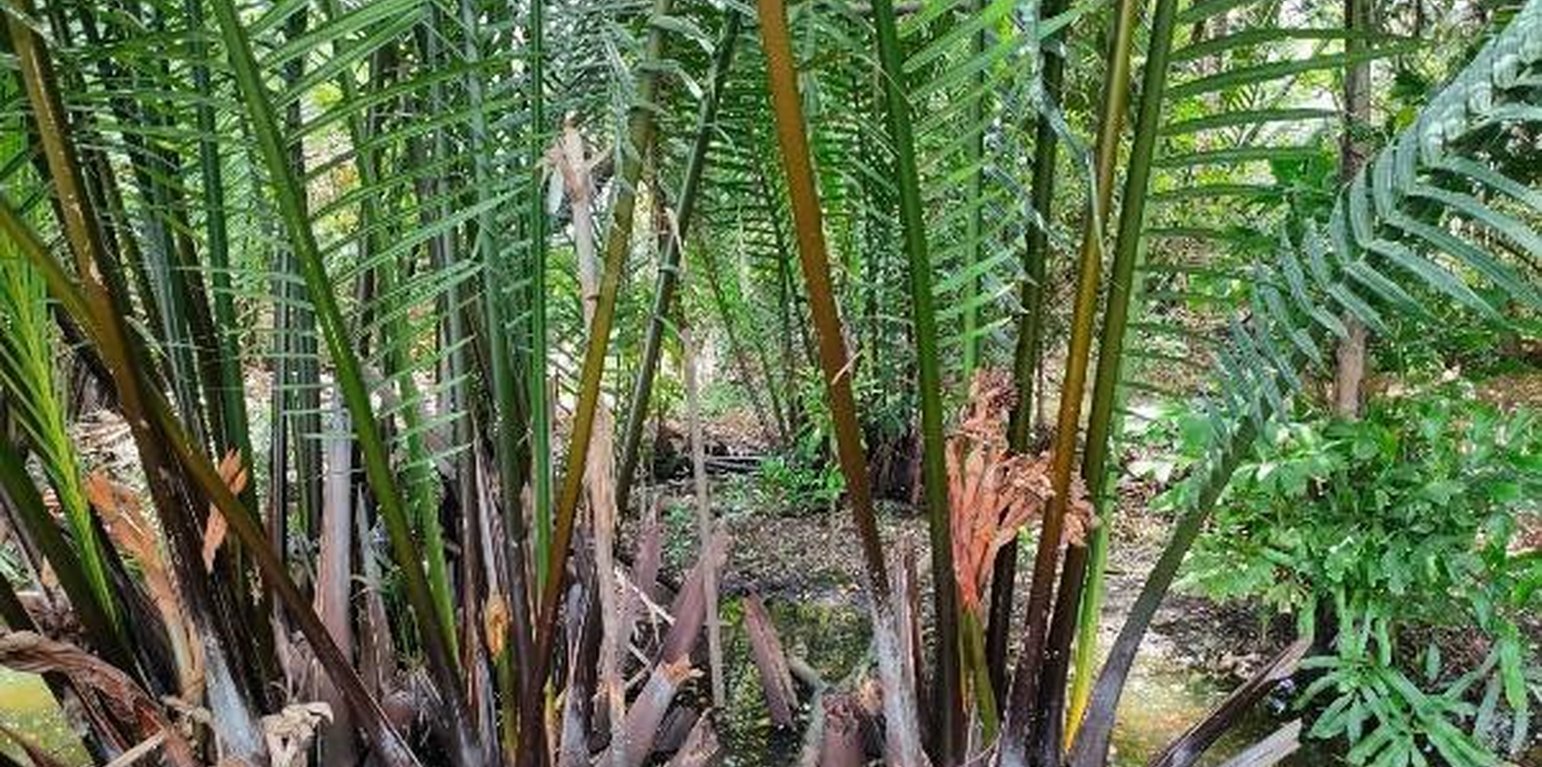




The story started with a small group of people in the area of Khung Bang Krachao. These people wanted to conserve the environment and develop resources in Phra Pradaeng District in Samut Prakan Province under an urban community forest park – the “Ked Forest Park”. It is state property land within the Metropolis. The community leader gathered people to conduct activities on the basis of natural resources and environment conservation. Many activities take place. For example, garden beds are cleaned and weeds removed. Planting and maintenance are conducted for indigenous edible and medicinal plants. This also includes collecting seeds of indigenous plants for propagation. Then, these seedlings are transferred to be planted in the forest park of urban communities.
The main purpose of this best practice is to conserve and propagate indigenous plant varieties, to have green areas available in the form of urban community forests for environmental restoration, to prevent and treat soil and water pollution and to make land use sustainable in a brackish water ecosystem. Products are cooked for tourists in the name of "indigenous vegetables, and local food". Apart from being responsible for taking care of conserving soil and water resources and increasing green areas, people in this community also transfer experiences and knowledge. Therefore, Ked Forest Park is considered to be a prototype of developing green-areas by communities. Currently, Suan Pa Ked (Ked Forest Park) is under the supervision of the Royal Initiative and Special Project Bureau, The Royal Forest Department in the form of a green area conservation network. This is promoting the public to participate in managing Khung Bang Krachao green areas in line with the concept of the Royal Initiatives of Her Royal Highness Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn. There is cooperation between government agencies, the private sector and educational institutes. The participation of communities is most important because ultimately, the trees which everyone plants, will benefit them.
This area has the capacity to absorb a huge amount of carbon dioxide as reported by the Royal Forest Department. Due to these exceptional ecological benefits, it was recognized as "The Best Urban Oasis of Asia" by the Time Asia magazine in 2006.
ទីតាំង: Suan Pa Ked Nom Klao, Moo 2, Soi Petch Hueng 16, Song Kanong sub-district (Soi Wat Pa Ked), Phra Pradaeng District, Samut Prakan Province, ប្រទេសថៃ
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ: មួយកន្លែង
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?: បាទ/ចា៎
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: 2007; 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖






| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (ដុល្លារ) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (ដុល្លារ) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Deepen the garden ditch in the area of 2.56 ha | Bed | 50,0 | 17,6 | 880,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | |||||
| Water pump | Machine | 2,0 | 147,0 | 294,0 | 100,0 |
| Compost | Tonne | 30,0 | 29,4 | 882,0 | 100,0 |
| 15-15-15 chemical fertilizer | Sack | 20,0 | 29,4 | 588,0 | 100,0 |
| Lime | Tonne | 10,0 | 88,2 | 882,0 | 100,0 |
| 500 liter plastic bucked | BucKed | 5,0 | 58,8 | 294,0 | 100,0 |
| Water salinity meter | Machine | 2,0 | 29,4 | 58,8 | 100,0 |
| 8 inch PVC with the length of 3 meters | Piece | 3,0 | 29,4 | 88,2 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | |||||
| Plant varieties including planting labor costs in the area of 2.56 ha | Tree | 10000,0 | 0,15 | 1500,0 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | |||||
| Materials used in building the nursery including labor costs | Square meters | 20,0 | 29,4 | 588,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 6'055.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 6'055.0 | ||||
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (ដុល្លារ) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (ដុល្លារ) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Management during planting and maintenance (1 year) | Force | 1,0 | 352,8 | 352,8 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | |||||
| Electricity costs | USD | 12,0 | 14,7 | 176,4 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 529.2 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 529.2 | ||||
Planting trees in the ecosystem of brackish-water forests and aquatic animal culture have brought about a variety of plant varieties and animal species such as egret.
Plants can lower groundwater levels, reducing salinity and waste water problems.