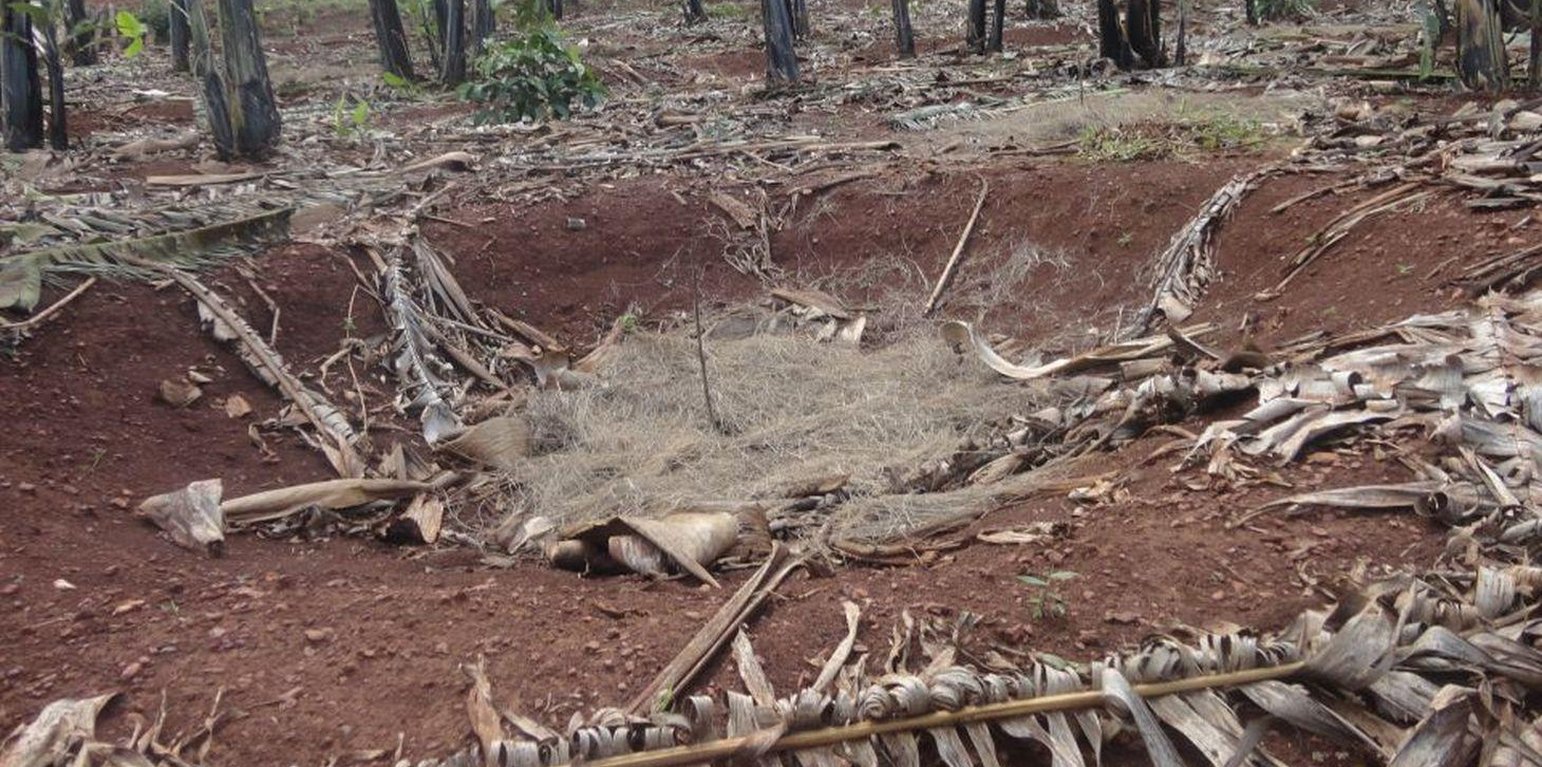




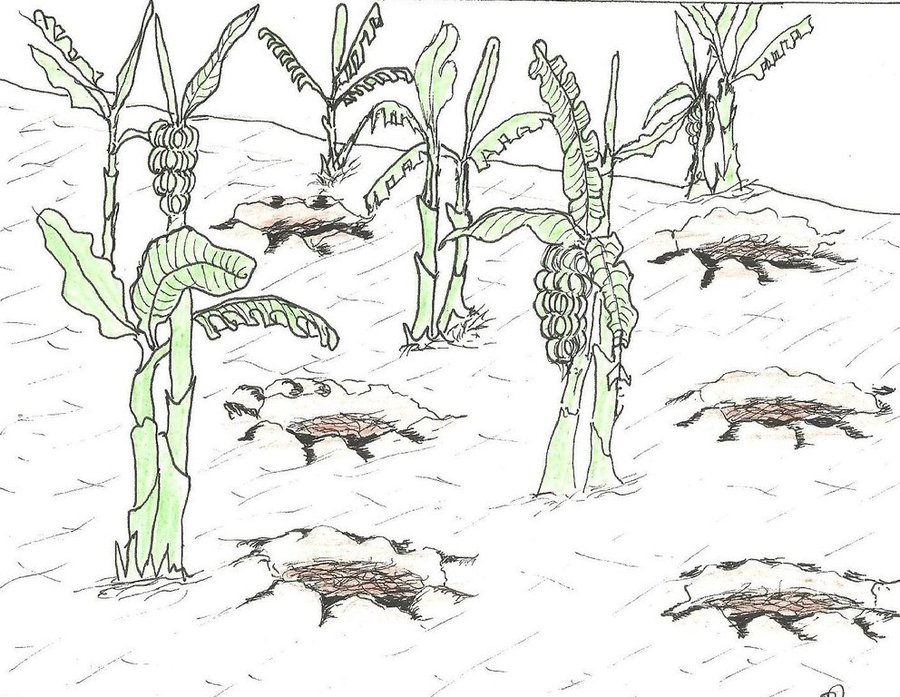
The planting pits are established between banana stems and filled with organic vegetative material mixed with decomposing manure to form a reservoir of nutrients for a long run. On gentle slopes covered with extensive banana plantations, the planting pits are dug at the center of banana stands. Before estbalishment of this technology, only the composting process was available for the conversion of organic domestic waste into manure. However, compost manure takes slightly longer to produce and is more bulky than conservation troughs making the latter easier to adopt. The technology can be applied to annual cropland as well. Application of the technology improves banana bunch size and plantation yield by over 300%.
Purpose of the Technology: The main objective is to improve soil fertility. The planting pits also check runoff thereby reducing soil erosion, improving moisture infiltration and retention, and enabling the plantation to withstand the dry months. Cabbages, beans and other high value vegetables can be grown directly on top of the trough.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The planting pits are established using simple tools such as the hand hoe, spade, panga and wheelbarrow. The hoe is used to dig up the soil and soften it. The soil is then scooped out using a spade, to create a bowl-shaped trough. The panga is used to chop the remains of harvested bananas (stems and leaves) which are then, carried to the troughs using a wheel barrow. The planting pit is 0.45 m to 0.60 m deep depending on the amount of manure available and 0.6 m wide. Each trough is about 0.60 m from the nearest banana stand. It is filled with chopped banana stems, followed by a layer of manure and then covered with mulch to prevent excessive evaporation of moisture. The planting pit is then covered with soil. After 3 to 4 months, the vigor of the banana stems improves. If the trough is opened by digging, roots are observed to have grown through the walls of the planting pit from all directions.
During the rainy season, the trough slowly fills with sediment from surface erosion. Weeding at the trough is done by uprooting the weeds using hands or a hand hoe.
Natural / human environment: Over time, the banana stands grow towards the trough. To maintain the distance between the stands, the suckers nearest to the trough are pruned.
ទីតាំង: Mbarara, Uganda, អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖




| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (UGX) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (UGX) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1,0 | 44,0 | 44,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1,0 | 7,0 | 7,0 | |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | |||||
| Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 91.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 0.04 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (UGX) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (UGX) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | |||||
| Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 34.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 0.01 | ||||
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 8 Kg
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 25 Kg
Bunch of bananas is bigger and heavier at harvest
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 20%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 67%
During the dry season or extended drought periods, only about 20% of the banana stands would have a fruiting stem; now well over two thirds of the stands do.
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 80 US$
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 200 US$
Monthly harvests for sale have increased from 20 to over 50 bunches
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 50%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 100%
Whereas extended drought posed food insecurity, this is no longer the case
The earning power has increased greatly. Children are going to school because tuition fees are no longer burdensome and health needs are easily met. The farmers practicing the technology report making some savings from their incomes unlike before.