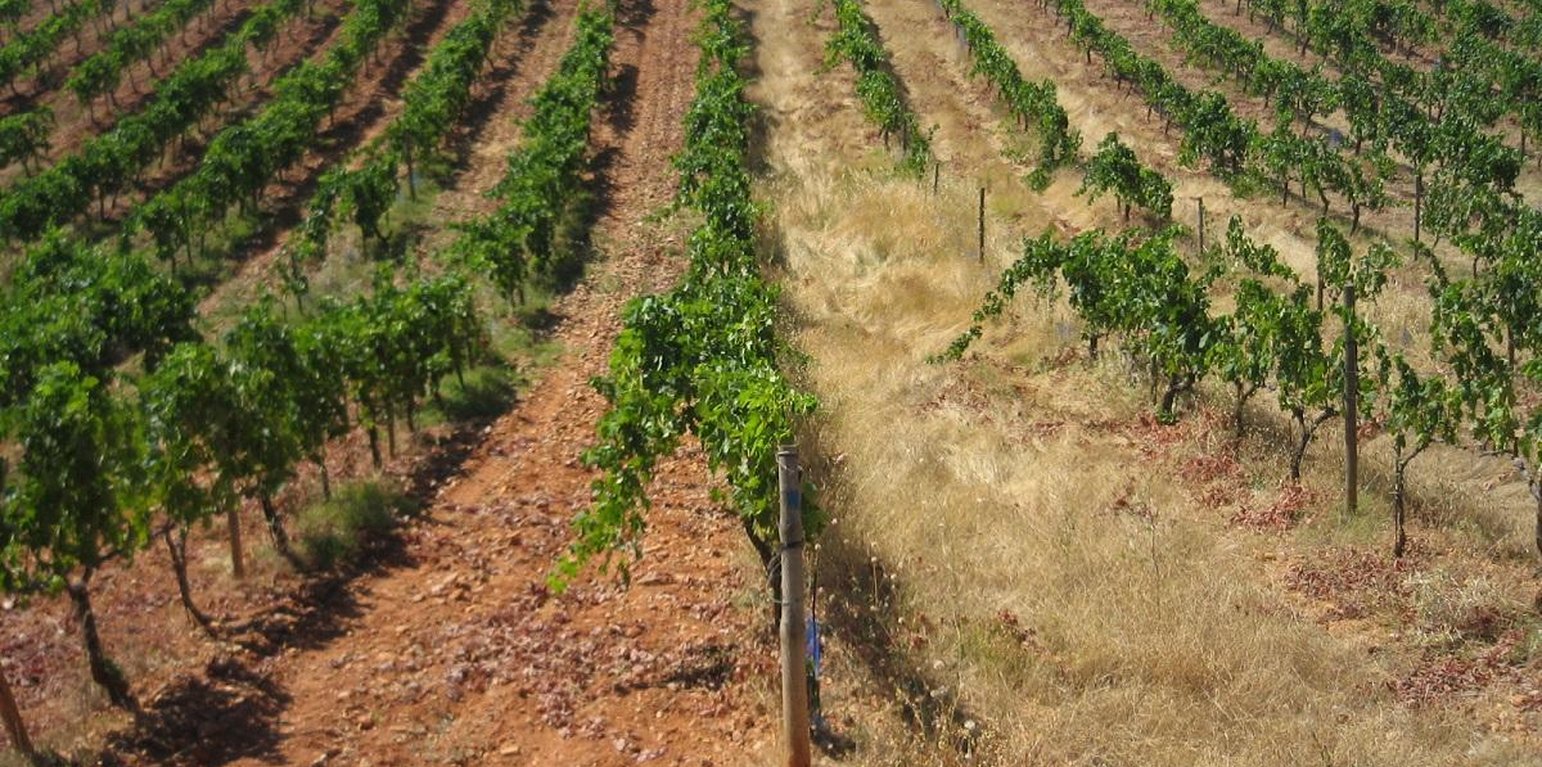




In total there were 66 rows of vineyards of the Tempranillo red variety, spaced 3 m apart with a distance of 2.5 m between vines. To date they have been worked using conventional tilling without herbicides: most of the work is done mainly in the winter, followed by two or three sessions in spring aimed at controlling the growth of weeds, which is conditioned by the spring rains.
The technology is based on minimum tillage and the use of Secale cereale L and Brachypodium distachyon (L.) as cover crops to protect the soil against erosion and to increase the organic matter.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purposes of this technology are to fight against erosion and water runoff and to increase soil organic matter.
Indirectly this technology contributes to increase biodiversity in the vineyards and it could have some positive effects on wine quality (related to the content of sugar and poliphenoles) as proved by some authors (Dry et al., 2001).
Cover crops usually increase the soil moisture but on the other hand, along the summer, the cover crops and the vines are in competition for the scarce water available in the area.
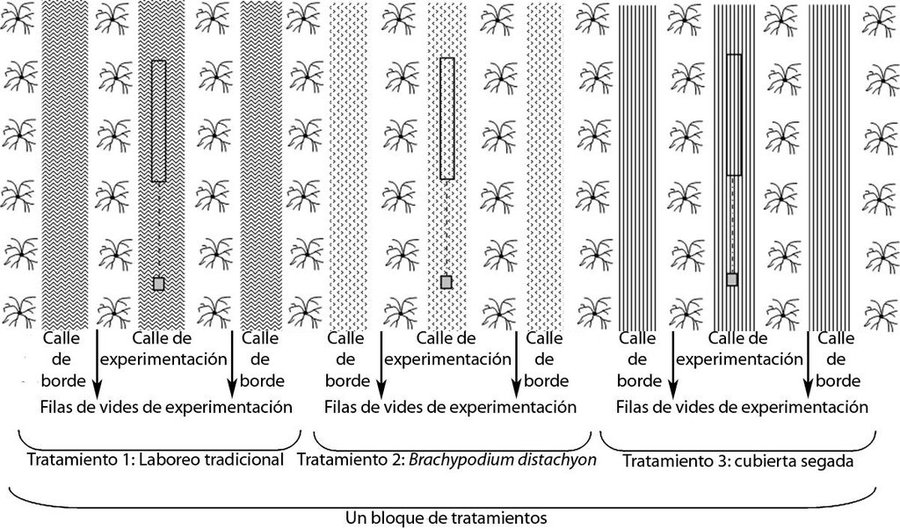
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The plant cover in the centre of the rows was sown in mid-November, following the copious rains in the autumn of 2006. A minimum tillage (15cm depth) is carried out before sowing. The seeding rates were 70 kg/ha for rye, Secale cereale L., and 40 kg/ha for purple false brome, Brachypodium distachyon (L.) P. Beauv. This latter cover had to be reseeded by hand since the seeds have to be buried at a very low depth. It sprouts in late winter or early spring and by late June it is already mature and dry, at which point it self-sows and it sprouts spontaneously again the following autumn. The Secale cover has to be cut in spring and re-sown in late autumn.
Once sown, the resulting vineyard was divided into alternating rows with three treatments: bare soil with traditional tilling, rows covered with Secale and rows covered with Brachypodium.
The maintenance activities consist of no tillage in winter and conservation of natural cover crops until spring.
Natural / human environment: The area is at an altitude of 800 m, in a semiarid Mediterranean climate where the recorded annual rainfall is below 400 mm and the average annual temperature is 14 ºC, with very hot and occasionally stormy summers and very cold winters. It rains primarily in spring and autumn.
The farmland is predominantly dry, especially where olives and vines are planted. Oaks (holm, Portuguese and hermes) can be found in nearby wild areas and in abandoned terrains. The study focused on the area of Campo Real in the southeast of Madrid, in the centre of Spain. The vineyard covers an area of some 2 ha of rolling hills and is located on top of limestone marl.
The farmer is the owner of the land where the technology was implemented as well as he owns other plots. The land user is one of the few organic producers in the region.
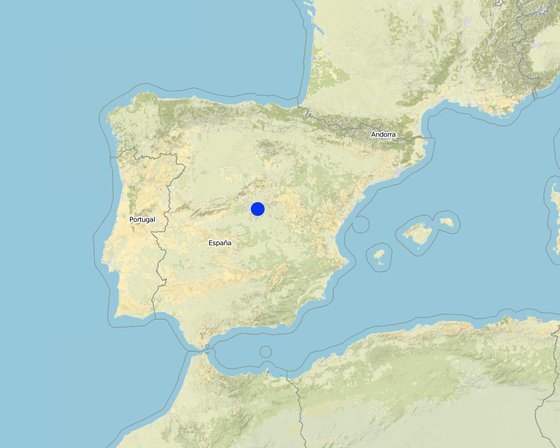
ទីតាំង: Campo Real, Madrid, Spain, ប្រទេសអេស្ប៉ាញ
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖








| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (euro) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (euro) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1,0 | 140,7 | 140,7 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 51,46 | 51,46 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 354,43 | 354,43 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 546.59 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 407.9 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (euro) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (euro) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1,0 | 140,7 | 140,7 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 51,46 | 51,46 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 113,23 | 113,23 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 305.39 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 227.9 | ||||
Depending on the cover crop (B. distachyon)
But not really used
Related to the quality and price of wine
No tillage
The farmers use to prefer the landscape of their vineyards with "clean" soil. They consider cover crops as weeds.
This SLM Technology contributes to soil improvement but has no direct impacts on human wellbeing of the land users. Due to organic labelling of the product, the price of wine may increase wich also increases farm income.
More than 80% of runoff reduction in B. distachyon and more than 60% for Secale.
93% in permanent cover crops
Due to less use of heavy machinery
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 1.27%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 1.6%
From 1.27% to 1.6% in three years for permanent covers