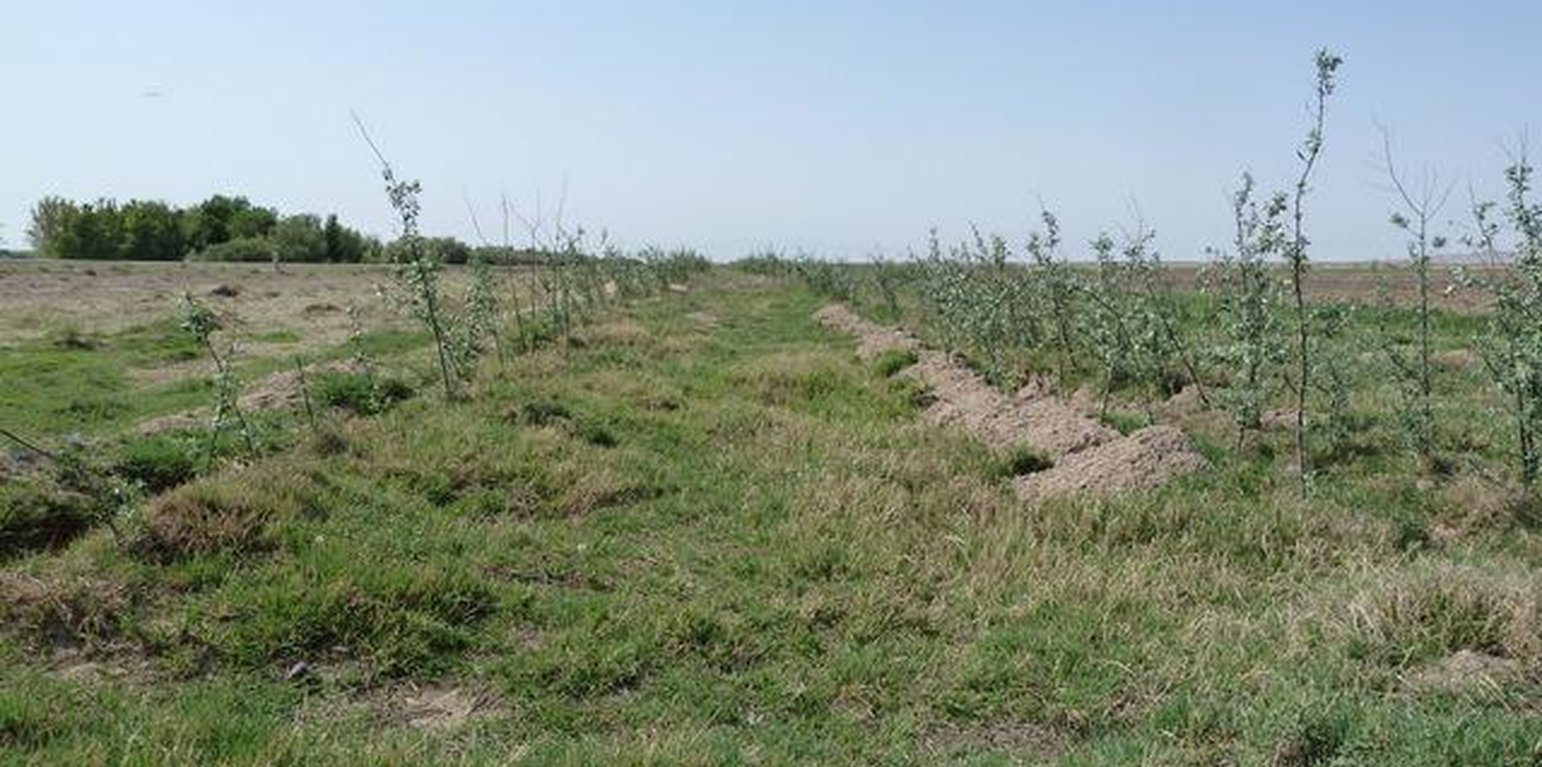
Shelterbelts with Russian Silverberry for the protection of irrigated fields
(ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន)
Tajikistan - Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM/ИСЦАУЗР)
ការពណ៌នា
Shelterbelts are used to protect irrigated land from deposition of sand and to reduce wind speed
This technology consists of shelterbelts made of Russian Silverberry (Elaeagnus angustifolia) to protect irrigated wheat and rice fields from strong winds.
In the Shaartuz area wind erosion poses huge problems to crop cultivation as topsoil is being removed and deposited as sediments on neighbouring fields. Dusty storms not only damage the crops but they also cause damage to the main surface, the fertile layer of soil. Sand also damages the irrigation canals, roads, gardens and streets in urban areas which forces people to leave such areas. Good yields cannot be achieved if fields are not properly protected.
A solution to this problem is the planting of shelterbelts around fields to slow wind speed and to prevent erosion of the arable soil layer. During Soviet times shelterbelts were planted on collective farms by the state forestry committee under contracts. After the collapse of the USSR and before the formation of Dehkan farms land users were not interested in investing in shelterbelts due to unprotected land use rights and unclear legal procedures. One farmer however tested the planting of a shelterbelt in 1992 when his son came back from his studies at the Agricultural University where he had learnt about the technology. They planted the first shelterbelt using a mixture of different tree species to protect newly irrigated fields. Due to financial constraints they could not invest in any other shelterbelts but in 2010 UNDP provided them with financial support to buy seedlings to increase the shelterbelt area. For this new shelterbelt the native Russian Silverberry (Elaeagnus angustifolia) was considered the most appropriate species as soils were highly saline and only this species proved tolerant.
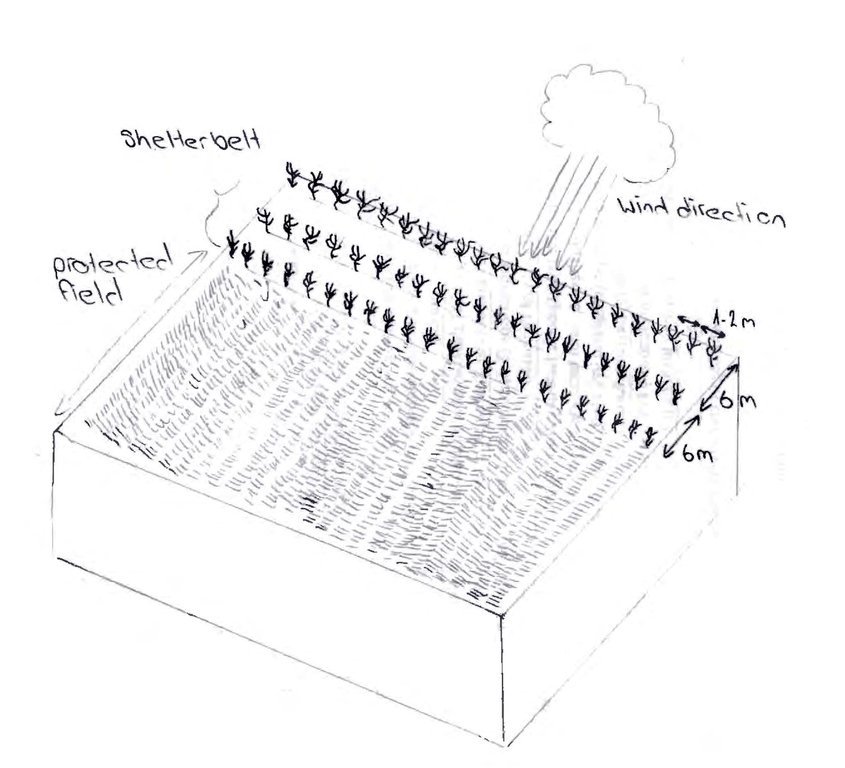
Trees were planted in three rows, along field boundaries and also along irrigation channels. Within rows trees were spaced at a 1m interval with a 6 m distance between rows. The plantations were established through “haschar” (voluntary neighbourhood help) with 30 people planting about 10,000 trees within one month. During the first three years after planting the saplings need regular irrigation and sanitary cleaning to help establish themselves. After 6-7 years the trees start drawing a lot of water from the soil which prevents the irrigated soils from damage through water logging. Russian silverberry can grow up to 12 m in 10-12 years.
Benefits of these shelterbelts are increased crop yields (wheat and rice) due to the protection from strong winds and decreased evapotranspiration. Thanks to the species association with nitrogen fixing root bacteria soil fertility is improved. The trees further produce edible fruits and provide valuable firewood that is consumed by the households. Russian Silverberry is resistant to pests and diseases and drought-tolerant once established; however, it requires a lot of water during the first few years. One constraint to the establishment of the shelterbelt is local people who often cut down branches for firewood. The farmer therefore has to guard his field whenever possible with the help of his family and staff he has employed to work on his field. Implementation of forestry initiatives began in 2009 and a total of 11 ha land was covered between 2009-2010. 11 farmers were involved in the project and establishment of the shelterbelts was initiated stage by stage during these two years. The project initiatives have also continued into 2011 as well. As other farmers do observe and understand the importance of shelterbelts, there has been a trend towards adoption of the technology by other farmers.
ទីតាំង
ទីតាំង: Shaartuz, Khatlon, ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ចំណុចយោងភូមិសាស្ត្រនៃទីតាំងជ្រើសរើស
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (approx. < 0.1 គម2 (10 ហិកតា))
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖
-
តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
ជាផ្នែកនៃប្រព័ន្ធប្រពៃណី (> 50 ឆ្នាំ)
-
ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
-
តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
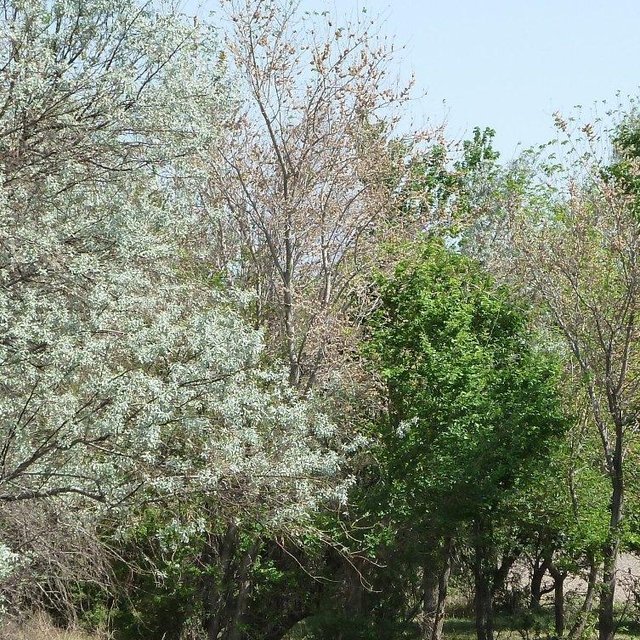

Shelterbelt with a variety of tree species planted in 1992/1993 (before implementation of the project) (Julie Zähringer (Baumackerstr. 51, 8050 Zürich))
គោលបំណងចម្បងៗ
-
ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
-
កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
-
ការពារតំបន់ទីជម្រាល/តំបន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមបញ្ចូលជាមួយបច្ចេកទេសផ្សេងទៀត
-
អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
-
កាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ
-
បន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
-
កាត់បន្ថយការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
-
បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
-
បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
ការប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ: ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវសាលី (និទាឃរដូវ), ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវ (តំបន់ខ្ពង់រាប)
- ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ): ផ្លែប៊ឺរី, Silverberry (Elaeagnus angustifolia)
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ: 1
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
-
ទឹកភ្លៀង
-
ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
-
ប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រពទាំងស្រុង
គោលបំណងទាក់ទងនឹងការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
-
ការបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ដែលមិនអាចអនុវត្តបាន
ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីដែលបានដោះស្រាយ
-
ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់ - Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ, Ed: អតិផរណា និង ការទម្លាក់, Eo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាព
-
ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី - Bh: ការបាត់បង់ទីជំរក, Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ
-
ការបាត់បង់ទឹក - Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
វិធានការ SLM
-
វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ - V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
គំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
លក្ខណៈបច្ចេកទេស
Shelterbelts consist of three rows of trees (Russian Silverberry). The rows are spaced 6 meters apart from each other and the interval between trees within the rows is 1-2 m.
Location: Shaartuz. Khatlon
Date: 27.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1500
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1-2
Trees/ shrubs species: Elaeagnus angustifolius (planted)
Author: Julie Zaehringer, Baumackerstr. 51, 8050 Zuerich
ការបង្កើតនិងការថែទាំ៖ សកម្មភាព ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
- ថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានគណនា៖
- រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ការគណនាថ្លៃដើម៖ Somoni
- អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ (ទៅជាដុល្លារអាមេរិក)៖ 1 USD = 4.5 Somoni
- ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមក្នុង ១ ថ្ងៃ៖ 5.50
កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលលើថ្លៃដើម
Labour was provided for free through the so-called "haschar" or neighborhood help.
សកម្មភាពបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
-
Planting of grafting material or tree seedlings (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: December)
ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល |
ឯកតា |
បរិមាណ |
ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Somoni) |
ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Somoni) |
% នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|
កម្លាំងពលកម្ម
|
| labour |
ha |
1,0 |
720,0 |
720,0 |
100,0 |
|
សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ
|
| seedlings |
ha |
1,0 |
1350,0 |
1350,0 |
|
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស |
2'070.0 |
|
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ |
460.0 |
|
សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
-
Irrigation of seedlings (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: regularly during first three years)
-
Sanitary cleaning of trees (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: None)
ធាតុចូលនិងថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល |
ឯកតា |
បរិមាណ |
ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Somoni) |
ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Somoni) |
% នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|
កម្លាំងពលកម្ម
|
| labour |
ha |
1,0 |
85,0 |
85,0 |
100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស |
85.0 |
|
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ |
18.89 |
|
បរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងជាមធ្យមប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
-
< 250 មម
-
251-500 មម
-
501-750 មម
-
751-1,000 មម
-
1,001-1,500 មម
-
1,501-2,000 មម
-
2,001-3,000 មម
-
3,001-4,000 មម
-
> 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
-
សើម
-
មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
-
មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
-
ស្ងួត
លក្ខណៈសម្គាល់នៃអាកាសធាតុ
Thermal climate class: temperate
ជម្រាល
-
រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
-
ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
-
មធ្យម (6-10%)
-
ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
-
ទីទួល (16-30%)
-
ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
-
ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី
-
ខ្ពង់រាប
-
កំពូលភ្នំ
-
ជម្រាលភ្នំ
-
ជម្រាលទួល
-
ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
-
បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
រយៈកម្ពស់ធៀបនឹងនីវ៉ូទឹកសមុទ្រ
-
0-100 ម
-
101-500 ម
-
501-1,000 ម
-
1,001-1,500 ម
-
1,501-2,000 ម
-
2,001-2,500 ម
-
2,501-3,000 ម
-
3,001-4,000 ម
-
> 4,000 ម
បច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្តនៅក្នុង
-
សណ្ឋានដីប៉ោង
-
សណ្ឋានដីផត
-
មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
ជម្រៅដី
-
រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
-
រាក់ (21-50 សម)
-
មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
-
ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
-
ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនៈភាពដី (ដីស្រទាប់ខាងលើ)
-
គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
-
មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
-
ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ក្រោមស្រទាប់លើ)
-
គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
-
មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
-
ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
កម្រិតសារធាតុសរីរាង្គក្នុងដីស្រទាប់លើ
-
ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
-
មធ្យម (1-3%)
-
ទាប (<1%)
ដង្ហើមទឹកក្នុងដី
-
ផ្ទៃខាងលើ
-
< 5 ម
-
5-50 ម
-
> 50 ម
ភាពអាចរកបាននៃទឹកលើដី
-
លើស
-
ល្អ
-
កម្រិតមធ្យម
-
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រព្រឹត្តិកម្ម)
-
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
-
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
-
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
-
ទឹកមិនអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាន
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖
តើមានបញ្ហាទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលដែរឬទេ?
ការកើតឡើងនៃទឹកជំនន់
ភាពសំបូរបែបនៃជម្រកធម្មជាតិ
ចរិតលក្ខណៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលប្រើបច្ចេកទេស SLM
ទីផ្សារ
-
សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
-
ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
-
ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន
-
តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
-
10-50% នៃចំណូល
-
ច្រើនជាង 50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព
-
មិនល្អខ្លាំង
-
មិនល្អ
-
មធ្យម
-
មាន
-
មានខ្លាំង
កម្រិតនៃការប្រើគ្រឿងយន្ត
-
ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
-
ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
-
គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ
-
នៅមួយកន្លែង
-
ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
-
ពនេចរ
បុគ្គល ឬក្រុម
-
ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
-
ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
-
សហករ
-
មានបុគ្គលិក (ក្រុមហ៊ុន, រដ្ឋ)
អាយុ
-
កុមារ
-
យុវវ័យ
-
វ័យកណ្តាល
-
មនុស្សចាស់
ផ្ទៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ក្នុងមួយគ្រួសារ
-
< 0.5 ហិកតា
-
0.5-1 ហិកតា
-
1-2 ហិកតា
-
2-5 ហិកតា
-
5-15 ហិកតា
-
15-50 ហិកតា
-
50-100 ហិកតា
-
100-500 ហិកតា
-
500-1,000 ហិកតា
-
1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
-
> 10,000 ហិកតា
មាត្រដ្ឋាន
-
ខ្នាតតូច
-
ខ្នាតមធ្យម
-
ខ្នាតធំ
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដីធ្លី
-
រដ្ឋ
-
ក្រុមហ៊ុន
-
ភូមិ
-
ក្រុម
-
ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
-
ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
សិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
-
ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
-
កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
-
ឯកជន
សិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
-
អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
-
ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
-
កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
-
ឯកជន
ប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន)
ផលប៉ះពាល់
ផលប៉ះពាល់សេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
ផលប៉ះពាល់វប្បធម៌សង្គម
contribution to human well-being
through increased crop yield
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
shelterbelts can provide habitat to birds, insects etc.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណ
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
from prevention of deposition
ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
អត្ថប្រយោជន៍បើប្រៀបធៀបនឹងថ្លៃដើមក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
រយៈពេលខ្លី
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
អត្ថប្រយោជន៍បើប្រៀបធៀបនឹងថ្លៃដើមក្នុងការថែទាំបច្ចេកទេស
រយៈពេលខ្លី
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ កើនឡើង
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ការទទួលយក និងការបន្ស៊ាំ
ភាគរយនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីនៅតំបន់ដែលបានទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
-
តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
ក្នុងចំណោមអ្នកទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេសនេះ តើមានប៉ុន្មានភាគរយដែលបានអនុវត្តន៍ដោយមិនបានទទួលការលើកទឹកចិត្តជាសម្ភារៈ?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ចំពោះលក្ខខណ្ឌប្រែប្រួលណាមួយដែលត្រូវបានបន្ស៊ាំ?
-
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
-
បម្រែបម្រួលទីផ្សារ
-
កម្លាំងពលកម្មដែលអាចរកបាន (ចំណាកស្រុក)
សេក្តីសន្និដ្ឋាន និងមេរៀនបទពិសោធន៍
ភាពខ្លាំង: ទស្សនៈអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
Reduced deflation and deposition of sand on fields and therefore improved crop growth
-
Increased crop yield as before the establishment of shelterbelts no crops could grow on this land
-
Reduced wind speed
-
Russian Silverberry produces edible fruits rich in vitamins
-
Increased production area
ភាពខ្លាំង: ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រង ឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ផ្សេងទៀត
-
Russian silverberry is a native tree species with high drought-tolerance and the ability to grow on nutrient-poor soils thanks to its root association with nitrogen fixing bacteria
-
Once established the shelterbelts do not need a lot of maintenance
-
Rehabilitation of unproductive, denuded land into productive cropland
ចំណុចខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ : ទស្សនៈអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីវិធីដោះស្រាយ
-
The shelterbelts have to be protected from being damaged by local people who want to cut them for firewood
Awareness raising; increase of firewood supply through tree planting
ចំណុចខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ : ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រង ឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ផ្សេងទៀតវិធីដោះស្រាយ
ឯកសារយោង
អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ
-
Alexandra Gavilano
-
Deborah Niggli
-
Joana Eichenberger
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: 15 ខែ មេសា ឆ្នាំ 2011
កែតម្រូវចុងក្រោយ: 2 ខែ វិច្ឆិកា ឆ្នាំ 2021
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ
-
Firdavs Faizulloev - អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM
-
Julie Zähringer - អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM
-
Firuz Ibragimov - អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM
ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតក្នុងប្រព័ន្ធគ្រប់គ្រងទិន្នន័យរបស់វ៉ូខេត
ឯកសារនេះត្រូវបានសម្របសម្រួលដោយ
ស្ថាប័ន៖
គម្រោង
- Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM I)
- Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)











