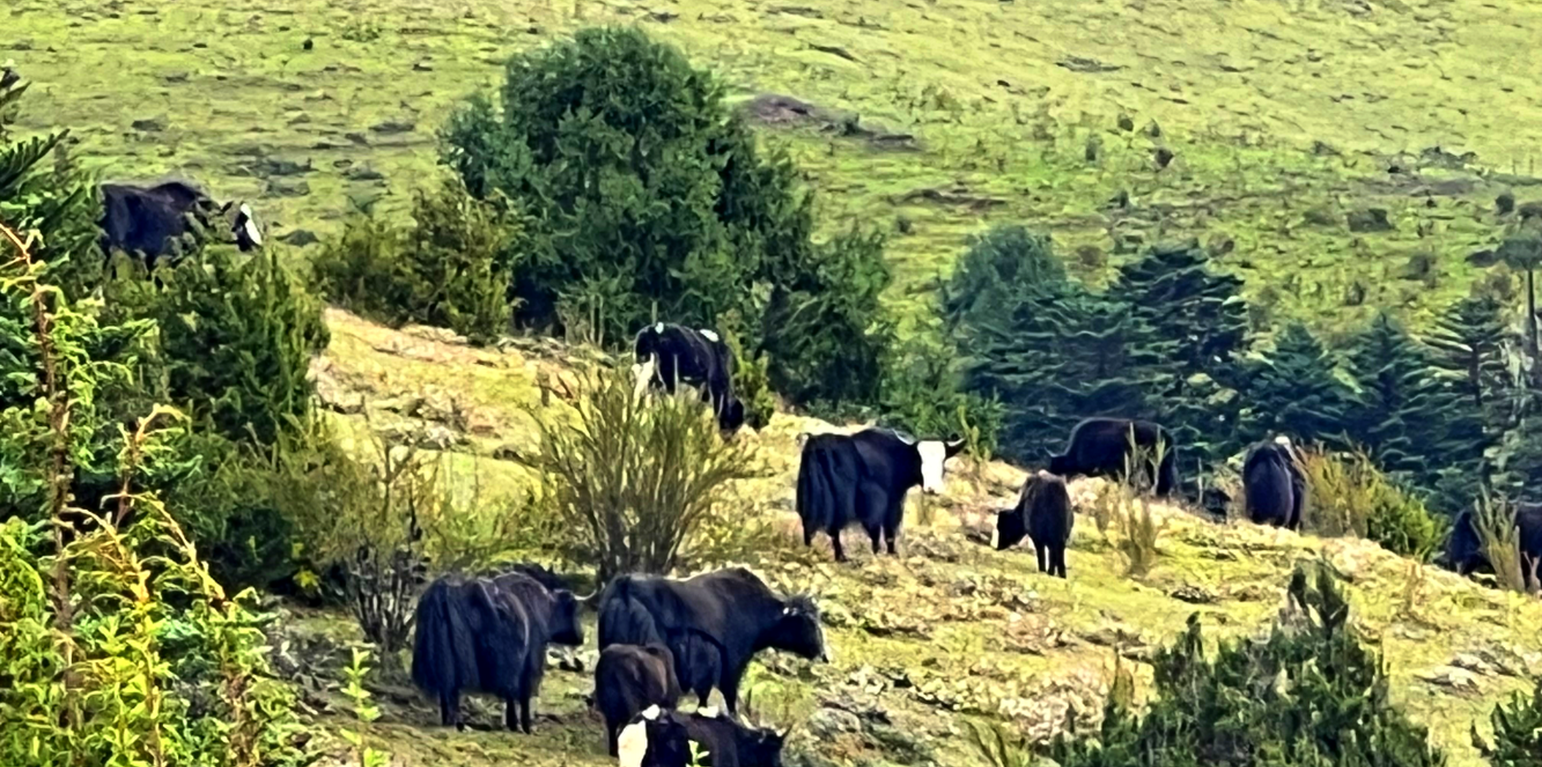




The practice of burning rangeland (“tsamdro”) is a longstanding tradition among highlanders, whose livelihoods depend on livestock including yaks, cattle, horses and sheep. It is mainly practiced by transhumant communities or individuals who rely on livestock for their livelihoods. They follow a migratory livestock husbandry system that takes them from the highlands to the lowlands dependent on the availability of fodder resources, while simultaneously avoiding the extremes of climate. In the past, rangeland was allocated to individuals, communities, or religious bodies through payment for a minimal annual grazing permit, granting grazing rights. When pasture was scarce, controlled fires were intentionally set in specific areas to rejuvenate the rangeland with fresh grass and control unpalatable grasses and shrubs. For instance, the transhumant nomadic communities of Dhur village, Choekhor Gewog, in Bumthang have adopted the practice of burning rangeland. This practice is implemented during the winter months, dependent on weather, vegetation status, and wind patterns. Rooted in traditional knowledge and cultural practices, the practice is slowly diminishing nowadays due to environmental concerns and labour shortages as young nomads migrate - seeking better employment in towns.
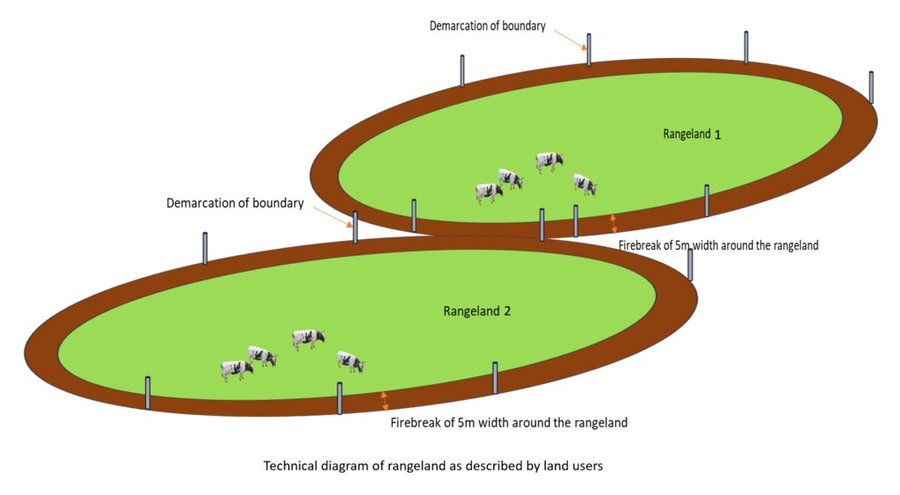
The technique serves multiple purposes. These include promoting the growth of fresh and palatable pasture rich in protein, increasing plant diversity, adding nutrients to the soil through ash, and reducing dead plant material that inhibits new plant growth. Additionally, rangeland burning contributes to the control of livestock pests, especially ticks and flies. While rangeland burning is a straightforward process, it requires careful planning of time and location, creation of fire breaks to prevent uncontrollable spread, and leaving the land fallow for 2 to 3 years after burning to encourage grass growth.
Land users appreciate the technology for reducing their workload in collecting wild fodder grasses, enhancing visibility by removing trees and shrubs, and reducing the risk of predators. However, risks include the potential for uncontrolled fires if not properly managed and harm to the ecosystem and biodiversity in and around the pastureland. Burning also contributes to the loss of carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas) to the atmosphere.

ទីតាំង: Dhur village, Choekhor Gewog (Block), Bumthang Dzongkhag (District), ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ: 2-10 កន្លែង
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ (approx. 0.1-1 គម2)
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?: ទេ
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: ច្រើនជាង 50 ឆ្នាំមុន (ប្រពៃណី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖


| ប្រភេទពូជ | ចំនួន |
| សត្វពាហនៈ - សត្វចិញ្ចឹមយកទឹកដោះ | 50 |
| សត្វពាហនៈ - សត្វចិញ្ចឹមយកទឹកដោះ | 55 |



| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (Bhutanese Ngultrum) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (Bhutanese Ngultrum) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Labours | person-days | 9,0 | 1200,0 | 10800,0 | 98,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| grass cutter | No | 1,0 | 15000,0 | 15000,0 | |
| Pipe | Bundle | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | |
| Spade | No | 3,0 | 500,0 | 1500,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 30'300.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 369.15 | ||||
Access to these services and infrastructure were based on their winter home, during the summer they would travel to the more higher altitudes where none of these services are available except for drinking water.
The land users shared that fodder production is relatively higher when practicing rangeland burning.
When comparing cut grass and grass in burned rangeland, the land users prefer the grass in the burned rangeland.
According to the land users, milk yield is better and higher from cattle fed on grasses from rangeland, which was burnt previously.
Land user also shared that burning rangeland provides enough food for their livestock which is sufficient throughout the year. This reduces the risk of production due to a shortage of grasses/feed.
Farm income is higher when compared to dairy supplemented with commercial feed in the winter. In addition, the establishment cost and implementation cost is also very low.
Vegetation cover is reduced because of this technology. This is because shrubs and trees are intentionally removed from the rangeland.
Plant diversity is also very minimal since tree saplings and shrubs are burned leaving only the pasture grass to grow on the land
Only grass is maintained as part of the technology. Habitat diversity is very low as trees and shrubs which also serve as habitats for many insects and arthropods are removed from rangeland.
It is reported in the literature that rangeland burning can reduce pest like tick and flies.
Burning of the rangeland leads to the production of several greenhouse gases, inevitably.