

The technology involves a combination of structural, vegetative and agronomic land use practices aiming at improving production of cassava (Manihot esculenta), improving potential of the soil and environmental function of the land. The technology is among a list of basket of choices of SLM practices recently introduced and adapted to the area by land user and experts working with SCC-Vi Agroforestry an NGO contracted/outsourced by the Tras-boundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project (Kagera TAMP) for provision of SLM advisory and extension services.
Contour bunds are constructed across the sloppy landscapes of average slope 5 – 8 % and are arranged in rows from the top to the bottom of the slope. The average distance between contour bunds is 15 meters. A contour bund is a row of long narrow furrow of average width 90cm and average depth 30cm dug across the slope using simple tools and leveled using A-frame method. Dug soils are piled below the slope to form a long strip earth of fanya chini bund. The average height and width of a bund is 30cm and 45cm respectively. Pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) are planted on contour bund to make them more stronger and productive. A single stand of pigeon pea has two plants and the distance between stands is 30 cm. Improved cassavas (Manihot esculenta) variety (mkombozi) that are resistant to cassava mosaic virus are planted in rows between contour bunds. Within rows, the space between cassavas is 1meter and between rows is 1meter. Manure application is applied before cassava planting at the rate of 2kgs per each plant hole. Cassava is usually planted on May and is harvested after one year. Cassava is planted together with groundnuts (Arachis hypogea) as a cover crop. Despite of having the nutritional advantage to farmers, pigeon pea and groundnuts also diversifies farmers’ livelihood income and have a key role of improving ecosystem through soil water conservation (prevent unproductive loss of green water) and improve soil fertility (through soil nutrient replenishment) and their after harvest remains are sources of organic matter.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is to:
1) Increase cassava productivity 2) Improved livelihood of the rural poor through diversification of income sources (cajanus cajan, groundnuts and cassava) and 3) conserve and restore ecosystem through soil fertility improvement (replacement of nutrients lost through uptake by plants), soil moisture improvement (by preventing blue water loss through runoff and green water loss through unproductive evaporation) and control of cassava pests and diseases (use of cassava varieties that are resistant to cassava mosaic virus).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities include land preparation, ploughing and harrowing, contour bund construction and leveling using A-frame, manure procurement and application. Maintenance and recurrent activities involves collection of cassava planting materials and planting, vegetative stabilization of the bunds by planting Cajanus cajan, planting of cover crops (groundnuts within cassava farm), weeding/gap filling and harvesting.
Natural / human environment: The natural environment includes crop land dominated with separate annual crops. A combination of structural and vegetative measure (contour bund strengthened and made more productive with Cajanus cajan). Climatic zone is sub humid with 210 length of growing period (LGP). Slope category is moderate lying between 5-8%. Soil texture is gravel sandy loam with medium soil depth.
On human environment, mechanization is dominated by use of handy tools and occasional use of tractors. Production system is mixed (both for subsistence and commercial purposes). Inputs used includes tools (hand hoe, machete, sickles, spade and mattock), light and heavy labour, manure, seeds and cassava planting materials with average annual costs of 1033.47 USD per hectare. Land ownership is individual not titles. The expected average annual gross revenue per hectare accrued from cassava alone is 20580 USD.
ទីតាំង: Missenyi District Council/Minziro village, Tanzania/Kagera region, ប្រទេសតង់សានី
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (approx. < 0.1 គម2 (10 ហិកតា))
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖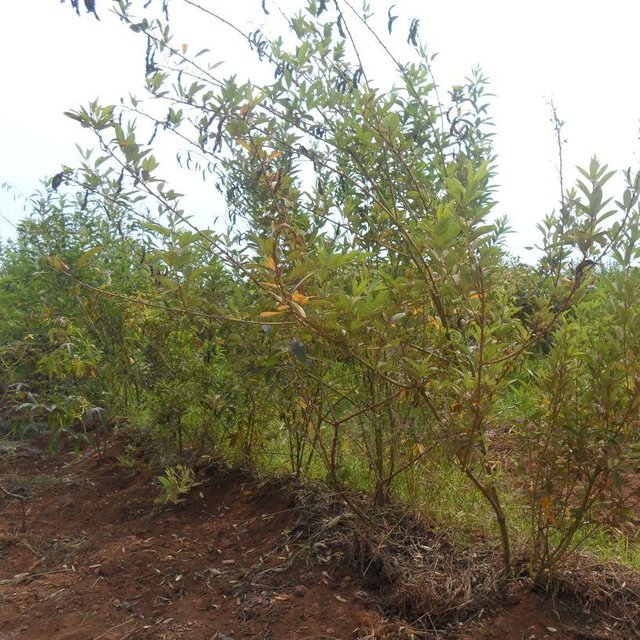






| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Tanzanian shillings) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Tanzanian shillings) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Planting cajanus cajan (perennial shrub) | person/days | 13,0 | 1,7 | 22,1 | 100,0 |
| Construction of contour bunds | person/days | 13,0 | 3,46 | 44,98 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Tractor (hired) | pieces | 1,0 | 95,0 | 95,0 | |
| Tools | pieces | 34,0 | 2,941 | 99,99 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| Seeds | kg | 6,0 | 27,0 | 162,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 424.07 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 0.25 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Tanzanian shillings) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Tanzanian shillings) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| land preparation for tractor operation/ cleaning/grass slashing (usually occasional depends on land complexity) | person/days | 13,0 | 1,7615 | 22,9 | 100,0 |
| land manual harrowing (after tractor tilling). | person/days | 13,0 | 3,55 | 46,15 | 100,0 |
| manure application | person/days | 13,0 | 3,55 | 46,15 | 100,0 |
| Planting of cassava and groundnuts. | person/days | 13,0 | 0,88 | 11,44 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| Groudnut seeds | kg | 200,0 | 0,4706 | 94,12 | 100,0 |
| Cassava cuttings | cuttings | 10000,0 | 0,011765 | 117,65 | |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | |||||
| Compost/manure | tons/ha | 10,0 | 13,235 | 132,35 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | |||||
| Labour: weeding cassava, groundnuts and pigeon pea (done concurrently) | person/days | 13,0 | 3,54 | 46,02 | 100,0 |
| Labour: Harvesting and transportation of groundnuts. | person/days | 13,0 | 0,88 | 11,44 | 100,0 |
| Harvesting and transportation of cassava (after one year) | person/days | 13,0 | 2,65 | 34,45 | 100,0 |
| Labour: harvesting cajanus cajan | person/days | 13,0 | 1,76 | 22,88 | 100,0 |
| Labour: Maintenance of the contour bunds (cleaning of the furrow floor/walls and reshaping of the bunds) | person/days | 6,0 | 3,83333 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 608.55 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 0.36 | ||||
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 1-2 kgs of cassava per crop stand
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 2.5-4 Kgs of cassava per crop stand
due to manure application.
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 50% risk
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 10-20% risk
due controll of soil erosion, soil fertility improvement and cantroll of moisture stress.
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 0 tons/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 20 tons/ha
Use of farm yard manure.
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 1 income source (cassava)
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 3 more sources.
additional income from cajanus cajan, groundnuts and beans
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 6
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 12
the technology is labour intensive and heavy labour is needed
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 3
incresed no of diets cajanus cajan and beans/protein, cassava/carbohydretes, groundnuts/oil
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 10%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 33%
access to varied food sources and capacity to invest in health services.
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 1
FFS SLM groups
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 5%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 20%
% land users aware of improved conservation/erosion knowledge
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 5%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 40%
women involvement in SLM activities
the technology resulted in increased crop production emanated from improved soil fertility and control of erosion. There is also diversification of income sources from cover crops (groundnuts) and cajanus cajan (cow pea) as well as improved diet due to varied food sources. All these contributed to improved livelihood and human well-being
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 30%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 5%
runoff speed reduced through the use of contour bund and cover crops
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 20%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 10%
evaporation reduced from use of civer crops.
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 10%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 20%
water stored in soil due to the use of contour bunds and cover crops
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 10%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 45%
increased percentage monthly soil coverage with cover crops (ground nuts and beans)
គុណភាពមុន SLM: low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: high
nutrients generated from the use of beans (phaseola vulgaris)
គុណភាពមុន SLM: low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: high
following use of farm yard manure
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 3
crop varieties planted in different phases on the same land
គុណភាពមុន SLM: low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: high
Farm yard manure is a good medium for increased microbial action and soil fauna
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 0%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 50%
increased possibilities for using pest and disease resistant varieties.
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 0%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 100%
Area put uder cultivation are usually protected and less prone to fire burning
គុណភាពមុន SLM: low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: high
indirect reduced water loos due to runoff
គុណភាពមុន SLM: low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: high
rainfall runoff impeded or trapped by contour bunds
គុណភាពមុន SLM: low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: high
reduced siltation of the natural water spring in the lower mountain/hilly floors.
គុណភាពមុន SLM: low
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: high
reduced distruction of public roads through eroded soil.