



Lantana Camara was introduced into India as an ornamental plant in 1809 by the British in Calcutta Botanical Garden. Lantana Camara negatively impacts biodiversity and native biota, disrupting the succession cycle, altering the structure and floral composition of native communities, and causing problems in agricultural lands in various regions of India. Its dense thickets outcompete native pastures, block the movement of grazers, and can cause poisoning. Its allelopathic activities also affect the growth of other species in its proximity. One of the measures to manage invasive species is by turning it into biochar.
Biochar is the charred biomass produced by slow pyrolysis in which organic material is heated under controlled temperatures (300-500°C) without oxygen. Lantana Camara is an ideal biomass for biochar production due to its high diversity and wide distribution. In addition to protecting ecosystems, invasive plant-derived biochar has potential applications in environmental remediation and soil amendment due to its unique structure, composition, and adsorption properties.
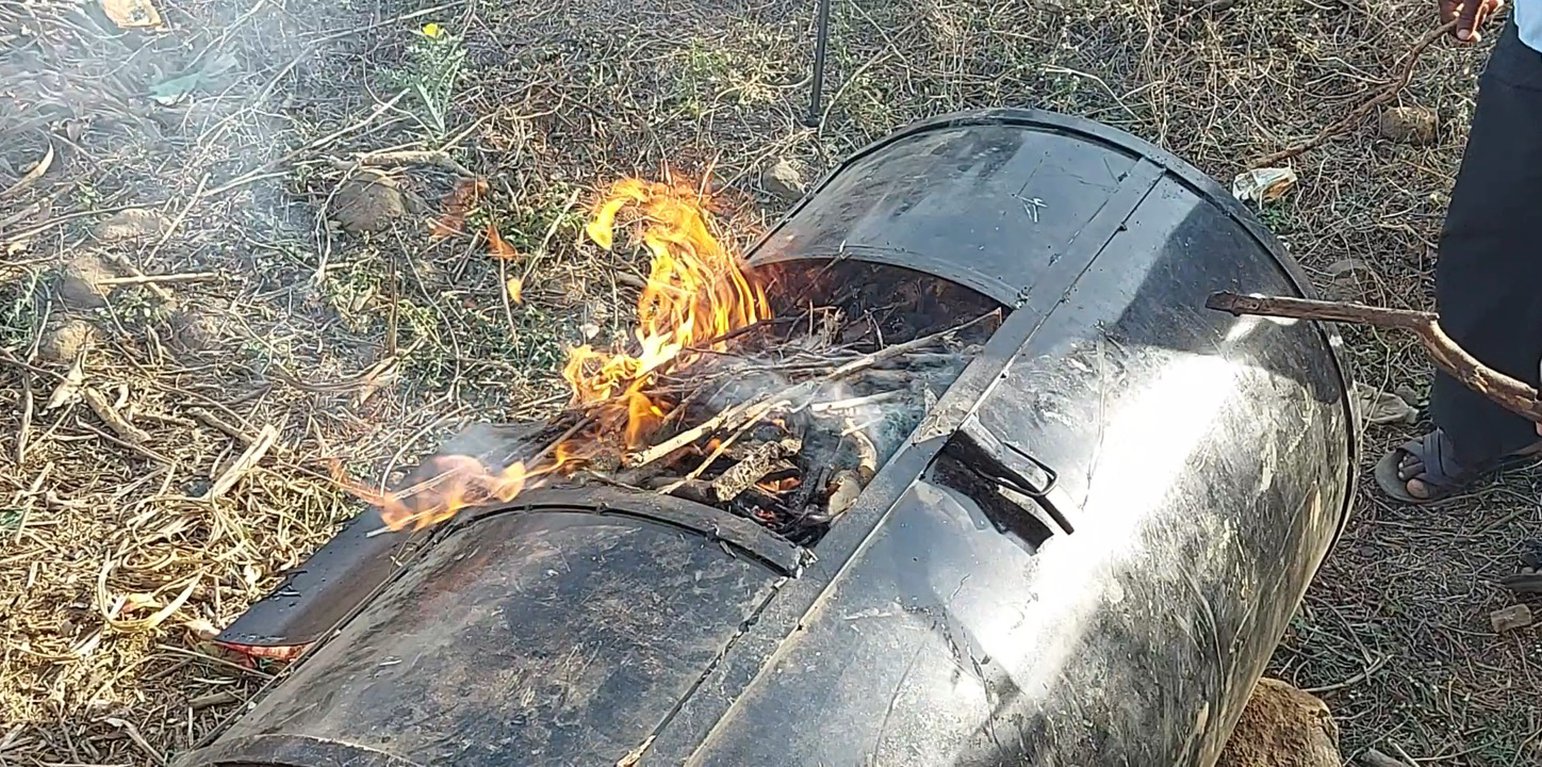
In the Mandla district of Madhya Pradesh, low-cost technologies for producing biochar are being practised. A low-cost portable kiln unit has been used in the Mandla District to cater to the needs of small and marginal farmers. One unit costs approximately Rs. 7000-12000 depending upon the design and location, including a metal drum, vent-making charges, and side fittings. The kiln is designed to work on the direct up-draft principle with bottom ignition. It is a vertical, single-barrel structure with a perforated base. The kiln has a square-shaped loading hole at the top, which can be closed at the end of conversion with a metal lid with a handle. The kiln has circular vents, a staggered arrangement to avoid rows, and a central vent to hold a wooden pole. Under open atmospheric conditions, the vents at the kiln base hasten hot gas movement through the bio-residues for uniform heat transfer by primary air movement. The kiln's top hole vents the released water vapours and hot gases. A strip of metal is welded around at 3/4th height of the kiln, to which two metal rods are welded on opposite sides to serve as lifting jacks. Dry Lantana Camara feedstock is placed inside the kiln unit, and a fire is lit at the bottom. Through a pyrolysis process, the organic compounds present in the biomass decompose at a specific temperature in an oxygen-limited environment.
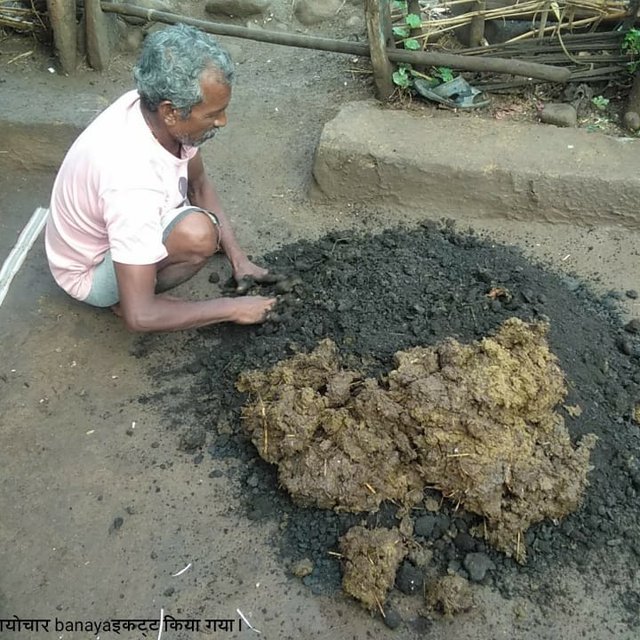
Prior to use, the stalks/twigs of lantana are manually cut into appropriate pieces 15-19 cm long and 0.9-1.0 cm in diameter using a commonly used axe in order to achieve better packing density. Dry residues are a prerequisite to hasten satisfactory and quicker conversion. The dried residues of lantana are placed in the unit and are burned from the bottom in an oxygen-limited environment. Generally, the burning process takes 6-8 hours through a slow pyrolysis process. Once complete, the kiln is quenched with soil and left to cool for 3-4 hours. This simple and affordable biochar production method can help manage invasive plant species and benefit agriculture, the environment, and energy. The conversion ratio from biomass to biochar in the case of Lantana is around 20-25%. Farmers have reported of burning around 100 kg of dried Lantana biomass to get ~20 kg of biochar in one operation of the unit. The application rate of biochar varies from crop to crop and the type of soil and other characters. In studied project farmers do apply 20 kg of biochar mixed with 20 kg of cow dung and 20 kg of cow urine in an area of around 1 acre.
The burned biomass of Lantana after the process looks like the coal sticks, these sticks are pulverised through a pulveriser to make a powdered material for application in the field. The biochar is mixed with an equal quantity of cow dung and cow urine before the application. Some farmers also mix the native soils in biochar to get better results.
ទីតាំង: Mandla, Madhya Pradesh, ប្រទេសឥណ្ឌា
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ: 10-100 កន្លែង
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?: ទេ
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: 2020
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖









| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (INR) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (INR) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Biochar Kiln | Number | 1,0 | 7000,0 | 7000,0 | 25,0 |
| Pulverizer unit | Number | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | 25,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 27'000.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 337.5 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (INR) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (INR) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Labor cost for removal of lantana | ha | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 25,0 |
| Preparation of biochar | Person-day | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Application of biochar in the field | Person-day | 0,5 | 200,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Transportation of lantana | Trip | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | |||||
| Cow dung | kg | 20,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Cow urine | kg | 20,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 5'900.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 73.75 | ||||
Approximately increase of 15-20% across the crops. Where biochar was used, since this has happened in multiple commodities specifying the number for any crop will not do justice.
Grain size, the strength of biomass and overall taste of the grains. These are the qualitative measures which can not be addressed in numbers.
Biochar maintains soil moisture thus, farmers need to use less quantity of water for irrigation.
Lantana Camara negatively impacts biodiversity and native biota. Its dense thickets outcompete native pastures, blocks the movement of grazers, and can cause poisoning. Its eradication helps improving the vegetative cover.
As the density of Lantana Camara in the forest increases, allelopathic interactions increase, and hence, species richness declines (Day et al., 2003).
The invasive alien species of Lantana Camara are removed from private and common land.