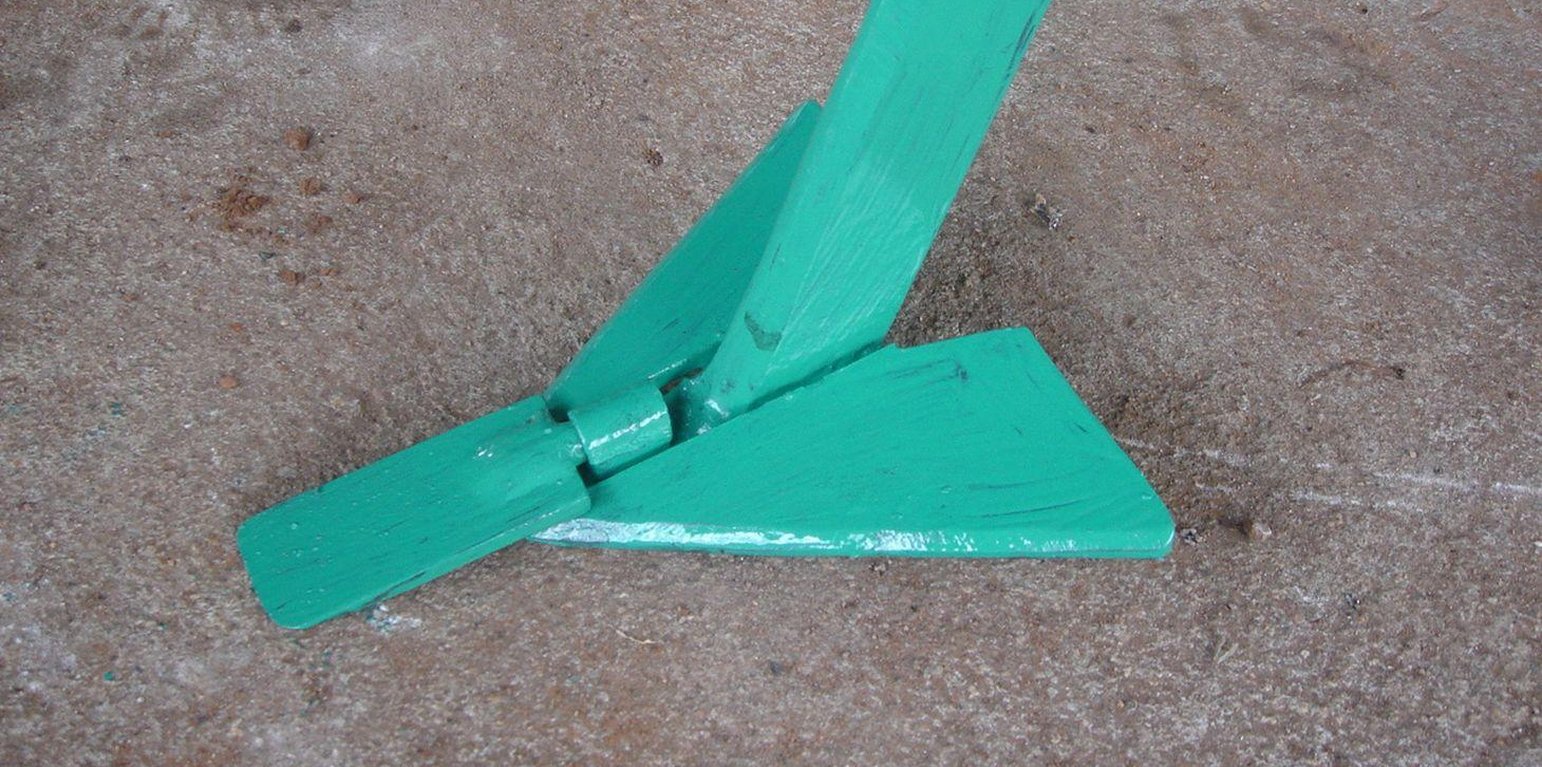




The strip tillage tool is an adaptation of a Magoye Ripper but is meant to be used in moist soil. In the strip tillage tool, sub-surface wings are attached to the ripper tine to increase the width of soil disruption which the ripper will be unable to achieve in moist soil. The sub-surface wings loosen the soil by lifting it slightly and letting it fall in place without inverting it. In this way, a strip of soil with a width of around 20cm is tilled up to 20cm deep and this is where the crop will be planted. The region between the strips is maintained as a no-till region for soil and water conservation.
Purpose of the Technology: The strip tillage tool is meant to be a transitional technology for farmers intending to adopt Conservation Agriculture (CA) in degraded soils. These soils will need routine loosening while the biological activities allow the soil structure to recover sufficiently until tillage is no longer required. Strip tillage is able to achieve deeper soil loosening with much less draft force, wear of tines and soil disturbance than ripping. The untilled region between the strips enables the benefits of soil cover such as improved infiltration, soil water storage and increased soil organic matter. Soil loosening by strip tillage does not produce large clods like ripping does but instead produces a fine seedbed that enables uniform emergence of the crop, and this together with the deep penetration results in early plant vigour. The strip tillage implement is also designed to allow the attachment of a planter unit to enable tillage and planting in one operation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of strip tillage based conservation agriculture mainly involves the purchase of the strip tillage implement and the replaceable tines. Liming acidic soils (low pH soils) followed by a final ploughing will be required to correct the soil PH which otherwise will be difficult to correct once conservation tillage has been established. Maintenance activities include strip-tilling the soil which may or may not include planting and fertilizing in the same operation. Weeding should preferably include the use of herbicides, implying that the major operations will include spraying. In addition to the normal conventional inputs, herbicides will also become a major input and cost.
Natural / human environment: The strip tillage technology is most suited to the bigger small-scale farmers with a capacity of 5ha to about 20ha. The strip tillage tool together with the planter will require a relatively substantial investment and only the bigger farmers will fully utilize its capacity. The strip tillage action will not be very effective in wet soils especially in the heavier soils, soil disruption is best achieved when the soil is slightly moist but not too dry as to require to high draft forces. Strip tillage is useful in soil with poor structure that will require routine loosening to maintain yields while the soil is being rehabilitated.
ទីតាំង: Mazabuka/Magoye, Zambia/Southern Province, ប្រទេសសំប៊ី
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (approx. 0.1-1 គម2)
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖








| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (ដុល្លារ) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (ដុល្លារ) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Strip Tillage implement | pieces | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Knapsack Sprayer | pieces | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 580.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 580.0 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (ដុល្លារ) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (ដុល្លារ) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Slashing and spreading crop residues | persons/day/ha | 8,0 | 2,5 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Liming soil | persons/day/ha | 2,0 | 2,5 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | persons/day/ha | 4,0 | 2,5 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 24,0 | 1,0 | 24,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| Seeds | kg/ha | 20,0 | 2,5 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | |||||
| Fertilizer | kg/ha | 400,0 | 0,8 | 320,0 | 100,0 |
| Herbicides | l/ha | 5,0 | 6,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | |||||
| Lime | kg | 1000,0 | 0,042 | 42,0 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | |||||
| Labour: Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 4,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Labour: Harvesting | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 4,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 621.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 621.0 | ||||
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 3tons/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: 5tons/ha
Due to early planting
Residues needed for soil cover
Better resistance
គុណភាពមុន SLM: 2-3ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM: >10ha
Due to increased production area and improved yield
More time and labour freed for other activities
Due to mechanised planting and herbicide use
Due to incresed yields
Improved nutrition due to crop diversification
Less time spent on farm operations
Farmers trained through cooperatives
Due to incresed soil Carbon, crop residues to reduce run off, and capacity building
Due to competition with neighbours cattle for crop residues
The technology was only introduced recently and not yet widely adopted to make an impact. However the few farmers that have adopted have been able to multiply their production capacities and incomes.
Due to better soil cover
Due to better soil cover
Improved soil structure
Due to good drainage
Due to better soil cover
Due to better soil cover
Due to non-inversion tillage
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Due to deep tillage
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Due to good drainage
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Due to soil organic matter (SOM) buildup
Resistance to chemical weed control
Due to Carbon (C) sequestration
Some chemicals get carried down the profile
Only if applied over an extensive area
Only if applied over an extensive area
Only if applied over an extensive area
Only if applied over an extensive area