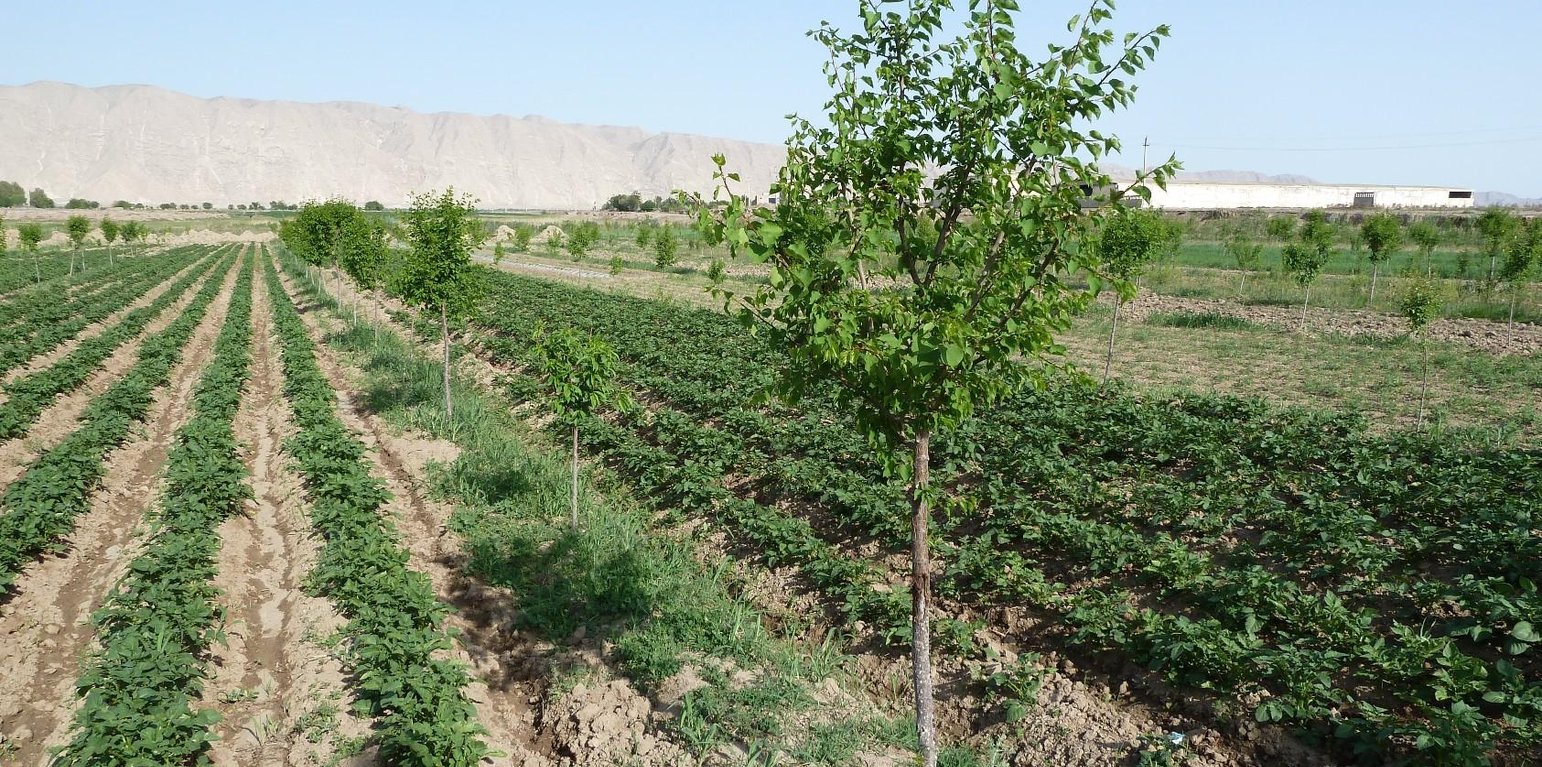




In the arid environment of Kabodion, large areas that had been irrigated during the Soviet times were abandoned after independence, and the irrigation facilities were neglected. Soils were highly degraded due to the long periods they had been without proper irrigation. On an area of poor quality soil, and previously abandoned plot of land covering about 6 ha, UNDP supported one family (Dehkan)to establish an agroforestry system by covering the costs of tree seedlings.
Purpose of the Technology: The aim of the technology was to improve agricultural production through a combination of measures such as improving soil fertility, increasing soil humidity through covering the soil with plastic sheets and preventing excess water drainage, and protection through a shelterbelt. Resilience to adverse climatic events is enhanced by increasing product diversification with a number of different tree, vegetable and crop species being planted.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: First, the soil had to be washed to reduce the high salt content. Plum, peach, sweet cherry and persimmon tree seedlings were planted in lines with intercropping of potatoes, watermelon, beans and wheat inbetween. The seedlings were purchased from the Kabodion nursery. Labour was provided in the form of "hashar" or voluntary neighbourhood help. On the windward side of the field, a shelterbelt consisting of White Poplar (Populus alba) trees was established to protect the field from wind erosion, and to reduce evapotranspiration. In order to improve soil structure annual crop rotations were practiced. Every 4 years 40 tones of cow dung are spread out per ha of land. The application of organic manure constitutes an important cost factor for the farmer, as 40 tons of manure costs about 180 to 220 USD. To improve soil humidity and to enable early planting for watermelons, cultivation seeds are planted under a tight plastic film with irrigation water filled underneath the sheet. As soon as the seedlings emerge a hole is made in the plastic to create space for the plants. Irrigation is applied only sparingly to prevent the soil from a new rise in salinity. The plot is situated on a gentle slope which facilitated the establishment of a drainage system by digging a trench at the foot of the field to absorb excess water. The farmer was able to cover the costs of this initial investment himself using the revenues from the first harvest. At the foot of this field, salt tolerant Russian Silverberry (Elaeagnus angustifolia) trees were planted to promote biodrainage to help prepare the adjacent land for conversion to agroforestry at a later stage. The farmer gained the knowledge that was necessary for the establishment of the system through attending the farmer field schools (see approach TAJ018).
Natural / human environment: This technology is suitable for other arid environments, and the economic benefits are high compared to the establishment and maintenance costs. When this was realised by the neighbouring farmers they adopted the technology on an area of land that was actually three times larger.
ទីតាំង: Khudokulov Jamoat, Khatlon, Kabodion, ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖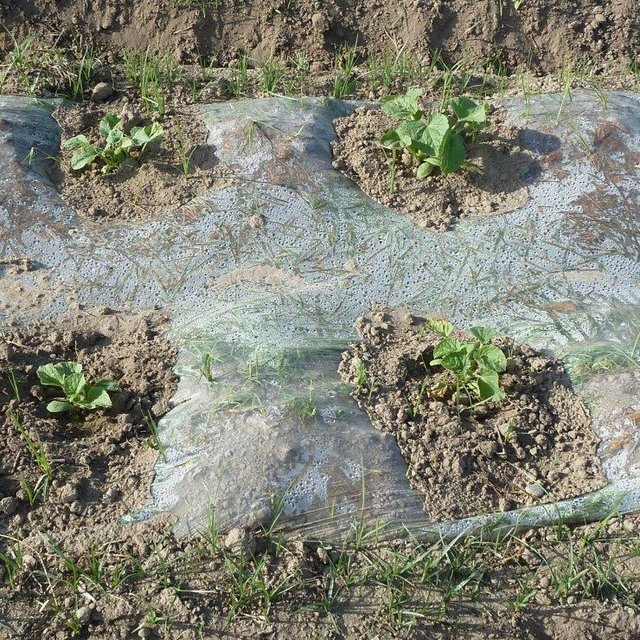









| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (SOM) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (SOM) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Planting of tree seedlings | Persons/day | 50,0 | 20,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Digging up irrigation ditch | Persons/day | 40,0 | 20,0 | 800,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 274,0 | 274,0 | |
| 1,0 | |||||
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| Tree seedlings | pieces | 844,0 | 3,14573 | 2655,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 4'729.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 1'050.89 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (SOM) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (SOM) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Daily irrigation for tree seedlings | Persons/day | 186,0 | 20,0 | 3720,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | |||||
| Organic/manure | tons | 40,0 | 25,0 | 1000,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | |||||
| Plastic cover | m | 1,0 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | |||||
| Tillage | ha | 1,0 | 430,0 | 430,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 5'151.8 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 1'144.84 | ||||
lucerne (alfalfa) production
diversification
before the land was denuded
vitamin-rich fruits are more readily available
through participation in farmer field schools
jealousy by other land users who would like to cultivate this land now they can see how productive it is
Farmer does not need to migrate to Russia anymore to find work, and could afford to buy a house.