Soil productivity improvement using a combination of technologies [ប្រទេសតង់សានី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ ALLAN BUBELWA
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1221 - ប្រទេសតង់សានី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Mwasikundima Iddifonce
Ngara District Council Kagera Tanzania
ប្រទេសតង់សានី
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - ប្រទេសតង់សានីឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - ប្រទេសតង់សានីឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Ngara District Council (Ngara District Council) - ប្រទេសតង់សានី1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
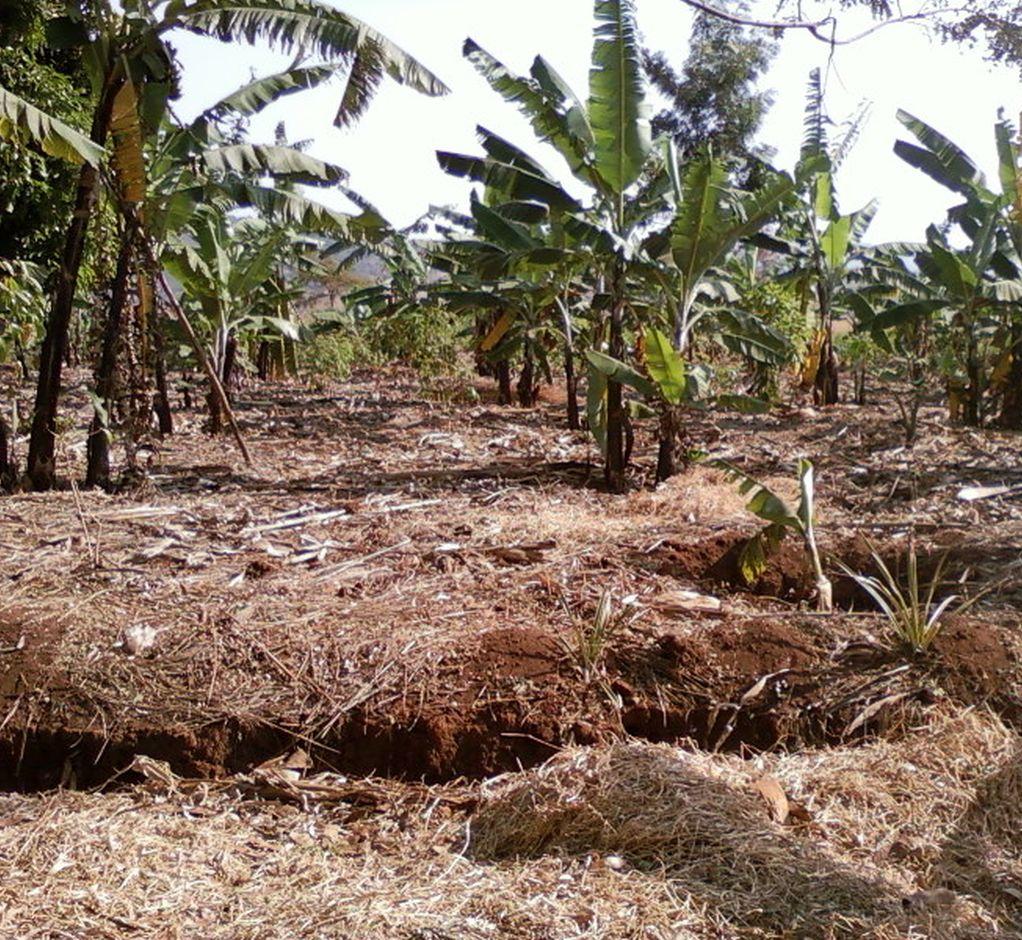
Use of compost basket pits, farm yard manure application, nutrient tapping sub soil agro-forestry, mulching application and productive vegetative stabilized cross slope barriers to improve soil health in Kibanja farming system.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
The technology was documented based on experiences of field SLM specialist and from the perspectives of land users (especially FFS group members) supported by the Trans boundary Agro Ecosystem Management project. The dominant crop in the technology area is banana. In this technology banana is widely spacing to 4m x 4m for the purpose of providing enough space for annual or recurrent soil nutrient feeding using compost ditches or baskets. Compost basket pits of 0.6 m depth and 3x3m width are dug between 4 banana plants. Baskets pits are dug recurrently and filled with farm manure, compost (crop residuals), leguminous green manure (tithonia) and ash and later covered with soil to activate nutrient release though microbial disintegration and avoid volatilization of greenhouse gas through direct sunlight. The size of a hole dug for the purpose of planting banana is 0.6 m depth and 0.6 m height. During digging top soil is separated from subsoil. In initial manure application, 2 tin of manure are mixed with the top soil and the mixture is put in the bottom of the hole. The center of the hole is marked with a stick and waiting is done for 1 or 2 before planting. During planting of banana, only two third 0.24m cubic of the hole is filling with soil and one third 0.12m cubic of the hole is left to form a water retention/harvest pit. Tithonia diversifolia (leguminous shrubs) are planted within the Kibanja farm purposefully for improving soil nutrient recycling though nitrogen fixing and at the same time is incorporate in compost to improve its quality. Infiltration ditches of 0.6 m depth and 0.6 m width and varying lengths are constructed for the purpose of impeding, trapping and harvesting water runoff. Fruit trees are planted in sub soil zone within the water infiltration ditches. The aim is to control nutrient competition between trees and annual/ biennial in the top soil or annual root zone and at the same time fruit tree roots in the subsoil zone is used as nutrient pump i.e. return nutrient lost through leaching to the top soil in form of mulching and litter. Improved banana varieties (FIAH 23) and certified endogenous germ plasma, de-trashing and de-suckering to maintain optimal plant geometry is part and per se of recommended husbandry practice
Purpose of the Technology: Improved food productivity, improved soil moisture content and water holding capacity. Improve nutrient recycling, organic matter content and biomass cycle. Prevent unproductive evaporation of green water and improving soil micro-climate. Combating land degradation through soil erosion caused by water runoff, chemical degradation due to nutrient leaching, biological degradation due the deadly BXW and other diseases and water degradation due to unproductive evaporation of the green water. And also plays significant role in adaptation and mitigation to drought climate. Improved economic returns accrued from surplus food production. Improve year round accessibility of food, shock resistance availability of food and varied food utilization and hence poverty reduction and improved health.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities: land tilling, harrowing, demarcation and spacing of holes for planting banana, digging holes, manure application before banana planting, planting bananas, to demarcate, level and space Fanya chini/infiltration ditches/trenches using A-frame and arm outstretched level, ditch/trench digging, vegetative stabilization of Fanya chini/infiltration ditches, planting of fruit trees within ditches. Maintenance activities: weeding to destroy noxious weeds, in between planting of maize, de-suckering to maintain optimal plant geometry, de-trashing, maintenance and replenishment of banana pits, harvest beans and maize, sediment removal and repairing of infiltration ditches/trenches.
Natural / human environment: Natural (bio-physical) environment: The technology area land use type is cropland with annual crops (maize and beans), perennial crops (banana and pineapples) and fruit tree (avocados and jackfruit “Artocarpus heterophyllus”). The technology involves a combination of the following measures: agronomic, vegetative and structural. Climatic zone is sub-humid with an average of 210 length of growing period (LGP). Average slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. Soil texture classes range from combination of top loam to a red clayey subsoil with medium soil depth categories. Main criteria for a human (socioeconomic) environment: the level of mechanization is hand tools. Production system is mixed (both subsistence and market oriented or commercial). The average costs of inputs required is 1472,62 USD. Land ownership is largely individual not titled and partly communal.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសតង់សានី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
United Republic of Tanzania, Kagera Region
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Ngara District council, Kirushya ward, Kirushya Village.
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- < 0.1 គម2 (10 ហិកតា)
មតិយោបល់:
The technology is documented from the perspectives of group of land users (SLM FFS) supported by the Trans Boundary Agro-Ecosystem Management Project.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Supported by the Trans Boundary Agro Ecosystem Management Project (Kagera TAMP) in year 2012, a group of 25 members of ENDELEVU Farmer Filed School (FFS) started to learn and test out application of the technology.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ)
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត
- ពពួកសណ្តែក - សណ្តែកបារាំង
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងជ្វា ពពួកដំឡូង ត្រាវ ផ្សេងៗ
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងមី
ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ) - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ចេក/plantain/abaca
- ម្នាស់
ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទ:
- ផ្លែប៊ឺ
- កាហ្វេ នៅតូចមិនទាន់មានម្លប់
- ផ្លែស្វាយ/ផ្លែមង្ឃុត/ផ្លែត្របែក
- jack fruits
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 2
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Poor soil moisture (moisture stress), poor soil fertility, loss of vegetative cover and unproductive loss of green water, erosion and washout of the top soil by rainfall runoff.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low banana productivity, unbearable persistence of the deadly BXW and other diseases, drought intolerance, food insecurity and a poverty stricken community.
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងជីជាតិដីតាមបែបចម្រុះ
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
- V2: ស្មៅនិងរុក្ខជាតិៗដែលដុះមានអាយុមិនលើសពី 2ឆ្នាំ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S2: ភ្លឺ ច្រាំង
មតិយោបល់:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues, pits
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear, scattered / dispersed
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bp: ការកើនឡើងនូវសត្វល្អិត ឬជំងឺ បាត់បង់នូវសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Flat cultivation along the slope, no use of slope cross barriers), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Use of unimproved local varieties susceptible to diseases and pests), change of seasonal rainfall (Unforeseen changes in rainfall), droughts (Long dry spell season), population pressure (Exessive use of land without fertility replenishment), poverty / wealth (incapacity to invest in sustainable land canservation measures.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of SLM knoledge.), governance / institutional (Weak institutions with lack of operational capacities)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (The principles governing use of SLM were taught before in colleges to field staff and agricultural advisers and therefore simple retraining courses and learning by doing on the job on the suffice)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Need training on construction of slope cross barriers e.g. on application of A-frame and arm outstretched methods and the principle behind BXW control and use of certified/improved banana varieties.)
Technical knowledge required for Sub national level (Regional and District): moderate (SLM participatory training techniques/skills.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Mulching
Material/ species: Hyparrhenia spps
Quantity/ density: 1500bu/ha
Remarks: Layed accross the slope at e reccommended depth of 15 cm.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farm Yard Manure, banana debris, tithonia
Quantity/ density: 15 ton/ha
Remarks: Applied during planting and in routine fertility replenishment.
Pits
Material/ species: Compost basket pits
Quantity/ density: 156
Remarks: Pits of 5.3m cubic dig between each 4 banana stools used annually for composting the banana field.
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 625
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4m
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: O : other
Trees/ shrubs species: Mangoes
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mangoes
Perennial crops species: Banana
Other species: Pineapples, Cassava and Yarms.
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 15
Structural measure: Fanya chini bund
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 15
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 15
Structural measure: Banana water infiltration pits
Spacing between structures (m): 4
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Construction material (earth): Soil dug to form trenches is thrown down slope to form embankment of fanya chini bund.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2 - 5%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Tanzanian shillings
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
1700,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
1.18
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land tilling (starting a new banana farm) | March |
| 2. | Harrowing | April |
| 3. | a) Demarcation and spacing of holes for planting banana. b) Digging of holes. | April |
| 4. | Applying manure during banana planting | May |
| 5. | Planting banana | May |
| 6. | Planting fruit trees (jack fruits and avocados) | May |
| 7. | a) Planting pineapples on Fanya chini bund. b) Selective boundary planting of Tithonia | September |
| 8. | a) To demarcate contour line using A-FRAME and arm stretched level method. b) Digging and construction of water retention ditches and fanya chini bund. | September |
| 9. | Tools (hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade, mattock, forked wooden poles and A-frame) |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | labour | ha | 1,0 | 713,15 | 713,15 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | tools | ha | 1,0 | 87,65 | 87,65 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 0,29 | 0,29 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 65,0 | 65,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | mulching materials | ha | 1,0 | 22,06 | 22,06 | |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 44,12 | 44,12 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 932,27 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 0,55 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 4 month(s)
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding to control and destroy noxious weeds. | February and October |
| 2. | In between planting of maize and beans. | February and October |
| 3. | De-suckering to maintain mother and two baby plants. | |
| 4. | De-trashing and trimming of unwanted leaves. | |
| 5. | Maintenance and replenishment of banana pits. | |
| 6. | Applying manure using banana compost basket pits | January |
| 7. | Harvesting of beans and maize. | |
| 8. | Mulching application | After harvest of maize and beans |
| 9. | Gap filling and trimming of unwanted leaves/branches (Avocados, Jack fruits and Pineapples) | within rain period |
| 10. | Maintenance by removing soil sediments. | During and after rainfall |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | labour | 1499,72 | 100,0 | |||
| សម្ភារៈ | Seeds beans (20 kg/ha) | ha | 1,0 | 8,24 | 8,24 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Seeds Maize (2 kg/ha) | ha | 1,0 | 0,77 | 0,77 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Mulching materials (75 bundles) | ha | 1,0 | 22,06 | 22,06 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Compost/manure (325 kg) | ha | 1,0 | 9,56 | 9,56 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 40,63 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 0,02 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: hand hoe, forked hole, machetes and sickles, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes and spade, hand hoe, forked hole, spade, mattock and A-frame
The costs were calculated based on per unity entity of land plot (quarter an acre plot) where the technology was demonstrated/tested .
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Labour is the most determinant factor.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
The average annual rainfal is 1300mm. The dry season is from June to August. Rainfall season starts from September to May. There is a dry spell in January/February and June - August is dry season.
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Thermal climate class: tropics. Average temperature is 21°C. The area receives bimodal type of rainfall with average lenght of growing period is 210 days
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- សណ្ឋានដីប៉ោង
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Landforms: Mountain slopes (ranked 1, the area is largely a convex mountanous land slope), plateau/plains (ranked 2) and ridges (ranked 3)
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil texture: Medium (ranked 1, range from combination of top loam to a red clayey subsoil) and coarse/light (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium (due to washout of the top soil by rainfall water runoff and excessive nutrient mining/uptake without replenishment)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (due to washout of the top soil by rainfall water runoff and poor mismanagement of crop residuals)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor (the slope nature of the landscape does not give water enough time to infiltrate instead water is lost downstream through runoff)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (soil textural class range from combination of top loam to a red clayey subsoil)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
> 50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Ground water table: >50m (ranked 1, water can be accessed in down the river valleys streams) and 5-50m (ranked 2)
Availability of surface water: Water is available in natural flowing downstream rivers
Water quality untreated: Poor drinking water (treatment required, water in river stream untreated is poor because is contaminated by runoff pollutants)
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
Species diversity is reduced by human induced activities e.g. farm opening and expansion, starting of new human settlements, uncontrolled fire burning e.t.c.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land (owning 1-2 ha, moden house, motorcycles).
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land (owning 0.5-1 ha, average house, bicycles).
20% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land (owning < 0.5 ha, poor house, no transport).
Off-farm income specification: In general most of the village community are average farmers who largely rely on on farm income.
Market orientation: Mixed (ranked 1, Production is both for domestic food production and commercial use) and subsistence (ranked 2)
Level of mechanization: Manual work (Largely manual by using hand tools)
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
មតិយោបល់:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha (5% of the land users), 0.5-1 ha (80% 0f the land users) and 1-2 ha (15 % of the land users)
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
មតិយោបល់:
The land is a state property, use right is largely individual not titled. water resources and grazing range lands are owned communally and are free for all.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
25 kg
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
50 kg
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
banana bunch
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃផលិតផល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
pending development and upscalling of value addition technology.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
caused by use of manure and grass mulch.
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
due to increased production and expected income from fruit tree and pineapples
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
imcome from fruit trees and pineapples
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
caused by increased workload.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0 - FFS
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1 - FFS
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
FFS has induced farmer group solidarity and togetherness.
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increase in SLM skills and knoledge due training issued through FFS. People visiting the area where the technology is tested or demonstrated
ស្ថានភាពក្រុមដែលមានបញ្ហាក្នុងសង្គម និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Active participation of both men and females
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Improved crop productivity and the diversification of income sources results to farmer capacity to meet eduction and health services. Production of pineapple and fruit tree (avocados and jack fruit) means increased number of food per table and balanced diet to farmer.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
ការប្រមូលស្តុកទុកទឹក
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
poor
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
improved
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
due to the use of water infiltration ditches and fanya chini bund
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
use of closs slope barriers and mulching.
រំហួត
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
poor
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
improved
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
educed unproductive loos of green water by use of mulching.
ដី
សំណើមដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
poor
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
improved
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
reduced unproductive loos of green water by use of mulching.
គម្របដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
use of mulching rotated by cover crops (beans) and trashline.
ការបាត់បង់ដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Use of closs slope barriers and mulching
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
the use of reguminous plants (beans and tithonia)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
use of farm yard manure and compost basket feeding
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
biomass due to improved managment of crop debris and residual and use of mulch.
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
improved habitat for micro fauna caused by use of manure and compost
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
reduced hazards towards drought and reduced growing period.
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
reduced volatization of methane gas due to good managment of FYM.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
reduced rainfall runoff to down ward stream
ខូចខាតដល់ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធសាធារណៈ/ឯកជន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
reduced damage to the nearby road infrastructure
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | មិនស្គាល់ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
The technology could be made to be more tolerant to flood by modifying retention ditches to drainage ditches and by introduction of wind breakers.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
Heavy investment and recurrent costs at the beginning but costs are surpassed by rewards in the long run.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
46 families and 100% of the area covered
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 51-90%
មតិយោបល់:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: External material support was used on area used for FFS.
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
23 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
4% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support 23 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: 80% farmers have adopted the technology partially without any material support.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: the technology increasingly adopted are mulching, spacing and compost basket feeding
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| The technology is easy to learn and understand by a common peasant farmer |
| The technology open a room for availability of improved varieties and diversification of income sources |
| Observable rewards in terms of increased production and environmental conservation. |
| Change of attitudinal and behavioral change (mind set) towards environmental conservation. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| The technology has provided options for farmers to blend their vast experience and innovations in managing their often-limited resources with new methods and advice from outside. |
| The promotion of the technology through FFS has strengthened partnership between farmers, extension providers, private sector and researchers. |
| The FFS programme has created unity in the people at grass root level |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| High initial investment capital needed due to high costs of farm inputs. | Farmer support by financial institutions |
| Technology promotion need closeness of extension services but there is no reliable plan for facilitators motivation. | Find reliable means and ways of motivating both field extension officers and grassroots facilitators (paraprofessionals). |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Finances for scaling up technology use in the future is questionable. | Link farmers with rural financial institutions and put more efforts in commercial and market oriented SLM activities. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
02/08/2014
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល