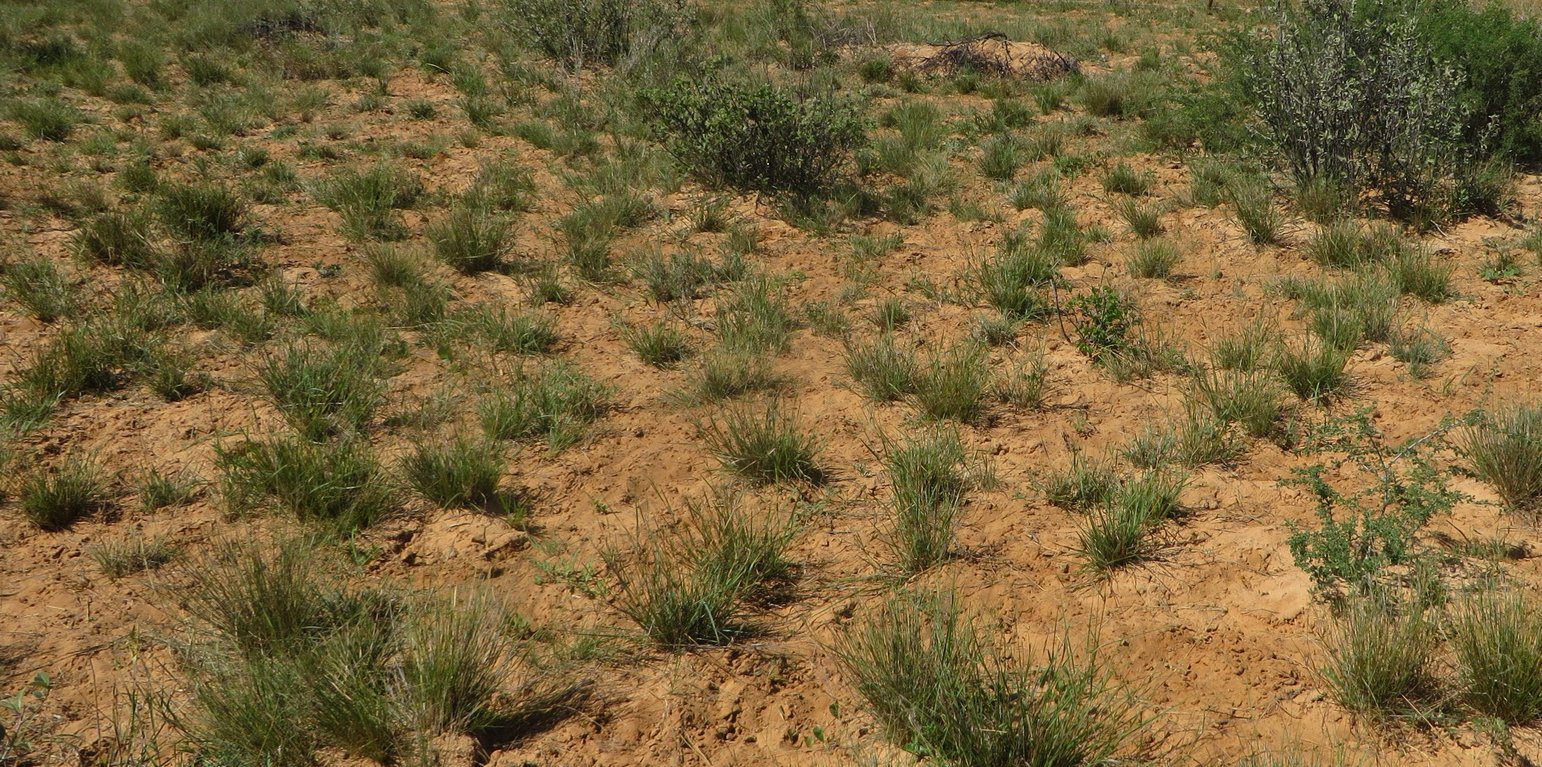




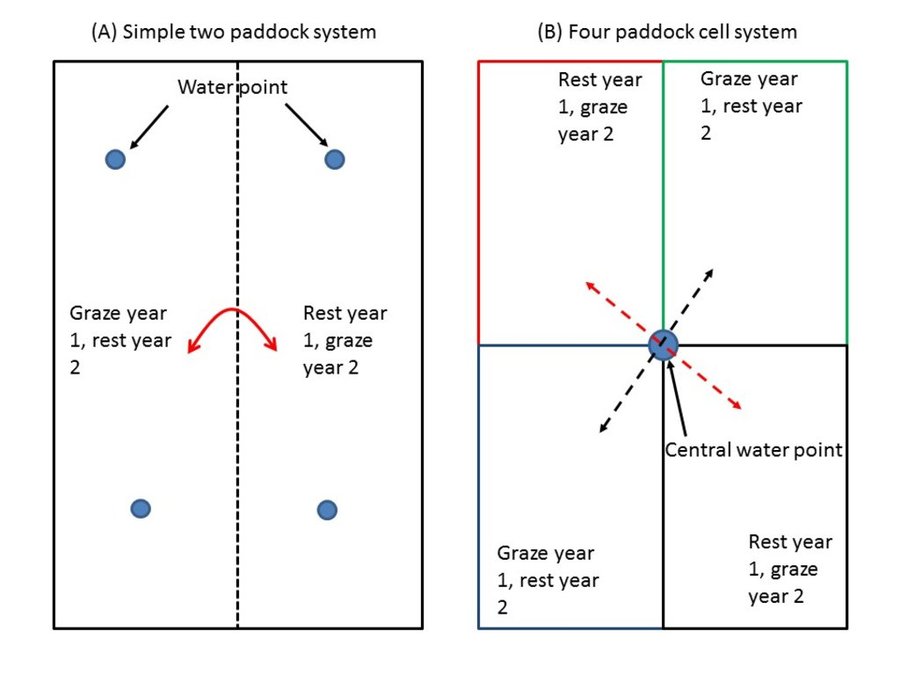
The Split Ranch Grazing Strategy (SRG) was developed by Riaan Dames in the North West province, South Africa. It is fundamentally different to popular rotational management systems and contains several conceptual advances. One key difference is that SRG provides a full-year uninterrupted recovery period for rangeland after grazing. This enables grasses to maximize nutrient recovery over the main pulses of nutrient mineralization in the early wet season, and to maximize root growth and associated nutrient storage over the late wet season and early dry season - when most root growth occurs. Optimal recovery periods should ideally, therefore, encompass the full wet season and the early dry season. This contrasts with rotational grazing where recovery and grazing periods are apportioned across these two periods, with resting periods often not occurring in key periods of nutrient uptake and root growth.
A major problem with having both grazing and recovery periods in the same season is that grassland is able to mature during recovery periods, greatly reducing forage quality and grass growth rates, thereby negatively impacting animal production. Another problem is that complex rotational grazing requires strategies investing much in a complex and expensive fencing infrastructure. The solution is a fundamentally different strategy where some paddocks are grazed the whole year to prevent grassland maturation and other paddocks are simultaneously rested to optimize recovery. In addition, paddocks should be as few, and as large as possible, to maximize livestock access to functional resource heterogeneity, thereby improving adaptive foraging options, while reducing costs of fencing (fencing can even be replaced by using physical boundaries (e.g. roads, rivers, etc.) and herding the livestock.
Livestock are maintained in the grazing paddocks until mid-dry season to ensure that grasses in the rested paddocks have completed root growth and ceased all other growth – thus fully rested and recovered. A full years rest allows maximum uptake and storage of nutrients in deep, strong root systems and crowns. Thus when these grasses are grazed in the next season they have not only efficient root uptake of moisture and nutrients from the soil but also can re-allocate nutrients stored in roots to leaf production after each grazing event, resulting in a productive supply of high-quality fresh leaf to livestock over the growing season.
Movement of livestock into the year-long rested paddocks halfway through the dry season ensures that they have a large reserve of forage. Concentration of livestock on half the available area (half the paddocks are rested and the other half grazed) ensures sufficient grazing pressure to maintain grassland in an immature, high-quality and rapidly-growing state for maximizing forage quality, leaf production and livestock production, further enhanced by greater adaptive foraging options in large paddocks. The technology was started in North West province South Africa, and is now being taken up in Botswana and Namibia. A model example is Tiisa Kalahari Ranch in the Ghanzi region of Botswana. The ranch has been partitioned into several four-paddock cells, each with their own cattle herd. Cattle graze two paddocks while the other two are rested for a full year. Cattle enter the rested paddocks, which have developed a large reserve of forage, in the mid dry season (July) once forage is depleted in the two grazed paddocks. This technology (SRG), used on the award-winning Danielskuil ranch in South Africa, has been employed at Tiisa for six years after being in a degraded state. Indications are that the rangeland has been steadily recovering with increases in abundance of high-quality grasses. Monitoring programs are being established to monitor the trends in cover of the various grass species over time.
ទីតាំង: Ghanzi, Tiisa Kalahari Ranch, Ghanzi Province, ប្រទេសបុតស្វាណា
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ: មួយកន្លែង
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (approx. 10-100 គម2)
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖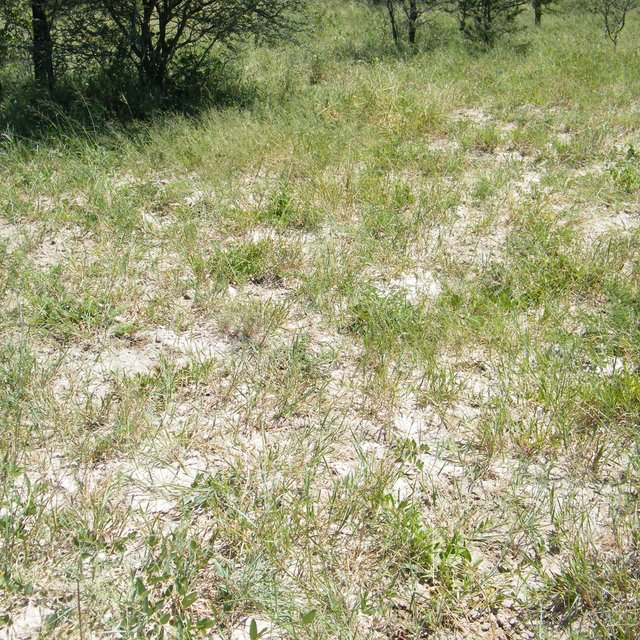






| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Pula (BWP)) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Pula (BWP)) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Labourers | paddocks | 7,0 | 24000,0 | 168000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Water trough, fitting and piping | paddocks | 7,0 | 8000,0 | 56000,0 | 100,0 |
| Solar pump | paddocks | 7,0 | 20000,0 | 140000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fencing | paddocks | 7,0 | 80000,0 | 560000,0 | 100,0 |
| Boreholes | paddocks | 7,0 | 20000,0 | 140000,0 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | |||||
| Loading facilities | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 1'094'000.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 1'094'000.0 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Pula (BWP)) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Pula (BWP)) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| supplementary feed | bale | 1,0 | 9,0 | 9,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 9.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 9.0 | ||||
For details see:
Fynn, R.W.S. Kirkman, K & Dames, R. (2017).
Forage quality improved by keeping the grass in an immature state. For details see:
Fynn, R.W.S. Kirkman, K & Dames, R. (2017).
Benefit from improved forage quality and larger spatial scales for adaptive foraging. For detail see:
Fynn, R.W.S. Kirkman, K & Dames, R. (2017).
Better soil cover and protection
Better soil cover and protection
Better soil cover and protection