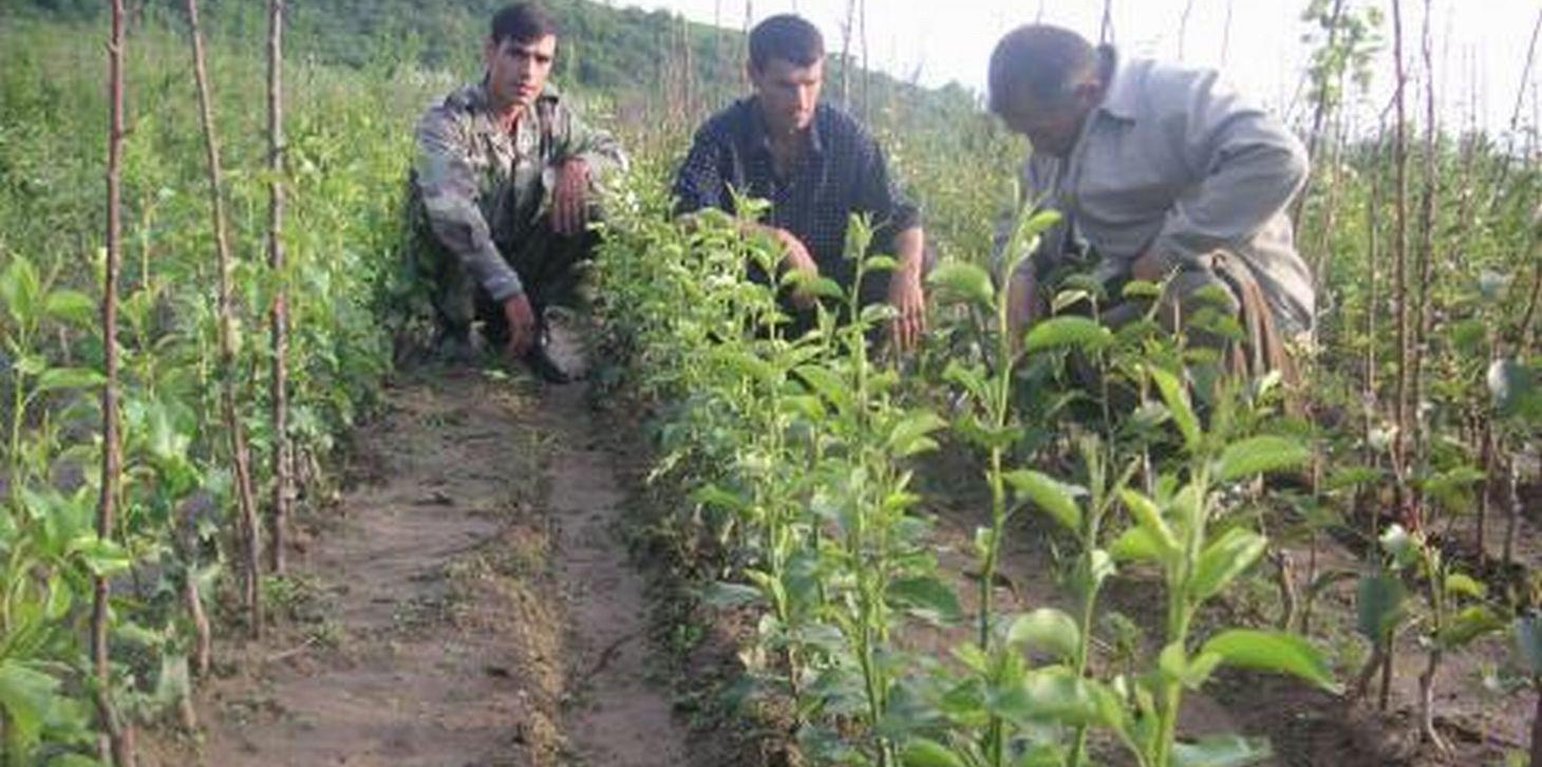




In 1995-96 the first tree nursery was established in the Vanj valley with support from the Mountain Societies Development Support Programme (MSDSP) of the Aga Khan Foundation. During Soviet times there were no tree nurseries in this region and seedlings had to be brought in from outside. Only the Pamir Biological Institute (PBI) was able to obtain seedlings for research purposes. A nursery of about 0.1 ha was established by one farmer on his own land. Tree species grown in the nursery include apple, peach, apricot, walnut, cherry and pear.
Purpose of the Technology: The main goal of the project was to make varieties of tree species adapted to different climatic conditions in GBAO locally available. The seedlings are used for other MSDSP projects, such as orchards for soil stabilisation, and are also purchased by private land users for their own land. In addition, the land user was taught how to establish a business by selling seedlings to other land users. There is a strong need for quality tree seedlings in the whole region and even people from as far away as Ishkhashim (7 hour journey by car) travel to Vanj valley to purchase seedlings from this nursery. The economic benefit for the land user is very high as during one year he can make more than 18,000 TJS (4000 USD) of profit from selling seedlings while the investments in fertilisers are comparably small.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The steps necessary for the establishment of a tree nursery are the following: (1) a suitable plot of flat land is chosen by the farmer, (2) the plot is fenced with dead branches to protect it from roaming animals, (3) in March, the farmer prepares several wooden boxes filled with humid soil in which he distributes 10 kg of seeds of different tree species and varieties. Those boxes have to be irrigated for a month while the seeds are germinating, (4) in April, the nursery plot is ploughed along the contour using animal traction and 1 ton of organic manure, 20 kg of phosphor and 2.5 kg of nitrogen is mixed with the soil, (5) seedlings are planted linearly along the contour with small irrigation ditches running parallel to the planting lines. These ditches were automatically established through the ploughing process, (6) two more times during the first season another 3 kg of nitrogen are applied. In the second year the grafting process is started and in the third year the farmer starts selling the seedlings. The farmer therefore splits up the nursery plot in three parts so that he can always have newly planted seedlings at the same time with second-year seedlings for grafting and third-year seedlings for selling
Natural / human environment: The technology was adopted by two other farmers from the village who had successfully applied to MSDSP for financial support for seeds and fertilisers. Many other farmers from neighbouring villages are interested. The bridge that is currently being built to allow for more trade between Afghanistan and Tajikistan might open further market opportunities for the land user. Furthermore this type of experience is being widely replicated in other districts and supported by MSDSP.
ទីតាំង: Vanj, Tajikistan, ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (approx. < 0.1 គម2 (10 ហិកតា))
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖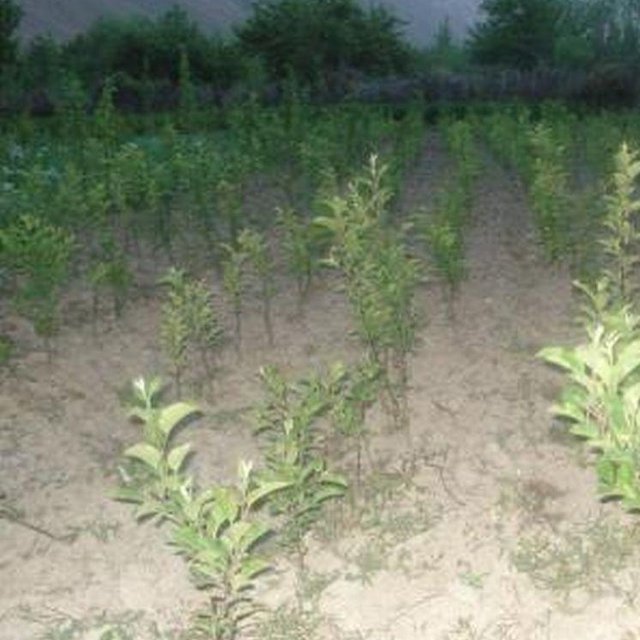





| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Somoni) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Somoni) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Fencing with dead branches | Persons/day | 80,0 | 20,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Ploughing and distribution of fertilisers | Persons/day | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Plant seeds in box with humid soil and irrigate | Persons/day | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Transfer seedlings to planting lines | Persons/day | 28,0 | 20,0 | 560,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| Seeds | kg | 10,0 | 5,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | |||||
| Fertilizer | kg | 30,0 | 3,0 | 90,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 2'370.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 526.67 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Somoni) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Somoni) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Apply nitrogen fertiliser | Persons/day | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Weeding | Persons/day | 28,0 | 20,0 | 560,0 | 100,0 |
| Grafting | Persons/day | 28,0 | 20,0 | 560,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | |||||
| Fertilizer | kg | 6,0 | 3,0 | 18,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 1'158.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 257.33 | ||||
Nursery established on cropland
The economic benefit for the land user is very high as during one year he can make more than 18,000 TJS (4000 USD) of profit from selling seedlings while the investments in fertilisers are comparably small.
Availability of fruits
More fruits provide a more balanced diet with more vitamins
Aesthetic value of trees
Higher income from selling the tree seedlings, about 3,000 USD per year, allowing people to provide better education for their children and better access to healthcare
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later