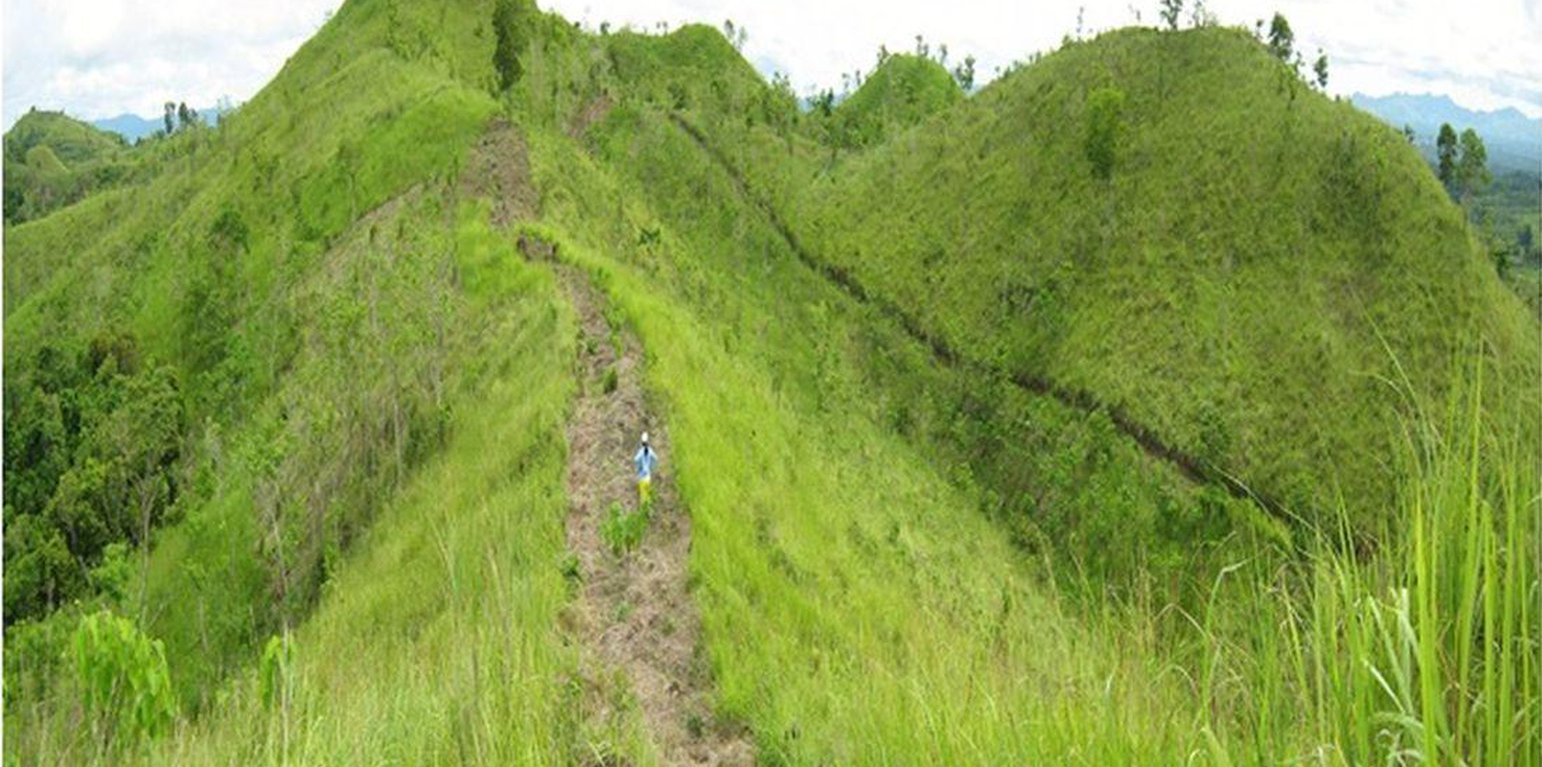




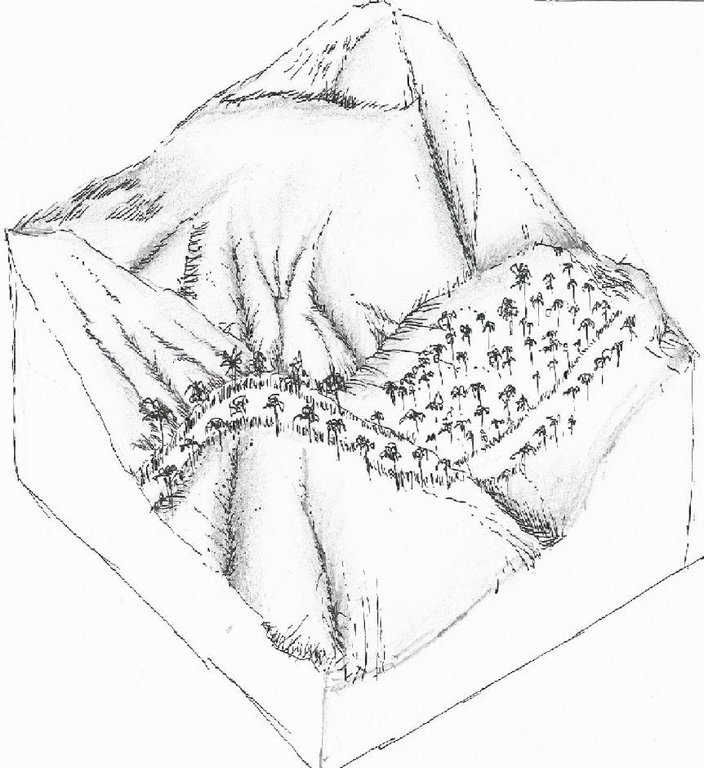
Firebreaks are 1,000-meter long, ten meters wide, located in the periphery/boundary and/or top of the ridge as barriers to slow or stop the progress of a fire. Greenbreaks are formed within the firebreaks by planting fire-resistant species in the gap portions such as kakawate (Gliricidia sepium), banana (Musa) abaca (Musa textilis), malunggay (Moringa oleifera), and cassava (Manihot esculenta). As a practice, fire breaks are established in every ten hectares to form a block, but it can vary depending on the slope of the area. Fires tend to spread quickly in higher slopes compared to flat areas, thus, more firebreaks are recommended.
Purpose of the Technology: Firebreaks/greenbreaks are established to protect the forest trees and wildlings from disturbances and wildfire. In case of forest fire, firebreaks/green breaks prevent the spread of fire from one block to another. Wildlings are seedlings derived from seeds scattered by birds, insects, animals and wind without human intervention, and allowed to grow naturally in the forest. The green breaks are planted with cash crops as immediate source of food and additional income for the land users.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The first step in creating fire breaks is the removal of all combustible materials such as deadwoods and cogon grasses (Imperata cylindrica) by using hoe or plow. Then, fire-resistant plant species such as kakawate (Gliricidia sepium) cuttings (i.e. 1-meter high) are staked at 1.5- meter spacing on both sides of the 10-meter wide firebreak. Kakawate is the preferred plant species because the leaves have high Nitrogen content and resistant to fire and drought. Maintenance of firebreaks/green breaks is done before the onset of the dry season. It is done through brushing of invasive weeds and plating of root crops. The pruning of kakawate is done every three years." Bayanihan" (rotational schedule of labour), a traditional communal concept of voluntary work is practiced during the establishment of the technology.
Natural / human environment: The area is part of the forest reserve in Danao, Bohol primarily intended for nature conservation and protection. It is about 100-500 m.a.s.l with moderately rolling to hilly slopes. It is under humid tropics climate with an average annual rainfall of 1500-2000 mm per year. The soil is loam, shallow depth, low fertility, with good drainage and medium water storage capacity. The area has high biodiversity as indicated by the presence of different indigenous trees and plants species, and wild animals and birds. The land users who apply the technology are small-holder farmers.These are members of a local cooperative. The population density is about 10-50 persons per sq. km. Since extraction of resources from the forest is prohibited, off-farm income is very important to the land users. Access to basic services and infrastructures are low.
ទីតាំង: Danao, Bohol, Brgy. San Miguel, ប្រទេសហ្វីលីពីន
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (3.6 km²)
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: ច្រើនជាង 50 ឆ្នាំមុន (ប្រពៃណី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖



| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (មិនមាន) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (មិនមាន) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| clearing of cogon grass in the firelines and Planting of kakawate cuttings | ha | 1,0 | 26,66 | 26,66 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 26.66 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 26.66 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (មិនមាន) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (មិនមាន) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| brushing/clearing as well as pruning of kakawate/per year | ha | 1,0 | 31,1 | 31,1 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 31.1 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 31.1 | ||||
Through the technology, People's Organization (PO) members were encouraged to plant cash crops as greenbreaks as an immediate source of food and additional income.