Farmer initiative within enabling environment [ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nicole Guedel
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2623 - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ (បើទាក់ទង)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 ការយោងមួយ (ច្រើន) ទៅលើ (កម្រង) បញ្ជីសំណួរនៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
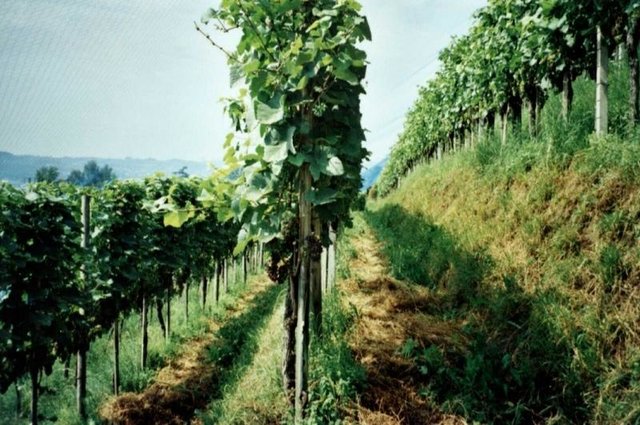

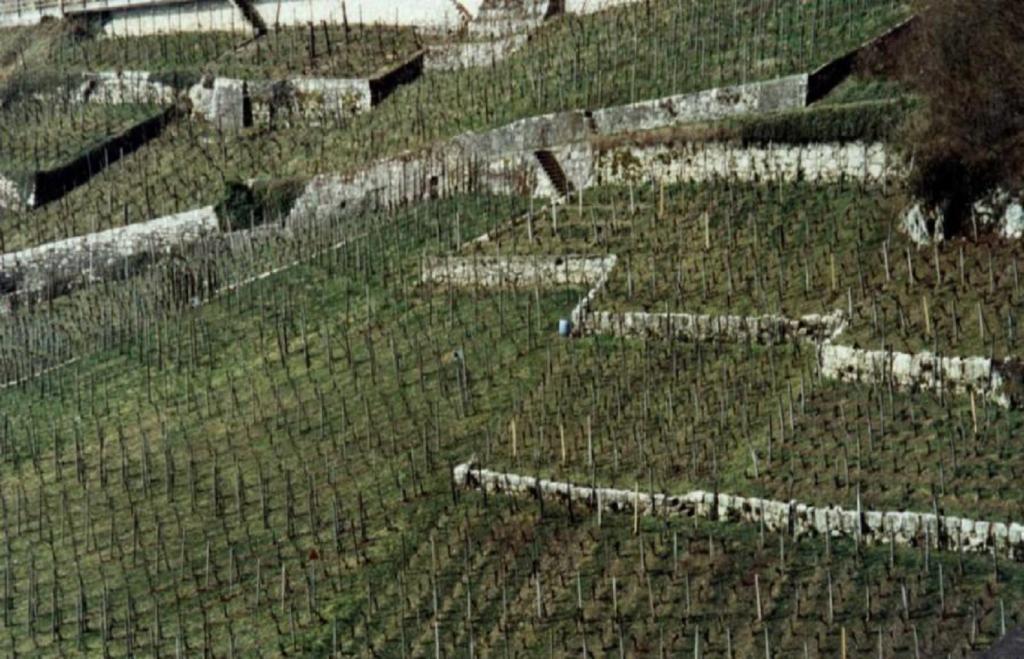
Contour small bench terraces with permanent green cover … [ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស]
Contour small bench terraces with stabilising permanent green cover in steep sloping vineyards.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nicole Guedel
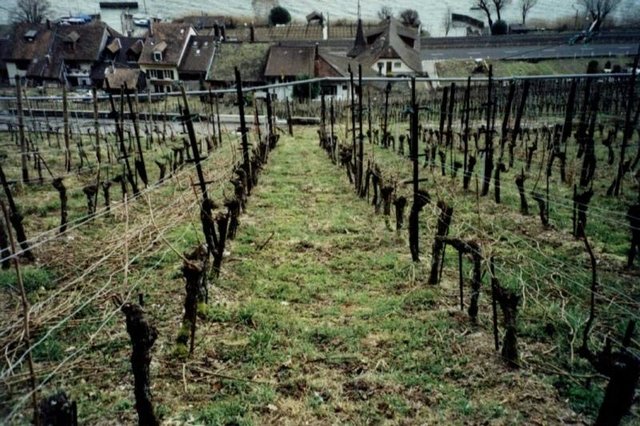

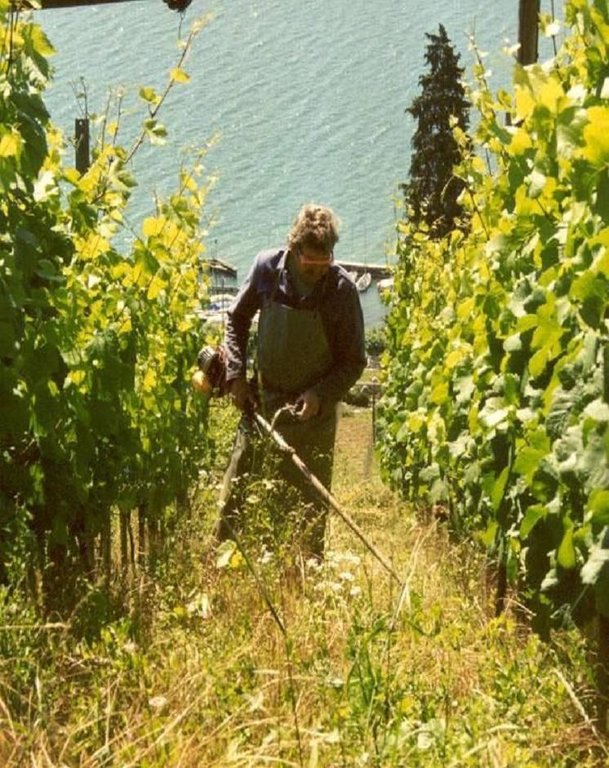
Green cover in vineyards [ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស]
Naturally growing or sown perennial grasses/herbs providing cover between rows in sloping vineyards, where the vines are usually oriented up and down slope.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nicole Guedel
2. ការពណ៌នាអំពីវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM
2.1 ពណ៌នាសង្ខេបខ្លីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
Initiative and innovation of land users, stimulated by government's technical and financial support.
2.2 ពណ៌នាលម្អិតពិវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
ពណ៌នាលម្អិតពិវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ:
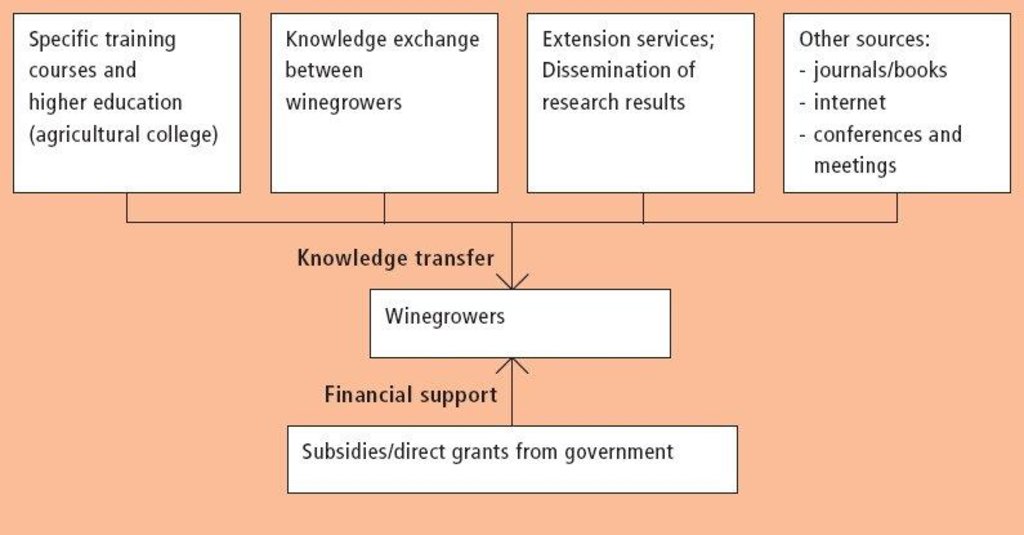
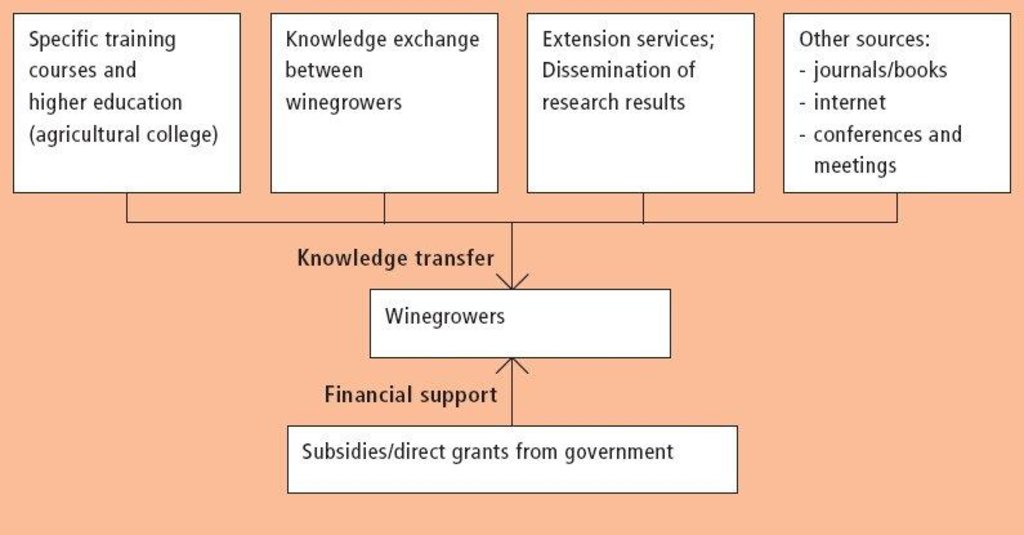
Aims / objectives: The application of green cover (a ???living mulch??? between vine rows) in viniculture within the case study area has been developed and spread, primarily, by experimentation and exchange of knowledge between winegrowers. Individual initiatives and personal contacts have been the most important elements. Other channels are: (1) higher education and specific training courses (the majority of winegrowers have undergone at least 3 years of agricultural college, including both applied and theoretical training); (2) participation in conferences and meetings; (3) self-teaching using the internet and national and international journals or books; and (4) extension services. Disseminated results from national research institutions also play an important role - over and above individual knowledge and experimentation. The approach is thus characterised by responsiveness of winegrowers to the various information sources listed above. This should be seen in the context of national agricultural policy which provides an ???enabling environment??? including payments to farmers: the production quotas of the 1950s were replaced in 2001 by direct grants (subsidies) based on area grown and/or other specific criteria, eg ecological services such as green cover. However, the technology of green cover spread spontaneously before direct incentives were tied to ???ecological production???. Government policy supports agriculture as a weak sector of the national economy, and guarantees, through subsidies, a high percentage of the overall national production. Subsidies in Swiss agriculture are amongst the highest in the world. These subsidies effectively keep wine production going. Vineyards are seen as an important part of the rural cultural heritage and as a characteristic feature of the landscape.
Methods: Recently, with this type of production system, there has emerged a further opportunity - to market wine under a label of controlled ecological production (???vinatura???). A step further is the label of ???organic production??? which, in addition to green cover, requires a range of other criteria to be strictly fulfilled (eg no use of chemical fertilizers/biocides). Customers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for such products. This is an example of a win-win situation: the environment is protected and simultaneously farmers are rewarded with a higher value for their output. Within the framework of subsidies to farmers and information availability, the ???approach??? to improved viniculture can therefore be viewed as an enabling environment for land users to take initiatives themselves. The diffusion of innovative technologies is also largely left to the land users.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
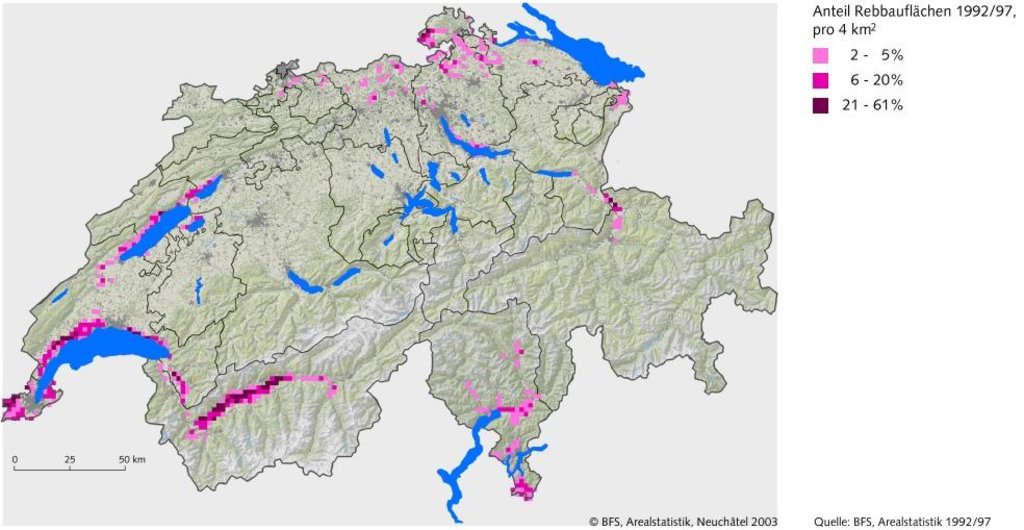
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Swiss viniculture area
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Switzerland
មតិយោបល់:
The approach is not limited to the SWC technology area described in QT SWI01 and SWI02. It is rather representative for Switzerland.
Map
×2.7 ប្រភេទនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
- ក្រុមប្រពៃណី/ក្រុមជនជាតិភាគតិច
2.8 គោលបំណង/ទិសដៅសំខាន់នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (viticulture as whole and its basic conditions (production of wine, financial questions, economy, technical aspects, equipment, ecology, viticulture and tourism))
The overall objective of national policy is, within a framework of subsidies, to allow farmers to develop and spread solutions themselves through access to sources of knowledge and information. The objectives of the farmers themselves are to improve their production systems through ecologically sound conservation.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - initial technical problem of soil degradation within vineyards: no off the shelf solutions - slow spread of technical solutions (such as green cover which requires fundamental changes in land users attitudes)
2.9 លក្ខខណ្ឌអនុញ្ញាត ឬរារាំងការអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសដែលស្ថិតនៅក្រោមវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
សង្គម/វប្បធម៌/ និងតម្លៃនៃសាសនា
- រារាំង
In a community of winegrowers who are used to either clean tillage (traditional method) or chemical weeding, green cover implies a change of values and priorities. This can cause conflicts especially between neighbours and within families
Treatment through the SLM Approach: First, rising awareness of advantages and possible disadvantages of green cover by (further) education, literature, meetings / conferences and internet by research institutions and extension services. The second step is conflict resolution on a one-to-one
ចំណេះដឹងស្តីពី SLM និងការទទួលបានការគាំទ្រផ្នែកបច្ចេកទេស
- រារាំង
The implementation of green cover is strongly dependent on factors on farm or parcel level (available infrastructure / equipment, age of vines, planting system (density and distance of vines, characteristics of supporting elements, poles, wire system...))
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Individual consultation with extension service where specific advice required
ផ្សេងៗ
- រារាំង
Natural environment: Climatic (drought, frost) and pedological (soil depth) factors can intensify water and nutrient competition to the vine, danger of frost and therefore hamper the implementation of green cover.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Information provided by mentioned sources. Examples of possible solutions: Green cover on every second interrow; green cover only in winter; agronomic measures to temporarily eliminate competition of cover vegetation (by cutting / mulching vegetation or r
3. ការចូលរួម និងតួនាទីរបស់ភាគីពាក់ព័ន្ធ
3.1 អ្នកពាក់ព័ន្ធដែលបានចូលរួមក្នុងវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ និងតួនាទីរបស់ពួកគេ
- អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/សហគមន៍
land user themselves (their network, exchange of knowledge, implementation)
Existing groups of land users
Working land users were mainly men (because the majority of Swiss winegrowers are men)
The integration of women is a key element of the approach. Nevertheless, there are moderate differences due to cultural factors: men are mainly in charge of agricultural activities, whereas women work in the household.
- រដ្ឋាភិបាលថ្នាក់មូលដ្ឋាន
Districts, communities, villages
- រដ្ឋាភិបាលថ្នាក់ជាតិ (អ្នករៀបចំផែនការ អ្នកសម្រេចចិត្ត)
3.2 ការចូលរួមរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/ សហគមន៍ក្នុងតំបន់ក្នុងដំណាក់កាលផ្សេងគ្នានៃវិធីសាស្រ្តផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
| ការចូលរួមរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីក្នុងតំបន់/សហគមន៍ក្នុងតំបន់ | សូមបញ្ជាក់នរណាត្រូវបានចូលរួម ព្រមទាំងពណ៌នាសកម្មភាពទាំងនោះ | |
|---|---|---|
| ការចាប់ផ្តើម/ការលើកទឹកចិត្ត | គំនិតផ្តួចផ្តើមដោយខ្ឡួនឯង | |
| ការរៀបចំផែនការ | អន្តរកម្ម | the basic idea was further enhanced by planning based on available information from various sources |
| ការអនុវត្តន៍ | គំនិតផ្តួចផ្តើមដោយខ្ឡួនឯង | responsibility for major steps; Responsibility of winegrowers of all steps |
| ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃ | គំនិតផ្តួចផ្តើមដោយខ្ឡួនឯង | Mainly: measurements/observations; partly: workshop/seminars, public meetings, reporting; Observation by land user. Some indicators are evaluated by extension services or research institutions. |
| Research | អន្តរកម្ម | on-station; Both on-farm and on-station |
3.3 គំនូសបំព្រួញ (ប្រសិនបើមាន)
3.4 ការសម្រេចចិត្តលើការជ្រើសរើសបច្ចេកទេស SLM
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើអ្នកណាជាអ្នកបានសម្រេចចិត្តក្នុងការជ្រើសរើសបច្ចេកទេសដើម្បីយកមកអនុវត្តន៍:
- អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដោយខ្លួនឯងផ្ទាល់ (គំនិតផ្តួចផ្តើមដោយខ្លួនឯង)
ចូរពន្យល់:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up)
4. ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព និងការគ្រប់គ្រងចំណេះដឹង
4.1 ការកសាងសមត្ថភាព/ បណ្តុះបណ្តាល
តើវគ្គបណ្តុះបណ្តាលបានផ្តល់ឱ្យអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី/អ្នកពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងៗទៀតដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ទម្រង់នៃការបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
- អនុវត្តន៍ជាមួយការងារ
- ពីកសិករទីកសិករ
- ទីតាំងបង្ហាញ
- ការប្រជុំជាសាធារណៈ
- វគ្គបណ្តុះបណ្តាល
ប្រធានបទបណ្តុះបណ្តាល:
There are various possibilities which include green cover as one of several topics: (1) agricultural college (three years, including both practical and theoretical knowledge); (2) further education (full time or short courses) at agricultural universities; (3) attendance at regional, national or international meetings/conferences, organised by research institutions, extension services, or
4.2 សេវាផ្តល់ប្រឹក្សាយោបល់
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីបានទទួលនូវសេវាផ្តល់ប្រឹក្សាដែរ ឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រសិនបើសេវាកម្មប្រឹក្សាយោបល់ត្រូវបានផ្តល់ឱ្យ:
- នៅលើដីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ពណ៌នា/ពន្យល់:
Adoption; Key elements: palette of information sources, informal contacts, discussions, observations of different systems under personal trials.1) Advisory service was carried out through: non-governmental agency, government's existing extension system 2) Advisory service was carried out through: non-governmental agency, government's existing extension system; Extension staff: mainly government employees
Advisory service is very adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
4.3 ការពង្រឹងសមត្ថភាពស្ថាប័ន (ការអភិរឌ្ឍន៍អង្គភាព)
តើស្ថាប័នទាំងអស់ត្រូវបានបង្កើតឡើង ឬពង្រឹងសមត្ថភាពតាមរយៈវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែរ ឬទេ?
- ទេ
4.4 ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃ
តើការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងវាយតម្លៃគឺជាផ្នែកមួយនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
មតិយោបល់:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users, other through observations; indicators: rate of erosion, organic matter content, soil moisture, water potential in vine leaves, compaction, soil structure, soil temperature, biodiversity, chemical analysis of wine, nutrient elements in soil and vines
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users, other through observations; indicators: change of attitude towards green cover, knowledge about SWC and awareness of natural environment, change of appearance of man-made landscape
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users, other through observations; indicators: costs, production, quality, manual labour, machine hours etc. Often data are not specifically gathered for green cover but total establishment and annual recurrent costs for different winegrowing systems can give some insight into the economic status of green cover
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations; indicators: diffusion of green cover (visual impression of the current status, time-series photos, descriptions from past)
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: number of households involved (with a questionnaire, personal estimation, visual impressions), Number of farmers receiving direct payments
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by other through observations; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Few changes to the technology or the approach have resulted directly from formal monitoring and evaluation.
4.5 ការស្រាវជ្រាវ
តើការស្រាវជ្រាវ គឺជាផ្នែកមួយនៃវិធីសាស្រ្តដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមផ្តល់ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមទៀតឱ្យបានលម្អិត និងចង្អុលបង្ហាញនរណាដែលបានធ្វើការស្រាវជ្រាវ:
Especially ecological and technical aspects are important elements of the research institutions concerning SWC: e.g. management of green cover such as dealing with competition of water and nutrients to the vine or promoting living space for animals (especially insects) beneficial to grape production (e.g. promoting predators of pests as a possibility of biological pest control). But also economic
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. ថវិកា និងសម្ភារៈឧបត្ថម្ភពីខាងក្រៅ
5.1 ថវិកាប្រចាំឆ្នាំសម្រាប់ផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM
មតិយោបល់ (ឧ. ប្រភពសំខាន់នៃមូលនិធិ/ម្ចាស់ជំនួយចំបង):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national): 70.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 30.0%
5.2 ការគាំទ្រផ្នែកហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ / សម្ភារៈដែលបានផ្តល់ទៅឱ្យអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីបានទទួលការគាំទ្រផ្នែកហិរញ្ញវត្ថ/សម្ភារៈសម្រាប់ការអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសដែរឬទេ:
បាទ/ចា៎
5.3 សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូលត្រូវបានផ្តល់បដិភាគ (រួមទាំងកម្លាំងពលកម្ម)
ប្រសិនបើកម្លាំងពលកម្មធ្វើដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី តើវាជាធាតុចូលដ៏សំខាន់មួយដែរ ឬទេ:
- ដោយស្ម័គ្រចិត្ត
មតិយោបល់:
Labour is a substantial input and exclusively done voluntary by land users - though the overall agricultural system is subsidised
5.4 ឥណទាន
តើឥណទានដែលបានផ្តល់នៅក្រោមវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយសម្រាប់សកម្មភាព SLM នេះយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច?
ទេ
6. ការវិភាគរកផលប៉ះពាល់ និងសេចក្តីសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
តើវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយជួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដើម្បីអនុវត្តន៍ និងថែទាំបច្ចេកទេស SLM?
- ទេ
- បាទ/ច៎ា បន្តិចបន្តួច
- បាទ/ច៎ា ជាមធ្យម
- បាទ/ច៎ា បានខ្លាំង
The approach (with all its elements) has led to greatly improved soil and water management.
6.3 សកម្មភាពផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែលប្រកបដោយចីរភាព
តើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីអាចធ្វើឱ្យមានចីរភាពនូវអ្វីដែលត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍តាមរយៈវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយដែរឬទេ(ដោយពុំមានការគាំទ្រពីអ្នកខាងក្រៅ)?
- បាទ/ចា៎
ប្រសិនបាទ/ច៎ា សូមរៀបរាប់ថាធ្វើយ៉ាងម៉េច:
Within the framework of the existing national policies the approach is sustainable.
6.4 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Very bottom-up oriented. The interest, the own initiative and the generation of own experience and knowledge is the dominant motor (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Maintain the enabling environment put in place by the government which is the framework for this approach.) |
| Many information sources and ways of receiving information are available and used frequently. |
6.5 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងរកដំណោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យក្នុងទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Winegrowing as a whole is highly dependent on financial incentives. Without direct payments, continuation of Swiss winegrowing and therefore green cover would be threatened ??¡§ at least under marginal conditions | Continue the incentive policy (though this may conflict with international efforts to reduce farm subsidies worldwide). |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Guedel N (2003) Boden- und Wasserkonservierung in Schweizer Rebbergen. Ein Beispiel im Rahmen von WOCAT. Unpublished
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Centre for Development and Environment, University of Berne
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Contour small bench terraces with permanent green cover … [ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស]
Contour small bench terraces with stabilising permanent green cover in steep sloping vineyards.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nicole Guedel

Green cover in vineyards [ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស]
Naturally growing or sown perennial grasses/herbs providing cover between rows in sloping vineyards, where the vines are usually oriented up and down slope.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nicole Guedel
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល