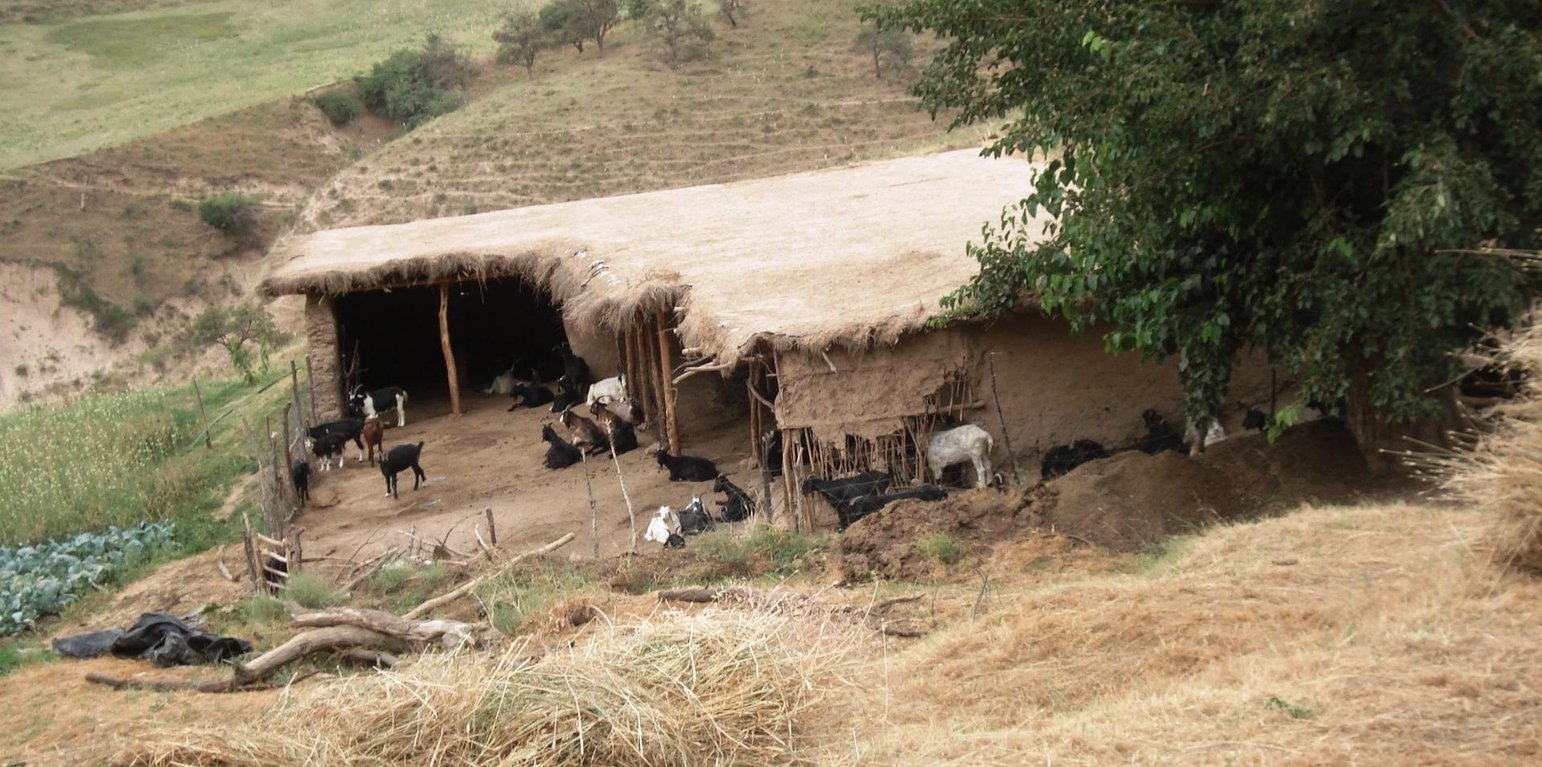




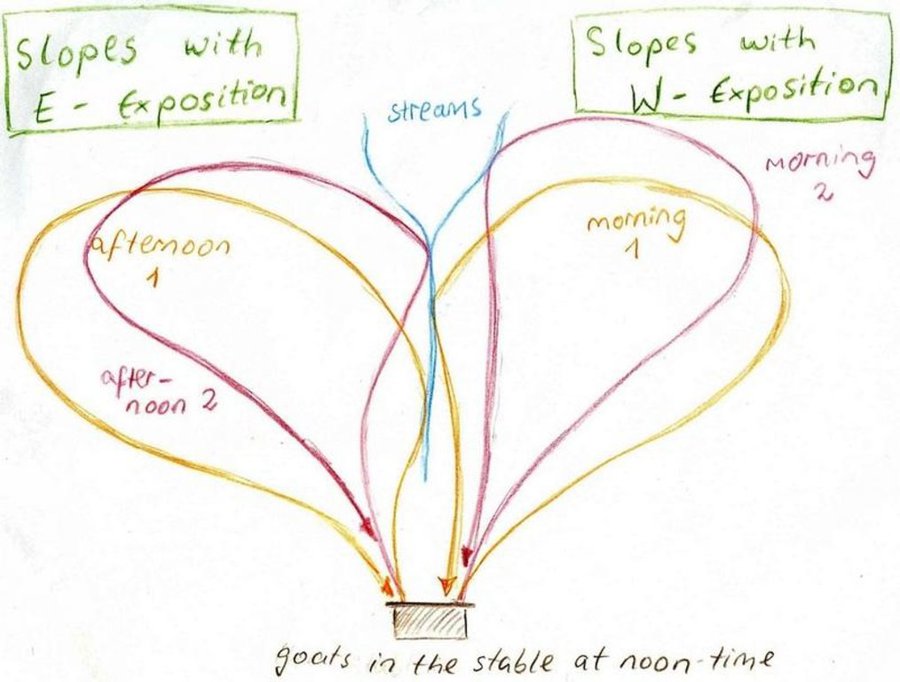
The around 50 goats are brought to the pastures early in the morning and will be brought back to their stable from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. After this, they will be accompanied to the pastures again. In the morning the west-exposed and in the afternoon the east-exposed pastures are visited. The same rotational scheme is applied over the whole year, which means that the same pastures are visited daily. The pastures are exclusively used by the land user fror more than the half of the year (from autumn to spring). In summer the pastures are also used by the village herd of the nearby village (Karsang). Herding is mostly the task of the land user's sons but sometimes he will accompany the animals by himself. Cows are let out on the pastures in the morning and come back in the evening by themselves.
Purpose of the Technology: The reason for west-facing grazing in the morning and east-facing in the evening is that grass is moist at these times of day. This is also why at noontime animals are not on the pastures. The animals are led slowly by the herder as to not tire them, to make them fatter and to avoid damages on vegetation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: No special pasture maintenance activities are undertaken.
Natural / human environment: The area is around one hour away from the village which actually controls the pastures (communal pastures). In addition snow lies longer in spring than further down. This means that the village herd only comes here from late spring to late summer, which decreases the pressure on the pastures. Together with the situation in a small depression that protects from high radiation in summer this contributes to the generally better pasture quality (greener, more grasses) compared with the village pastures in proximity to the villages. An important factor contributing to the generally good conservation state are the reduced livestock numbers. They are only reduced because the land user is close to these more distant pastures and the village is quite far away.
ទីតាំង: Faizabad, Region of Republican Subordination, ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (approx. 0.1-1 គម2)
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖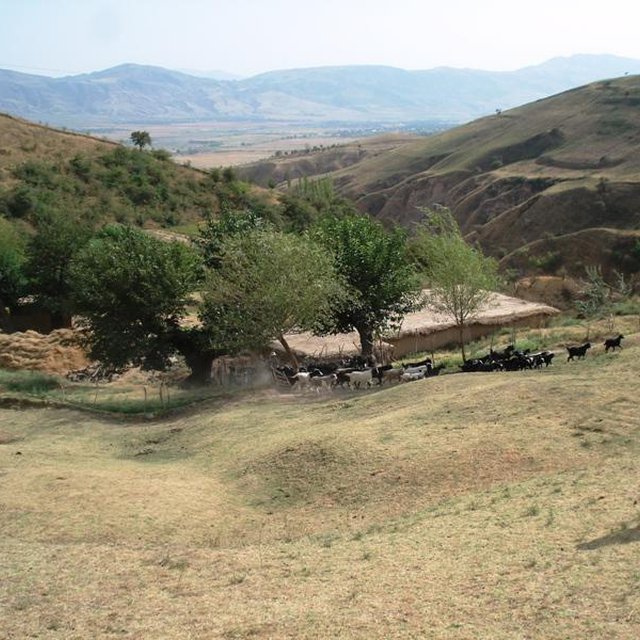

| ប្រភេទពូជ | ចំនួន |
| សត្វពពែ | 50 |




| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Somoni) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Somoni) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| ផ្សេងៗ | |||||
| Buying livestock | Goats | 50,0 | 87,7 | 4385,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 4'385.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 1'282.16 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Somoni) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Somoni) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Herding daily | days | 365,0 | |||
| ផ្សេងៗ | |||||
| Salt for animals | for one year | 1,0 | 12,0 | 12,0 | |
| Fooder for livestock | winter | 1,0 | |||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 12.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 3.51 | ||||
His animals yield higher prices on the market than average livestock.
The productive success of the land user lets him appear richer than the rest of the village.
Having a big herd on a big pasture area is a guarantee for better self-sufficiency.
Especially in the establishment phase there was jealousy about the success, especially in fruit-production.
Especially biomass is reduced by daily grazing.
Especially the proportion of grasses is higher compared with other village pastures