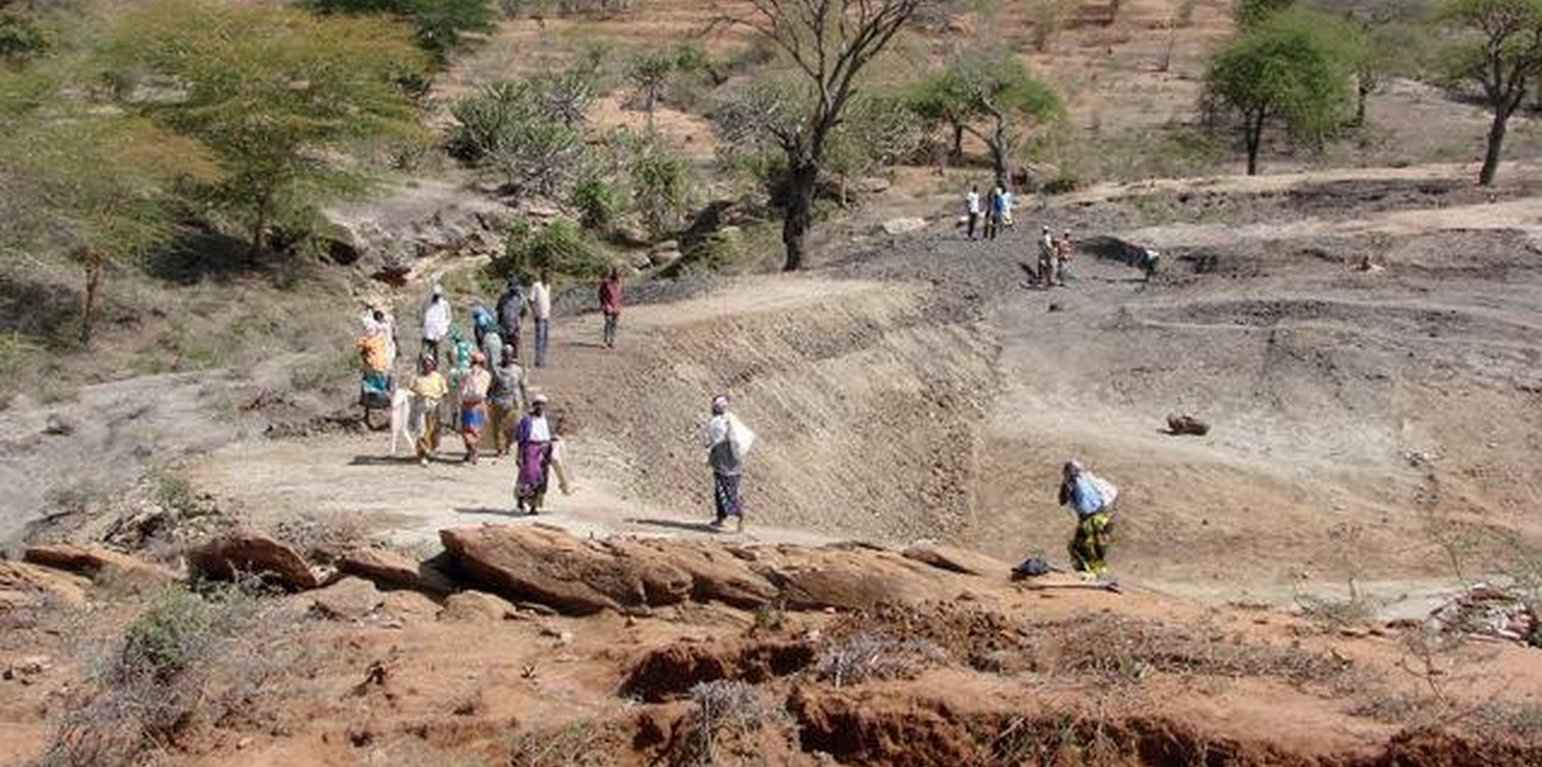




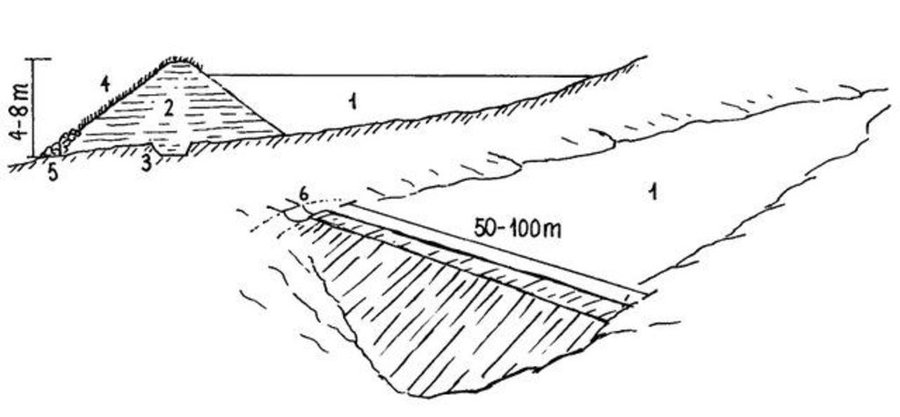
Small earth dams are water harvesting storage structures, constructed across narrow sections of valleys, to impound runoff generated from upstream catchment areas.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Construction of the dam wall begins with excavation of a core trench along the length of the dam wall which is filled with clay and compacted to form a ‘central core’ that anchors the wall and prevents or minimizes seepage. The upstream and downstream embankments are also built using soil with a 20-30% clay content. During construction – either by human labour, animal draught or machine (bulldozer, compacter, grader etc.) – it is critical to ensure good compaction for stability of the wall. It is common to plant Kikuyu grass (Pennisetum clandestinum) to prevent erosion of the embankment. The dam is fenced with barbed wire to prevent livestock from eroding the wall. Typical length of the embankment is 50-100 m with water depth ranging 4-8 m. An emergency spillway (vegetated or a concrete shute) is provided on either, or both sides, of the wall for safe disposal of excess water above the full supply level. The dam water has a maximum throwback of 500 m, with a capacity ranging from 50,000 – 100,000 m3.
Natural / human environment: The dams are mainly used for domestic consumption, irrigation or for watering livestock. If the dams are located on communal lands, their establishment requires full consultation and involvement of the local community. The government provides technical and financial assistance for design, construction and management of these infrastructures. Community contribution includes land, labour and local resources. The community carries out periodic maintenance of the infrastructure – including vegetation management on embankment, desilting etc. – and of the catchment areas (through soil and water conservation practices).
ទីតាំង: Southern Province, ប្រទេសសំប៊ី
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖





| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (មិនមាន) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (មិនមាន) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Dam and spillway construction | unit | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | 20,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Tools | unit | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 20,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| Seeds | unit | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 20,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | |||||
| Fertilizer | unit | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 20,0 |
| Biocides | unit | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 20,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | |||||
| Stone | unit | 1,0 | 15000,0 | 15000,0 | 20,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 50'000.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 50'000.0 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (មិនមាន) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (មិនមាន) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Maintenance of dam | unit | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Tools | unit | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| Seeds | unit | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | |||||
| Stone | unit | 1,0 | 1500,0 | 1500,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 4'000.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 4'000.0 | ||||