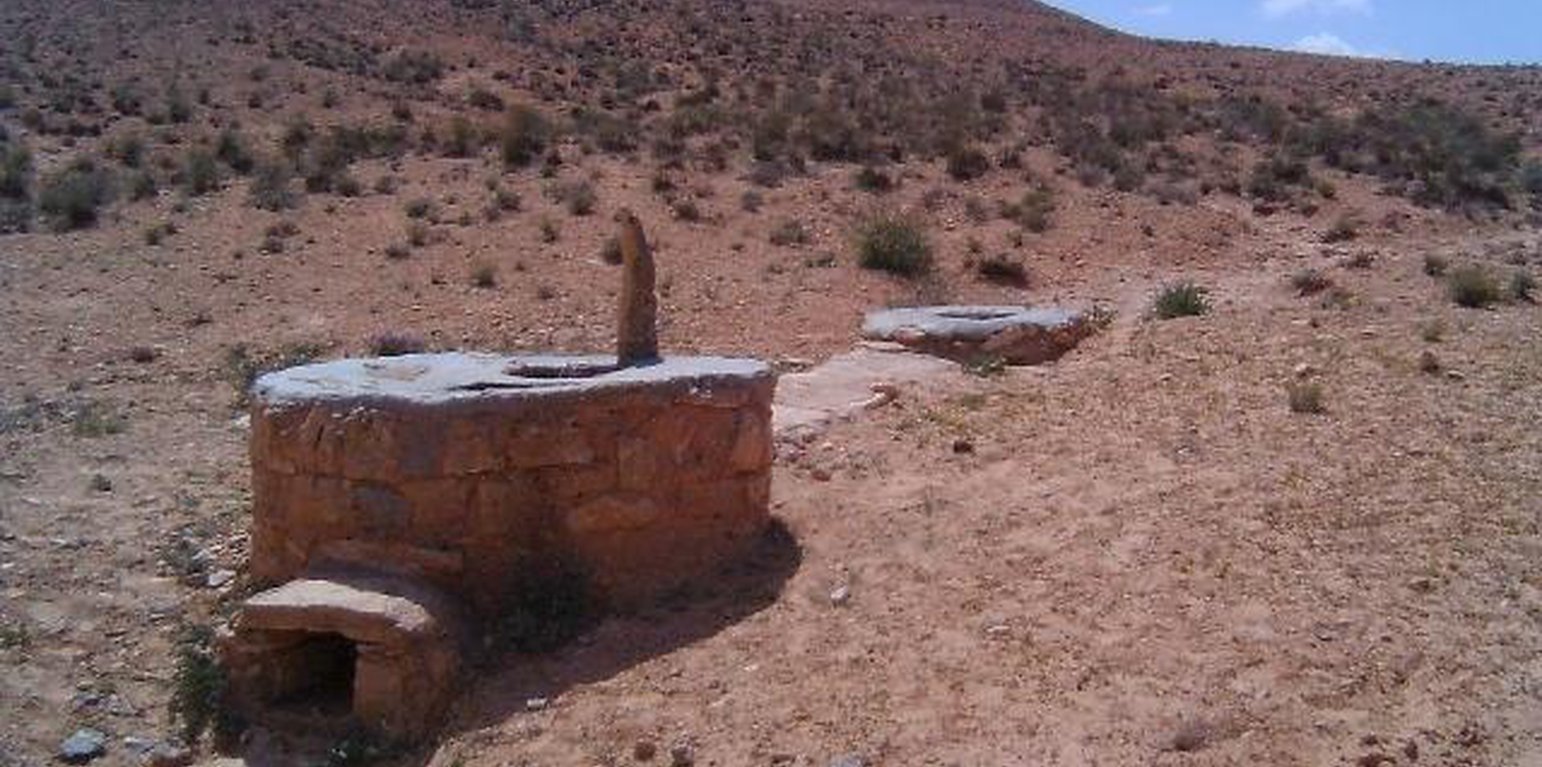




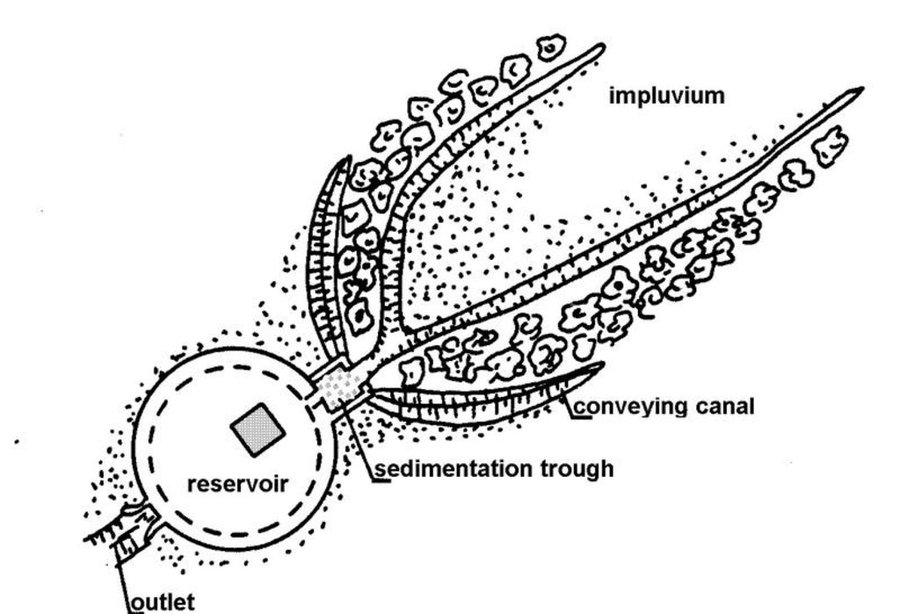
Cisterns were traditionally used to provide drinking water. In the cistern system, runoff water is collected and stored in stone-faced underground cisterns, of various sizes, called majel (private reservoirs) and fesquia (communal reservoirs). Basically, a cistern is a hole dug in the ground and lined with a gypsum or concrete coating, in order to avoid vertical and lateral infiltration. Each unit consists of three main parts: the impluvium, the sediment settlement basin, and the storage reservoir. The impluvium is a sloping piece of land delimited by a diversion channel (hammala).
Purpose of the Technology: It is estimated that a tank with a capacity of 35 m3 can meet the annual water needs of a family and its livestock (Ennabli, 1993).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In flat areas, where it is possible also to exploit floods via a diversion dyke, one also finds artificially paved runoff areas. A small basin before the entrance of the cistern allows the sedimentation of runoff loads. This improves the stored water quality and reduces maintenance costs. Big cisterns have, in addition to the storage compartment, a pumping reservoir from which water is drawn (Ouessar, 2007).
Natural / human environment: Small private and communal cisterns (5 to 200 m3) and big cisterns (up to 70,000 m3), mainly built during the Roman and Arab-Muslim eras, can be found throughout the water-deficient zone south of the 400-mm isohyet .
ទីតាំង: Medenine nord, Medenine, ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (approx. 10-100 គម2)
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: ច្រើនជាង 50 ឆ្នាំមុន (ប្រពៃណី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖





| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (TND) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (TND) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1,0 | 250,0 | 250,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | |||||
| ha | 1,0 | 150,0 | 150,0 | ||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 400.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 307.69 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (TND) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (TND) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | |||||
| ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | ||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 130.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 100.0 | ||||
negligible (0-5%)