Rainwater Harvesting for Olive Production
(ប៉ាឡេស្ទីន រដ្ឋ)
ការពណ៌នា
Microcatchment water harvesting captures, stores and allows safe overflow of excess surface runoff collected during heavy rainfall events. The intercepted and deep-infiltrated water enhances soil moisture at/around the microcatchment structure. This eventually boosts plant productivity in dry areas, mitigates land degradation, and benefits the local farming communities’ livelihoods
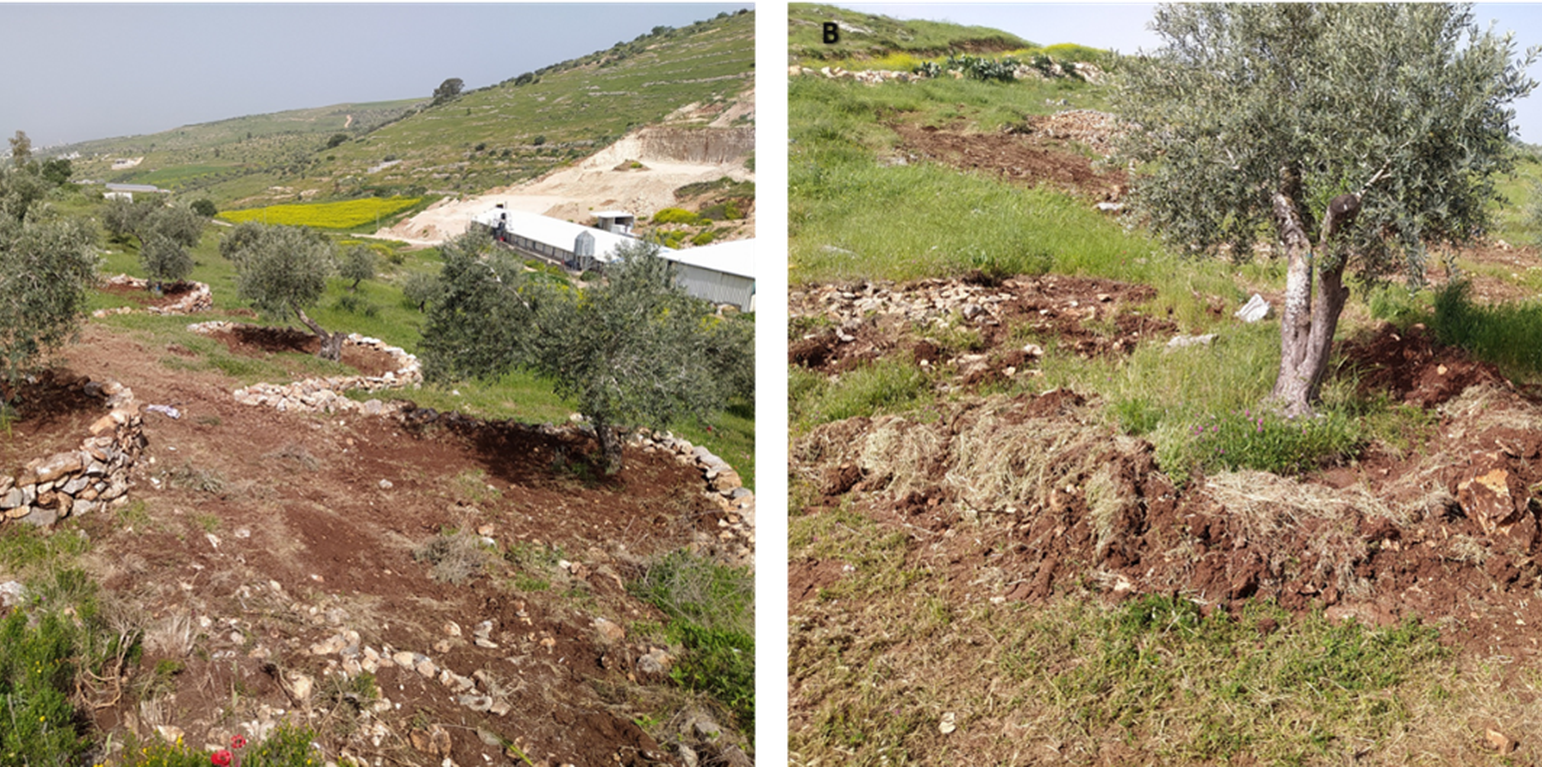
In Palestine, rainfed olives are traditionally cultivated within undulating landscapes with an average annual precipitation ranging between 400 and 700 mm. Olive trees are well known for their resilience to droughts. However, degraded and steeply sloping areas have limited water infiltration and storage capacity: a large proportion of rain forms surface runoff, further speeding up land degradation through erosion and the removal of fertile topsoil, leading to decreased soil health and productivity. The International Center of Agriculture Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA) among others, recognised these issues and superimposed microcatchment water harvesting structures on existing rainfed olive trees in marginal and degraded drylands of Palestine. This technique aims to improve yields by increasing soil moisture through capturing runoff and enhancing infiltration. Thereby, it also decreases the potential for land degradation through surface runoff. This has positive impacts on the local land users and land owners. These are often considered marginalised groups because they lack access to off-farm work and finance to invest in their farms. Additionally, these farmers are directly experiencing the negative impacts of climate change, such as more frequent droughts which can be linked to declining yields, and decreasing farm income. Depending on local climate, topographic and soil conditions, olive trees are usually spaced 5-10 meters apart to avoid competition for water.
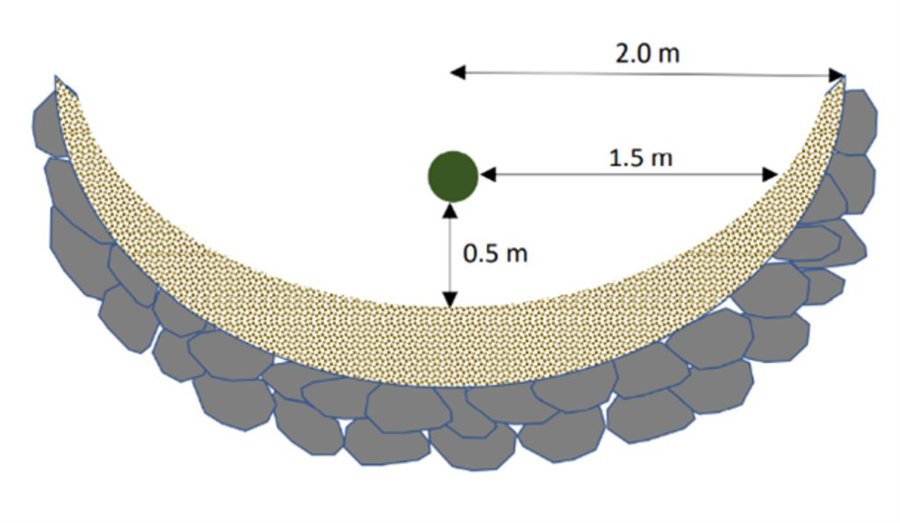
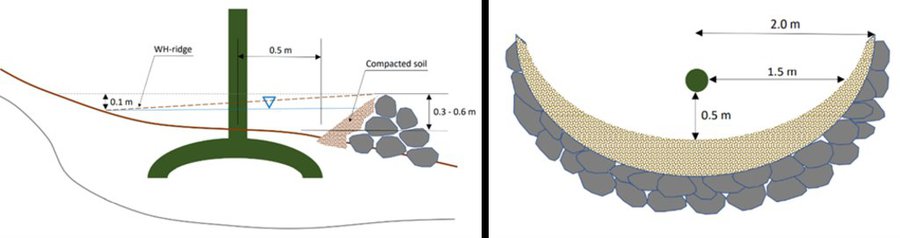
The land is first surveyed and then the microcatchment water harvesting structures (technically termed “semi-circular bunds”) are designed with the tips of the structures on the contour. They are constructed around 0.5 meters downslope of each olive tree in a semi-circle of around 4 meters diameter. The structures are created through stone foundation and bunds topped with a compacted soil layer. The height of the structures varies between 0.3 meters and 1.2 meters. As a first step, stones are placed and fixed in a semi-circular shape. Secondly, the soil inside the structure is slightly levelled. Thirdly, more stones are placed to heighten the bunds. Lastly, excavated and surround soil is put over the stones and thoroughly compacted. The estimation of establishment cost is 7 USD per meter of bund, implying a total cost of approximately 7000 USD per hectare.
The life-duration of the water harvesting system implemented in highly sloping areas, is estimated at 15 years with yearly maintenance cost estimated at 3 USD per tree – 300 USD per hectare. Without maintenance, the life-cycle of the system will be less.
Land users appreciate the technology because it improves their olive yields and thus income. They state that the topsoil maintained in situ, and the improved soil moisture, have positive effects on their harvest. Land users also acknowledge that implementing and maintaining increases the workload. Nevertheless, due to the local material requirements, the costs are low and thus perceived as positive.
Data presented in this documentation are partly made available under the project 'Testing and Out-scaling in situ Water Harvesting Technologies in Palestine' led by ICARDA in collaboration with the Applied Research Institute Jerusalem, Palestinian Ministry of Agriculture, and National Agricultural Research Centre in Palestine. The project is under the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) – a regional project “Implementing the 2030 Agenda for water efficiency/productivity and water sustainability in NENA countries” directly under the Regional Water Scarcity Initiative. The Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency funded the project.
ទីតាំង
ទីតាំង: ប៉ាឡេស្ទីន រដ្ឋ
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ: មួយកន្លែង
ចំណុចយោងភូមិសាស្ត្រនៃទីតាំងជ្រើសរើស
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (approx. 0.1-1 គម2)
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?: ទេ
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: 2021
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖
-
តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
ជាផ្នែកនៃប្រព័ន្ធប្រពៃណី (> 50 ឆ្នាំ)
-
ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
-
តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
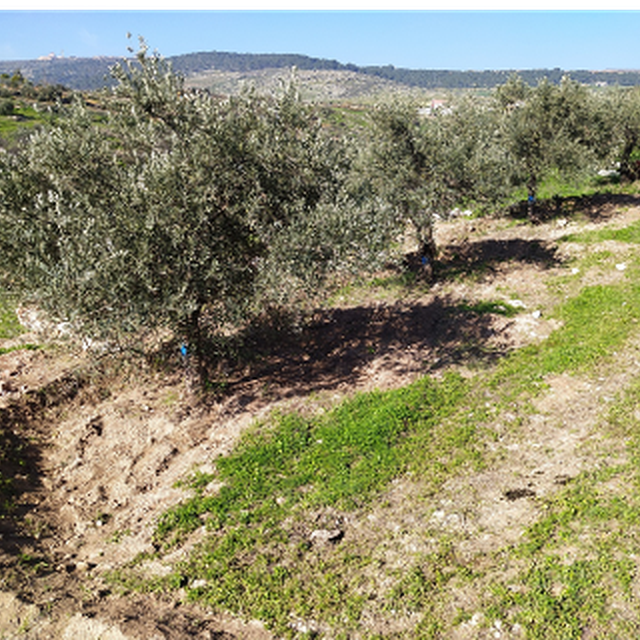

An older water harvesting structure (ARIJ)
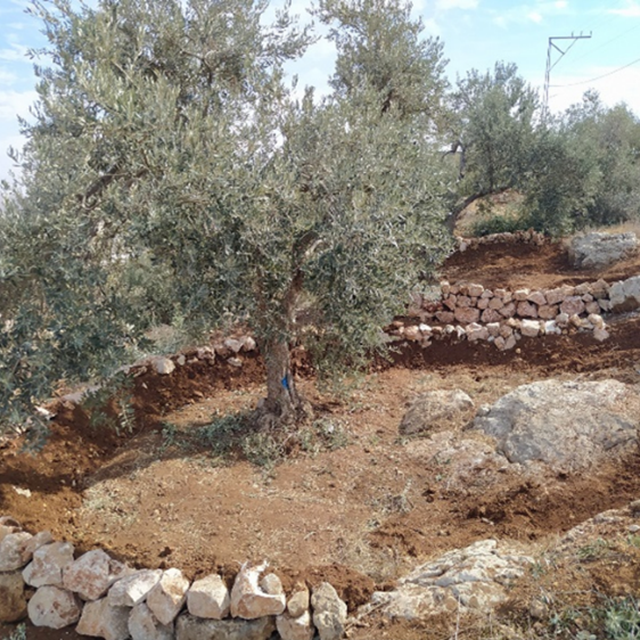

Freshly implemented water harvesting structure (ARIJ)
គោលបំណងចម្បងៗ
-
ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
-
កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
-
ការពារតំបន់ទីជម្រាល/តំបន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមបញ្ចូលជាមួយបច្ចេកទេសផ្សេងទៀត
-
អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
-
កាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ
-
បន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
-
កាត់បន្ថយការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
-
បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
-
បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
ការប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ ទេ
-
ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ: អូលីវ
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ? ទេ
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ? ទេ
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
-
ទឹកភ្លៀង
-
ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
-
ប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រពទាំងស្រុង
គោលបំណងទាក់ទងនឹងការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
-
ការបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
-
ដែលមិនអាចអនុវត្តបាន
ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីដែលបានដោះស្រាយ
-
ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក - Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ, Wg: ការកកើតឡើងនូវកំទេចកំទីដីស្រទាប់ក្រោម, Wm: ការបាក់ដី
-
ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់ - Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ
ក្រុម SLM
-
គ្រប់គ្រងការដាំព្រៃឈើ
-
វិធានការអនុវត្តកាត់ទទឹងទីជម្រាល
-
ការស្តុកទុកទឹក
វិធានការ SLM
-
វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ - S2: ភ្លឺ ច្រាំង, S7: ការប្រមូលទឹកស្តុកទុក/ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក/ សម្ភារៈស្រោចស្រព
គំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
លក្ខណៈបច្ចេកទេស
Microcatchment rainwater harvesting design, with detailed cross-sectional (left) and top (right) views; definition of dimensions
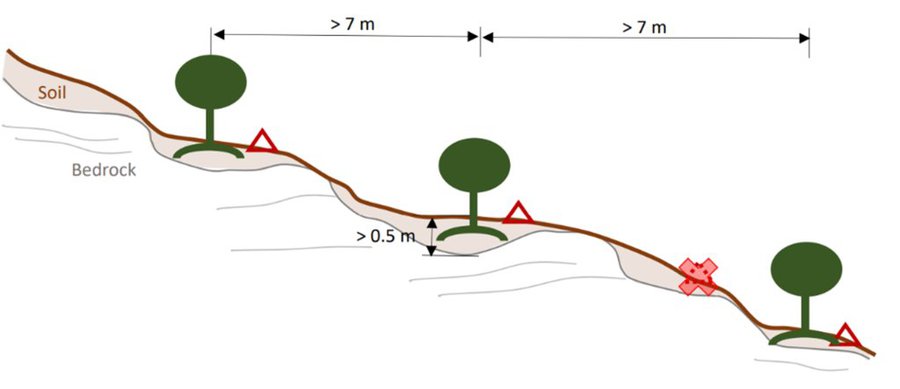
Microcatchment rainwater harvesting design in hillslope direction; definition of spacing constrained by the local ‘soil pocket’ hillslope pattern.
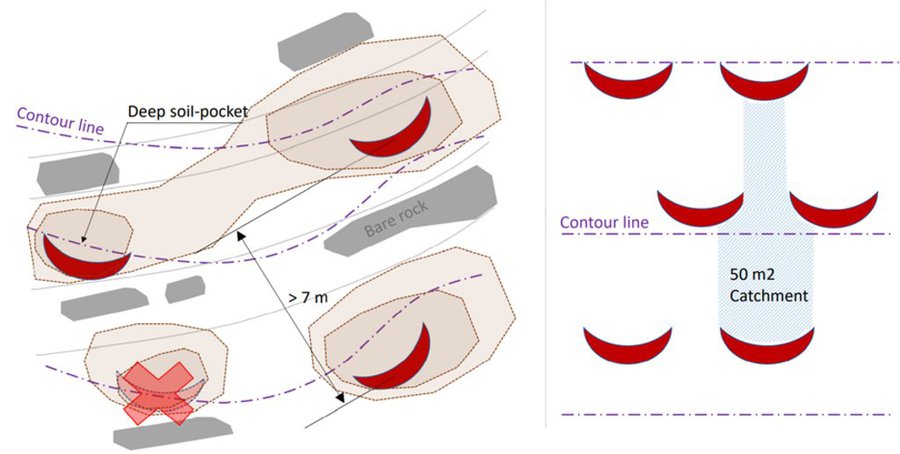
Microcatchment rainwater harvesting design from a top view; definition of minimum microcatchment areas contributing to the rainwater harvesting pits.
Microcatchment rainwater harvesting design, with detailed cross-sectional (left) and top (right) views; definition of dimensions.
ការបង្កើតនិងការថែទាំ៖ សកម្មភាព ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
- ថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានគណនា៖ ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី៖ 1 Hectare)
- រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ការគណនាថ្លៃដើម៖ ដុល្លារ
- អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ (ទៅជាដុល្លារអាមេរិក)៖ 1 USD = មិនមាន
- ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមក្នុង ១ ថ្ងៃ៖ មិនមាន
កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលលើថ្លៃដើម
មិនមាន
សកម្មភាពបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
-
Field survey for contours (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: None)
-
Place Stones (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: None)
-
Soil Removal (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: None)
-
Stone bund around tree (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: None)
-
Stone bund topped with excavated soil (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: None)
ថ្លៃបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសសរុប (ប៉ាន់ស្មាន)
7000,0
សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
-
Incidental repairs (ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់: None)
ថ្លៃថែទាំបច្ចេកទេសសរុប (ប៉ាន់ស្មាន)
300,0
បរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងជាមធ្យមប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
-
< 250 មម
-
251-500 មម
-
501-750 មម
-
751-1,000 មម
-
1,001-1,500 មម
-
1,501-2,000 មម
-
2,001-3,000 មម
-
3,001-4,000 មម
-
> 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
-
សើម
-
មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
-
មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
-
ស្ងួត
លក្ខណៈសម្គាល់នៃអាកាសធាតុ
មិនមាន
ជម្រាល
-
រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
-
ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
-
មធ្យម (6-10%)
-
ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
-
ទីទួល (16-30%)
-
ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
-
ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី
-
ខ្ពង់រាប
-
កំពូលភ្នំ
-
ជម្រាលភ្នំ
-
ជម្រាលទួល
-
ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
-
បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
រយៈកម្ពស់ធៀបនឹងនីវ៉ូទឹកសមុទ្រ
-
0-100 ម
-
101-500 ម
-
501-1,000 ម
-
1,001-1,500 ម
-
1,501-2,000 ម
-
2,001-2,500 ម
-
2,501-3,000 ម
-
3,001-4,000 ម
-
> 4,000 ម
បច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្តនៅក្នុង
-
សណ្ឋានដីប៉ោង
-
សណ្ឋានដីផត
-
មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
ជម្រៅដី
-
រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
-
រាក់ (21-50 សម)
-
មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
-
ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
-
ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនៈភាពដី (ដីស្រទាប់ខាងលើ)
-
គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
-
មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
-
ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ក្រោមស្រទាប់លើ)
-
គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
-
មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
-
ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
កម្រិតសារធាតុសរីរាង្គក្នុងដីស្រទាប់លើ
-
ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
-
មធ្យម (1-3%)
-
ទាប (<1%)
ដង្ហើមទឹកក្នុងដី
-
ផ្ទៃខាងលើ
-
< 5 ម
-
5-50 ម
-
> 50 ម
ភាពអាចរកបាននៃទឹកលើដី
-
លើស
-
ល្អ
-
កម្រិតមធ្យម
-
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រព្រឹត្តិកម្ម)
-
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
-
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
-
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
-
ទឹកមិនអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាន
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖ ទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលដែរឬទេ?
ការកើតឡើងនៃទឹកជំនន់
ភាពសំបូរបែបនៃជម្រកធម្មជាតិ
ចរិតលក្ខណៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលប្រើបច្ចេកទេស SLM
ទីផ្សារ
-
សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
-
ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
-
ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន
-
តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
-
10-50% នៃចំណូល
-
ច្រើនជាង 50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព
-
មិនល្អខ្លាំង
-
មិនល្អ
-
មធ្យម
-
មាន
-
មានខ្លាំង
កម្រិតនៃការប្រើគ្រឿងយន្ត
-
ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
-
ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
-
គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ
-
នៅមួយកន្លែង
-
ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
-
ពនេចរ
បុគ្គល ឬក្រុម
-
ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
-
ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
-
សហករ
-
មានបុគ្គលិក (ក្រុមហ៊ុន, រដ្ឋ)
អាយុ
-
កុមារ
-
យុវវ័យ
-
វ័យកណ្តាល
-
មនុស្សចាស់
ផ្ទៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ក្នុងមួយគ្រួសារ
-
< 0.5 ហិកតា
-
0.5-1 ហិកតា
-
1-2 ហិកតា
-
2-5 ហិកតា
-
5-15 ហិកតា
-
15-50 ហិកតា
-
50-100 ហិកតា
-
100-500 ហិកតា
-
500-1,000 ហិកតា
-
1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
-
> 10,000 ហិកតា
មាត្រដ្ឋាន
-
ខ្នាតតូច
-
ខ្នាតមធ្យម
-
ខ្នាតធំ
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដីធ្លី
-
រដ្ឋ
-
ក្រុមហ៊ុន
-
ភូមិ
-
ក្រុម
-
ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
-
ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
សិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
-
ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
-
កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
-
ឯកជន
សិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
-
អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
-
ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
-
កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
-
ឯកជន
ប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន)
ផលប៉ះពាល់
ផលប៉ះពាល់សេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
Improved soil moisture provides resilience for droughts, reducing failure risk
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
Not damaging the bunds may hinder land management
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
Inputs for repair and implementation is required
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
Because soil moisture is increased, yield is as well and risk is decreased
បន្ទុកការងារ
Building and repairing the bunds requires labour
ផលប៉ះពាល់វប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
Local farmers were included in the process, improving their knowledge
ស្ថានភាពក្រុមទទួលផលតិចពីសេដ្ឋកិច្ច និងសង្គម (ភេទ អាយុ ជាតិសាសន៍ ។ល។)
អាក្រក់ជាងមុន
ប្រសើរជាងមុន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ការប្រមូលទឹក (លំហូរ ទឹកសន្សើម ព្រិល ។ល។)
ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណ
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន (ទឹកក្រោមដី ទឹក-springs)
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម (មិនត្រូវការ)
ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
អត្ថប្រយោជន៍បើប្រៀបធៀបនឹងថ្លៃដើមក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
រយៈពេលខ្លី
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
អត្ថប្រយោជន៍បើប្រៀបធៀបនឹងថ្លៃដើមក្នុងការថែទាំបច្ចេកទេស
រយៈពេលខ្លី
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ ថយចុះ
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
ការទទួលយក និងការបន្ស៊ាំ
ភាគរយនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីនៅតំបន់ដែលបានទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
-
តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
ក្នុងចំណោមអ្នកទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេសនេះ តើមានប៉ុន្មានភាគរយដែលបានអនុវត្តន៍ដោយមិនបានទទួលការលើកទឹកចិត្តជាសម្ភារៈ?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ចំពោះលក្ខខណ្ឌប្រែប្រួលណាមួយដែលត្រូវបានបន្ស៊ាំ?
-
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
-
បម្រែបម្រួលទីផ្សារ
-
កម្លាំងពលកម្មដែលអាចរកបាន (ចំណាកស្រុក)
សេក្តីសន្និដ្ឋាន និងមេរៀនបទពិសោធន៍
ភាពខ្លាំង: ទស្សនៈអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
-
Increased yield
-
Decreased land degradation
ភាពខ្លាំង: ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រង ឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ផ្សេងទៀត
-
Reduced and reversed land degradation
-
Increased yield
ចំណុចខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ : ទស្សនៈអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីវិធីដោះស្រាយ
-
Increases the workload
In the current state this cannot be overcome. However, alternative structures may be considered e.g., pre -fixed.
-
Limited availability of suitable stones
The purchase of stones or alternative materials such as wood or clay, or alternative structures such as pits.
ចំណុចខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ : ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រង ឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ផ្សេងទៀតវិធីដោះស្រាយ
ឯកសារយោង
អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ
-
William Critchley
-
Rima Mekdaschi Studer
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: 12 ខែ កញ្ញា ឆ្នាំ 2022
កែតម្រូវចុងក្រោយ: 25 ខែ ឧសភា ឆ្នាំ 2023
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ
-
Mira Haddad - Research Associate – Spatio-temporal assessment – Resilient Agrosilvopastoral Systems (RASP) – Restoration Initiative on Dryland Ecosystems (RIDE)
-
Stefan Strohmeier - Scientist, Soil and Water Conservation – Resilient Agrosilvopastoral Systems (RASP)
-
Vinay Nangia - Research Team Leader – Soils, Waters, and Agronomy
-
Boubaker Dhehibi - Senior Natural Resources Economist – Resilient Agrosilvopastoral Systems (RASP) – Social, Economic, and Policy Team (SEPT)
ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតក្នុងប្រព័ន្ធគ្រប់គ្រងទិន្នន័យរបស់វ៉ូខេត
ឯកសារនេះត្រូវបានសម្របសម្រួលដោយ
ស្ថាប័ន៖
- International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - ប្រទេសលីបង់
គម្រោង
- ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiative
ឯកសារយោងសំខាន់ៗ
-
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mira Haddad, Abdallah Alimari, Sameer Shadeed, Stefan Strohmeier, Issam Nofal, Anas Sayeh, Ibtisam I. O. AbuAlhaija, Mohammad Besharat, Imad Ghenma, Vinay Nangia. (6/3/2023). Potential Of Water Harvesting as a Strategic Tool for Resilience, Sustainable Livelihoods, and Drought Mitigation in the Olive Farming System in Palestine. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/68288