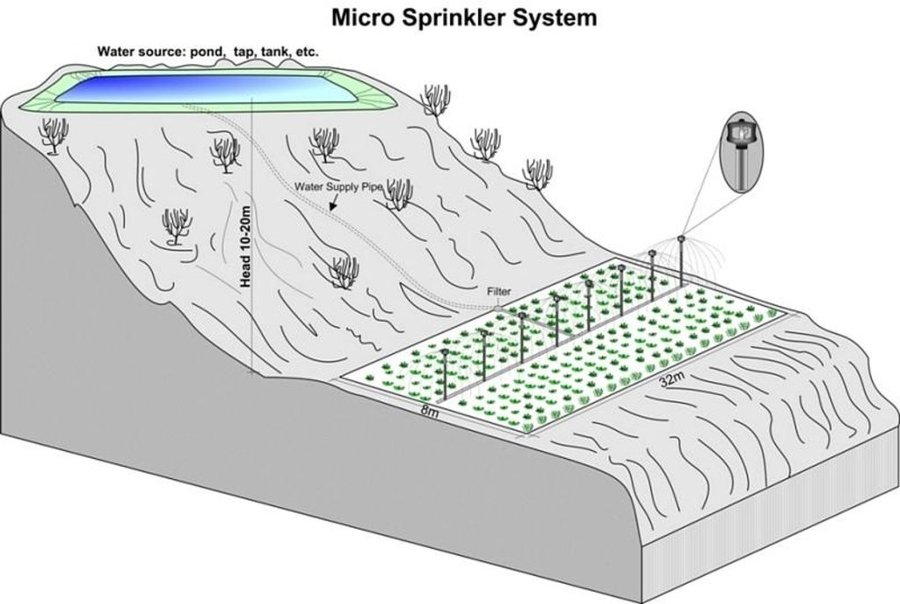
Micro sprinklers are available in a variety of configurations. They operate at a low-pressure, with water delivered at a pressure equivalent to 10-20m of head, and at a low discharge rate of 0.1-0.2 lps - equivalent to the average discharge of a 1/2 inch size public tap. A pre-assembled micro-irrigation system generally consists of 4 to 8 sprinkler heads at 4m intervals connected by half inch piping. Micro sprinklers are most suitable for closely cropped vegetables like onion and garlic. PARDYP demonstrated, tested, and promoted the system to show land users the potential to use irrigation water very efficiently, which is important because water is in short supply for much of the year after the monsoon finishes in September. In the test area, much of the land is left fallow after the monsoon crops have been harvested as it is difficult to grow winter crops because of the lack of irrigation
water.
The system is easy to install and move around. It needs a reliable source of water, such as a water harvesting tank or a tap, located about 10-20m above the field to be irrigated. A water tank can be installed at the appropriate height to give an adequate water head. The preassembled micro-sprinkler heads are inserted into the ground on a support stand and are connected to the water source via a conveyance pipe. The water passes through a filter before entering the sprinkler heads to prevent the sprinklers becoming clogged up; the system needs regular cleaning.
ទីតាំង
ទីតាំង: Kavrepalanchowk/ Jhikhu Khola watershed, ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ចំណុចយោងភូមិសាស្ត្រនៃទីតាំងជ្រើសរើស
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (approx. 0.1-1 គម2)
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖
-
តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
ជាផ្នែកនៃប្រព័ន្ធប្រពៃណី (> 50 ឆ្នាំ)
-
ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
-
តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
គោលបំណងចម្បងៗ
-
ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
-
កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
-
ការពារតំបន់ទីជម្រាល/តំបន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមបញ្ចូលជាមួយបច្ចេកទេសផ្សេងទៀត
-
អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
-
កាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ
-
បន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
-
កាត់បន្ថយការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
-
បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
-
បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
-
Improve efficiency of water use
ការប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ: ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត, ពពួកសណ្តែក - ផ្សេងៗ, ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងបារាំង, ដំណាំយកគ្រាប់ - ល្ង គ្រាប់ផ្កាប៉ុបពី មូតាដ ផ្សេងៗ, wheat, tomatoes
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ: 3
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
-
ទឹកភ្លៀង
-
ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
-
ប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រពទាំងស្រុង
គោលបំណងទាក់ទងនឹងការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
-
ការបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ដែលមិនអាចអនុវត្តបាន
ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីដែលបានដោះស្រាយ
-
ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក - Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
ក្រុម SLM
-
ការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព (រួមទាំងការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ)
វិធានការ SLM
-
វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង - M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
គំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
លក្ខណៈបច្ចេកទេស
Micro-sprinkler irrigation system and technical specification.
Location: Patalekhet and Kuttal. Kavrepalanchowk district
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, water spreading (efficiently)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: from conventional irrigation (flood / bucket) to efficient irrigation.
Author: A.K. Thaku
ការបង្កើតនិងការថែទាំ៖ សកម្មភាព ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
- ថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានគណនា៖ ក្នុងឯកតាបច្ចេកទេស (ឯកត្តា៖ Micro-sprinkler irrigation volume, length: 4 to 8 sprinkler heads at 4 m intervals)
- រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ការគណនាថ្លៃដើម៖ ដុល្លារ
- អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ (ទៅជាដុល្លារអាមេរិក)៖ 1 USD = មិនមាន
- ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមក្នុង ១ ថ្ងៃ៖ 2.10
កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលលើថ្លៃដើម
The system itself is a dominating factor affecting the cost.
សកម្មភាពបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
-
Identify an appropriate water source (water harvesting tank, tap, pump) (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: beginning of the growing season)
-
Fix the micro-sprinkler heads in the ground with their support stands (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: growing season)
-
Connect sprinkler system with water source through conveyance pipes (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: growing season)
ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល |
ឯកតា |
បរិមាណ |
ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (ដុល្លារ) |
ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (ដុល្លារ) |
% នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|
កម្លាំងពលកម្ម
|
| Installing micro-sprinkler system |
Persons/unit |
2,0 |
2,1 |
4,2 |
100,0 |
|
សម្ភារៈ
|
| Sprinkler heads, pipes etc. |
unit |
1,0 |
12,2 |
12,2 |
|
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស |
16.4 |
|
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ |
16.4 |
|
សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
-
Regular monitoring of the sprinklers’ performance (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: during irrigating period / regularly)
-
Cleaning nozzles if clogging problem occurs (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: during irrigating period / regularly)
ធាតុចូលនិងថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល |
ឯកតា |
បរិមាណ |
ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (ដុល្លារ) |
ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (ដុល្លារ) |
% នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|
កម្លាំងពលកម្ម
|
| Maintaining sprinkler system |
Persons/unit |
1,0 |
2,1 |
2,1 |
100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស |
2.1 |
|
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ |
2.1 |
|
បរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងជាមធ្យមប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
-
< 250 មម
-
251-500 មម
-
501-750 មម
-
751-1,000 មម
-
1,001-1,500 មម
-
1,501-2,000 មម
-
2,001-3,000 មម
-
3,001-4,000 មម
-
> 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
-
សើម
-
មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
-
មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
-
ស្ងួត
លក្ខណៈសម្គាល់នៃអាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងជាមធ្យមប្រចាំឆ្នាំគិតជា មម៖ 1070.0
Thermal climate class: subtropics
ជម្រាល
-
រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
-
ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
-
មធ្យម (6-10%)
-
ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
-
ទីទួល (16-30%)
-
ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
-
ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី
-
ខ្ពង់រាប
-
កំពូលភ្នំ
-
ជម្រាលភ្នំ
-
ជម្រាលទួល
-
ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
-
បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
រយៈកម្ពស់ធៀបនឹងនីវ៉ូទឹកសមុទ្រ
-
0-100 ម
-
101-500 ម
-
501-1,000 ម
-
1,001-1,500 ម
-
1,501-2,000 ម
-
2,001-2,500 ម
-
2,501-3,000 ម
-
3,001-4,000 ម
-
> 4,000 ម
បច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្តនៅក្នុង
-
សណ្ឋានដីប៉ោង
-
សណ្ឋានដីផត
-
មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
ជម្រៅដី
-
រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
-
រាក់ (21-50 សម)
-
មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
-
ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
-
ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនៈភាពដី (ដីស្រទាប់ខាងលើ)
-
គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
-
មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
-
ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ក្រោមស្រទាប់លើ)
-
គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
-
មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
-
ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
កម្រិតសារធាតុសរីរាង្គក្នុងដីស្រទាប់លើ
-
ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
-
មធ្យម (1-3%)
-
ទាប (<1%)
ដង្ហើមទឹកក្នុងដី
-
ផ្ទៃខាងលើ
-
< 5 ម
-
5-50 ម
-
> 50 ម
ភាពអាចរកបាននៃទឹកលើដី
-
លើស
-
ល្អ
-
កម្រិតមធ្យម
-
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រព្រឹត្តិកម្ម)
-
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
-
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
-
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
-
ទឹកមិនអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាន
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖
តើមានបញ្ហាទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលដែរឬទេ?
ការកើតឡើងនៃទឹកជំនន់
ភាពសំបូរបែបនៃជម្រកធម្មជាតិ
ចរិតលក្ខណៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលប្រើបច្ចេកទេស SLM
ទីផ្សារ
-
សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
-
ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
-
ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន
-
តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
-
10-50% នៃចំណូល
-
ច្រើនជាង 50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព
-
មិនល្អខ្លាំង
-
មិនល្អ
-
មធ្យម
-
មាន
-
មានខ្លាំង
កម្រិតនៃការប្រើគ្រឿងយន្ត
-
ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
-
ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
-
គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ
-
នៅមួយកន្លែង
-
ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
-
ពនេចរ
បុគ្គល ឬក្រុម
-
ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
-
ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
-
សហករ
-
មានបុគ្គលិក (ក្រុមហ៊ុន, រដ្ឋ)
អាយុ
-
កុមារ
-
យុវវ័យ
-
វ័យកណ្តាល
-
មនុស្សចាស់
ផ្ទៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ក្នុងមួយគ្រួសារ
-
< 0.5 ហិកតា
-
0.5-1 ហិកតា
-
1-2 ហិកតា
-
2-5 ហិកតា
-
5-15 ហិកតា
-
15-50 ហិកតា
-
50-100 ហិកតា
-
100-500 ហិកតា
-
500-1,000 ហិកតា
-
1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
-
> 10,000 ហិកតា
មាត្រដ្ឋាន
-
ខ្នាតតូច
-
ខ្នាតមធ្យម
-
ខ្នាតធំ
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដីធ្លី
-
រដ្ឋ
-
ក្រុមហ៊ុន
-
ភូមិ
-
ក្រុម
-
ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
-
ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
សិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
-
ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
-
កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
-
ឯកជន
សិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
-
អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
-
ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
-
កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
-
ឯកជន
ប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
ផលប៉ះពាល់
ផលប៉ះពាល់សេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
due to increased vegetable production
ផលប៉ះពាល់វប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
an informal network of sprinkler users formed
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
livelihood and human well-being
vegetableproduction became possible with use of less water, production increased.
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើអេកូឡូស៊ី
សំណើមដី
due to precise delivery of water (0.1 - 0.2 lps)
ការបាត់បង់ដី
due to uniform application of water to crops grown on slopping land
Made the irrigation of multiple vegetables possible
as users can shift the system around to irrigate
ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
អត្ថប្រយោជន៍បើប្រៀបធៀបនឹងថ្លៃដើមក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
រយៈពេលខ្លី
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
អត្ថប្រយោជន៍បើប្រៀបធៀបនឹងថ្លៃដើមក្នុងការថែទាំបច្ចេកទេស
រយៈពេលខ្លី
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ កើនឡើង
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ការទទួលយក និងការបន្ស៊ាំ
ភាគរយនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីនៅតំបន់ដែលបានទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
-
តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
ក្នុងចំណោមអ្នកទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេសនេះ តើមានប៉ុន្មានភាគរយដែលបានអនុវត្តន៍ដោយមិនបានទទួលការលើកទឹកចិត្តជាសម្ភារៈ?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
ចំនួនខ្នងផ្ទះ និង/ឬតំបន់ដែលគ្របដណ្តប់
515 households in an area of 0.1 - 1 sq km. (200 - 500 persons / sq km)
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ចំពោះលក្ខខណ្ឌប្រែប្រួលណាមួយដែលត្រូវបានបន្ស៊ាំ?
-
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
-
បម្រែបម្រួលទីផ្សារ
-
កម្លាំងពលកម្មដែលអាចរកបាន (ចំណាកស្រុក)
សេក្តីសន្និដ្ឋាន និងមេរៀនបទពិសោធន៍
ភាពខ្លាំង: ទស្សនៈអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
Sprinkler showers drive away insects
-
Is equally useful to irrigate fallow land to increase soil moisture.
ភាពខ្លាំង: ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រង ឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ផ្សេងទៀត
-
Extremely useful for closely spaced, leafy vegetables such as onions, garlic and spinach grown in small areas.
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Suitable for row crops like bitter gourd during their initial stage of growth; and also good for a wide range of row crops (tree crops and vegetables) that require low-fl ow irrigation.
-
Most appropriate for sloping land
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Can be used on level land if tank placed
at appropriate height
-
Easy to transport, and possible to use for different crops in rotation
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Position of the sprinkler head should be changed to acquire 100% overlap of watered areas.
-
Allows uniform distribution of water and longer watering time with less runoff; therefore reduces soil loss from sloping land and increases soil moisture status.
How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology should be shared with a wider audience
ចំណុចខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ : ទស្សនៈអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីវិធីដោះស្រាយ
-
Sometimes sprinklers stop functioning as they do not rotate and can become disconnected from the pipe
Regular checking and cleaning
-
Are susceptible to being stolen as they can be easily dismantled
Regular site visits by the farmer
ចំណុចខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ : ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រង ឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ផ្សេងទៀតវិធីដោះស្រាយ
-
Requires sufficient head pressure therefore less suitable for plain lands.
It can be used in plain lands with alternative arrangements i.e. by constructing a platform for drum/ tank at appropriate height.
ឯកសារយោង
អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ
-
David Streiff
-
Alexandra Gavilano
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: 7 ខែ មិថុនា ឆ្នាំ 2011
កែតម្រូវចុងក្រោយ: 5 ខែ កញ្ញា ឆ្នាំ 2019
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ
-
Madhav Dhakal - អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM
-
Sanjeev Bhuchar - អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM
-
Isabelle Providoli - អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM
ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតក្នុងប្រព័ន្ធគ្រប់គ្រងទិន្នន័យរបស់វ៉ូខេត
ឯកសារនេះត្រូវបានសម្របសម្រួលដោយ
ស្ថាប័ន៖
- ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
គម្រោង
ឯកសារយោងសំខាន់ៗ
-
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD: ICIMOD








