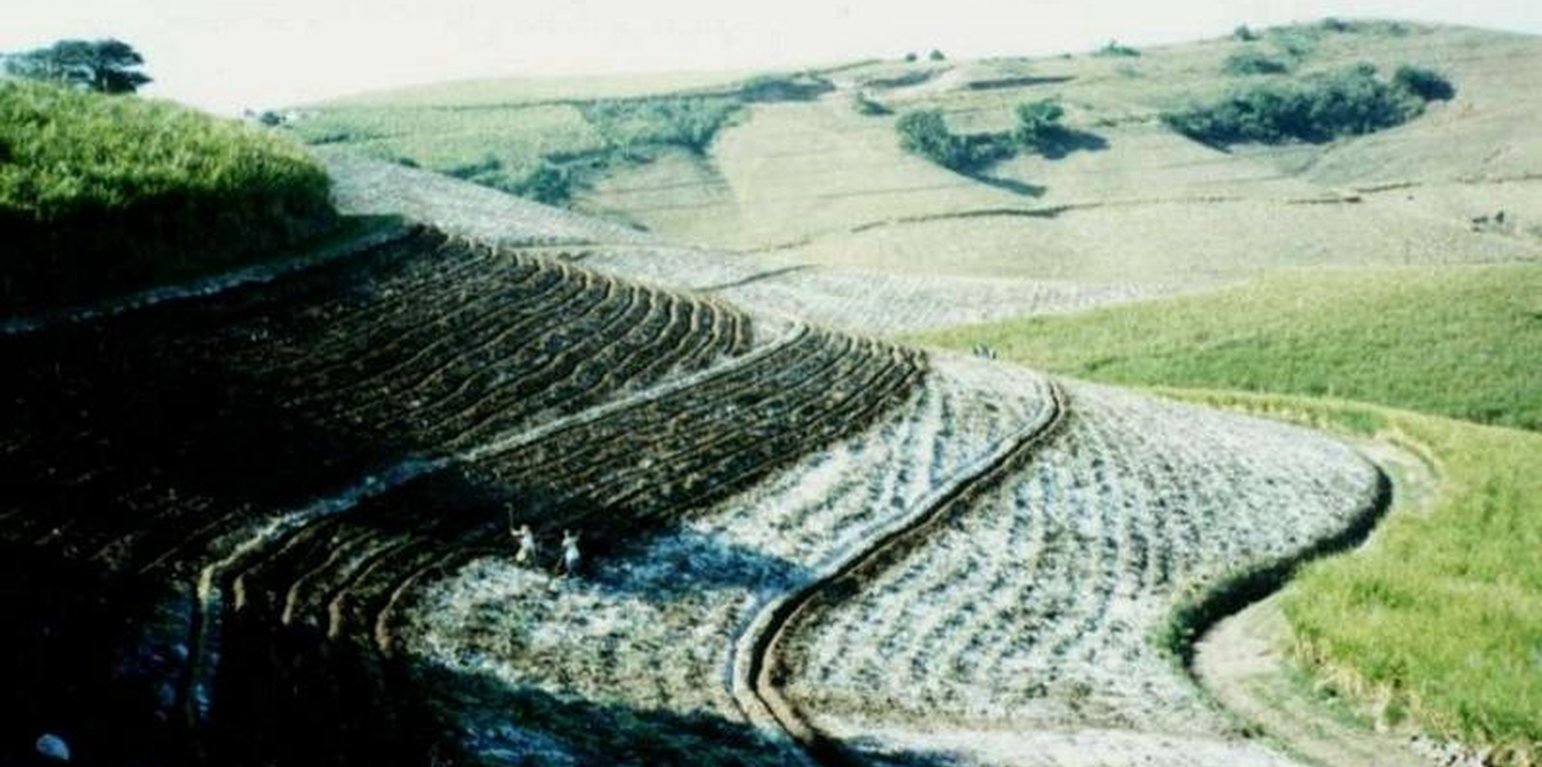




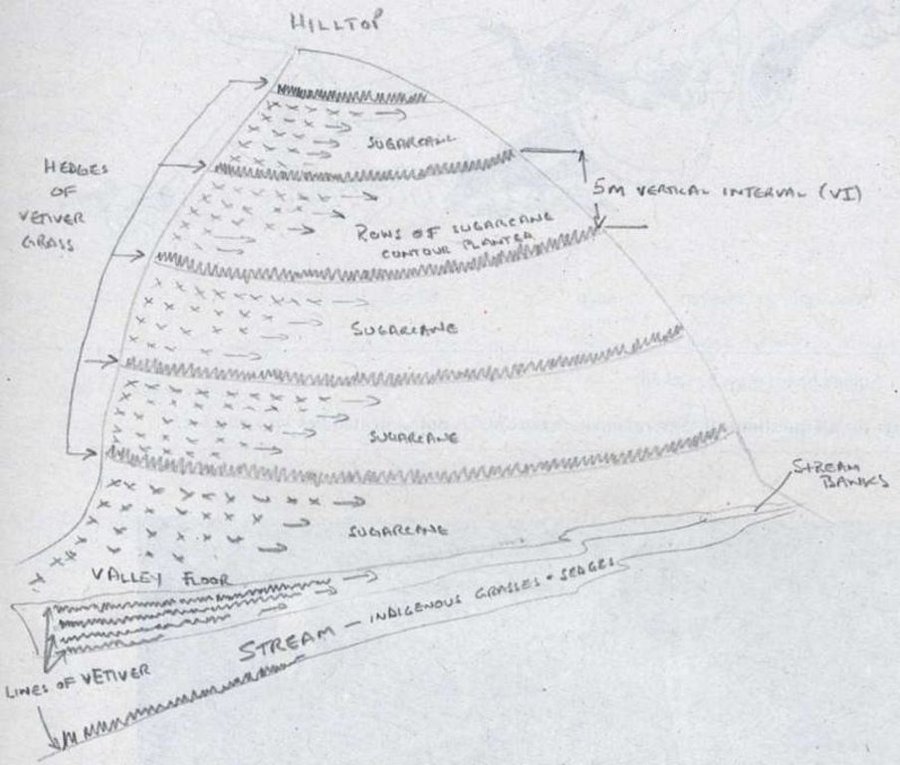
This example of vetiver grass barriers comes from a commercial farm in Kwa-Zulu Natal, South Africa, where sugar cane is grown on a large scale under a rainfall regime of around 1,000 mm per year. Vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides), which had been growing naturally on the farm for years in isolated clumps, began to be used in 1989 to form vegetative hedges along the contour.
The purpose of these hedges is to protect the land from surface erosion by creating semi-permeable barriers, allowing excess runoff to filter through but holding back sediment. Infiltration is thus increased and moisture conserved in-situ. Although sugar cane in itself protects the soil quite well when the canopy is closed, after harvest on the moderate to steep slopes (10% to >30%) and erodible soils of the north coast of Kwa-Zulu Natal, extra protection is required. The vetiver system is supplemented by other soil conservation measures such as strip cropping, terraces, mulching and minimum tillage – all of which are used to some extent on this farm. Vetiver also helps by permanently marking the contour line, which then guides land preparation. In common with other vegetative barriers, vetiver lines lead to the formation of terraces over time, through the effect of tillage and water erosion between the strips.
Vetiver clumps are dug up and separated into slips (tillers), cut to a length of 10 cm and then planted 10–15 cm apart along the contour, also by stream banks, and by roadsides, just before the rains. This ensures good establishment. Single lines are used in this farm, though double lines are more effective at creating a hedge, and are the normal recommendation. Work starts at the top of the slope, and continues downwards. The cross-slope grass hedges are sited at 5 m vertical intervals on slopes of more than 10%, in lines about 200 m long. The cost of vetiver grass planting depends very much on slope (and thus the number of lines to be planted), availability of materials and labour.
Maintenance is very important, as vetiver often requires ‘gapping-up’ to keep the barrier dense, and it needs also to be cut back before the dry season to prevent it burning. The cut material can be used for mulching. Vetiver is poorly palatable, and therefore not useful as fodder. The maximum height of a vetiver hedge is kept down to approximately 50 cm. This minimises shading and competition, keeps the fire risk low, increases tillering (for production of vegetative splits) and ensures adequate density.
ទីតាំង: Lower Tugela district, KwaZulu/Natal, ប្រទេសអាហ្រ្វិកខាងត្បូង
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (8.0 km²)
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖






| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (ដុល្លារ) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (ដុល្លារ) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Plant and fertilize | persons/day/ha | 15,0 | 2,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| hoe | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| Vetiver | cubic meter | 1,0 | 66,0 | 66,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | |||||
| Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 140.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 140.0 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (ដុល្លារ) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (ដុល្លារ) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Maintaining plot | persons/day/ha | 5,0 | 2,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| hoe | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | |||||
| Biocides | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Slips | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 25.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 25.0 | ||||
Contains a lot of oil, only when mature (after 2 years) but does not affect the roots
Row spacing
The planting is aligned for next planting
From 8-12 cuttings before replanting sugarcane (+-15 years); 3000-3500 R/ha cost for replanting the sugarcane.