Vermicomposting [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Shreedip Sigdel
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Gadaula proyog gari mal banaune prabidhi (Main Contributor: Samden Sherpa, ICIMOD)
technologies_1695 - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Sherpa Samden Lama
ICIMOD
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Vermicomposting or worm composting is a simple technology for converting biodegradable waste into organic manure with the help of earthworms.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Earthworms are valued by farmers because, in addition to aerating the soil, they digest organic matter and produce castings that are a valuable source of humus. Vermicomposting, or worm composting is a simple technology that takes advantage of this to convert biodegradable waste into organic manure with the help of earthworms (the red worm Eisenia foetida) with no pile turning, no smell, and fast production of compost. The earthworms are bred in a mix of cow dung, soil, and agricultural residues or predecomposed leaf-litter. The whole mass is converted into casts or vermicompost, which can be used as a fertilizer on all types of plants in vegetable beds, landscaping areas, or lawns.
Purpose of the Technology: Worms are so effective at processing organic waste that they can digest almost half their own weight in debris every day. Vermicomposting is a simple composting process that takes advantage of what earthworms do naturally, but confines the worms to bins making it easier for farmers to feed them and to harvest their nutrient-rich compost. Since all worms digest organic matter, in principle, any type of worm can be used; however, not all are equally well adapted to living in bins since some worms prefer to live deep in the soil while others are better adapted to living closer to the surface. The red worm (Eisenia foetida) is ideal for vermicomposting because its natural habitat is close to the surface and it is accustomed to a diet rich in organic matter, this makes it ideally suited to digesting kitchen scraps and to living in bins.
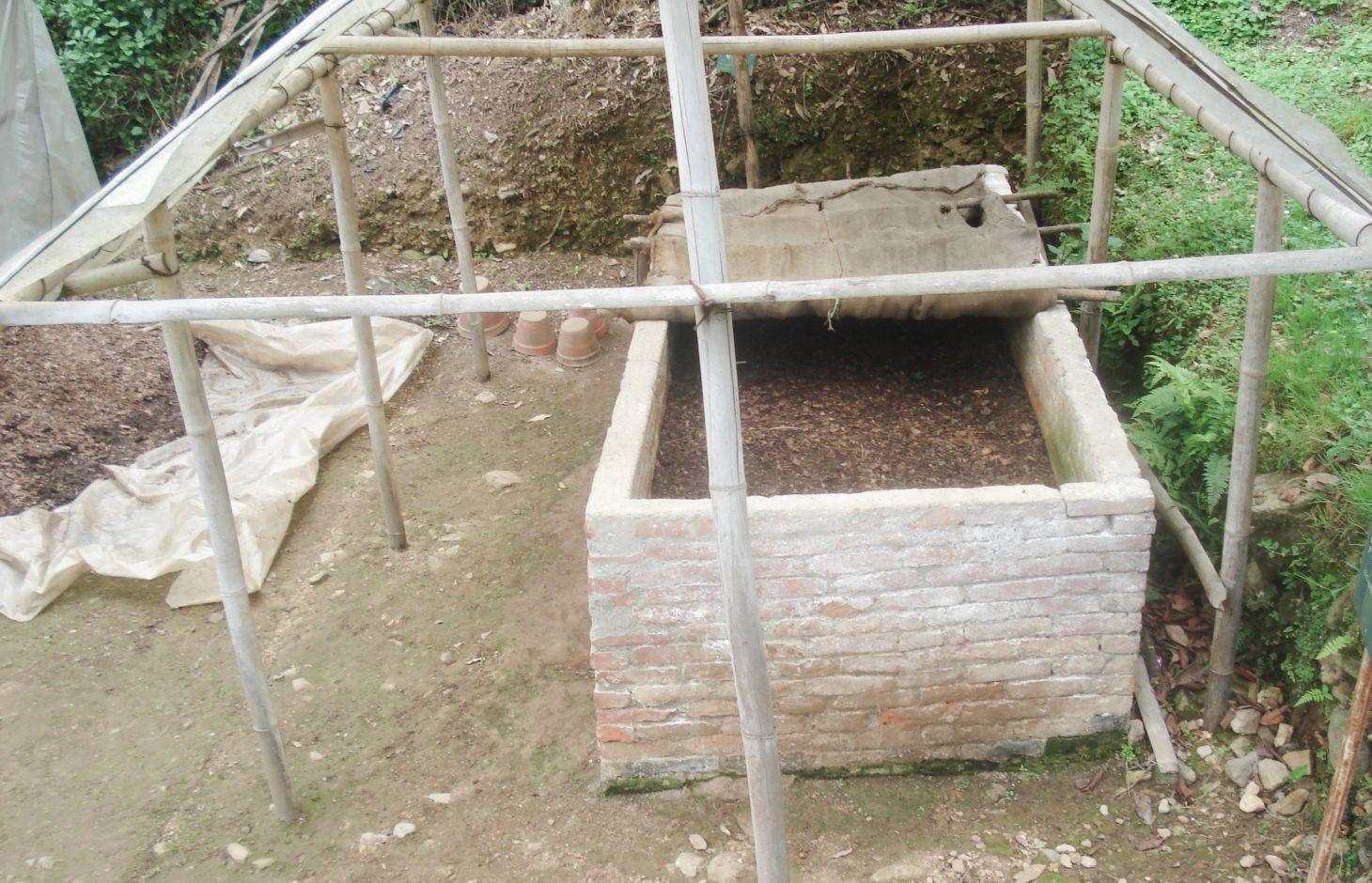
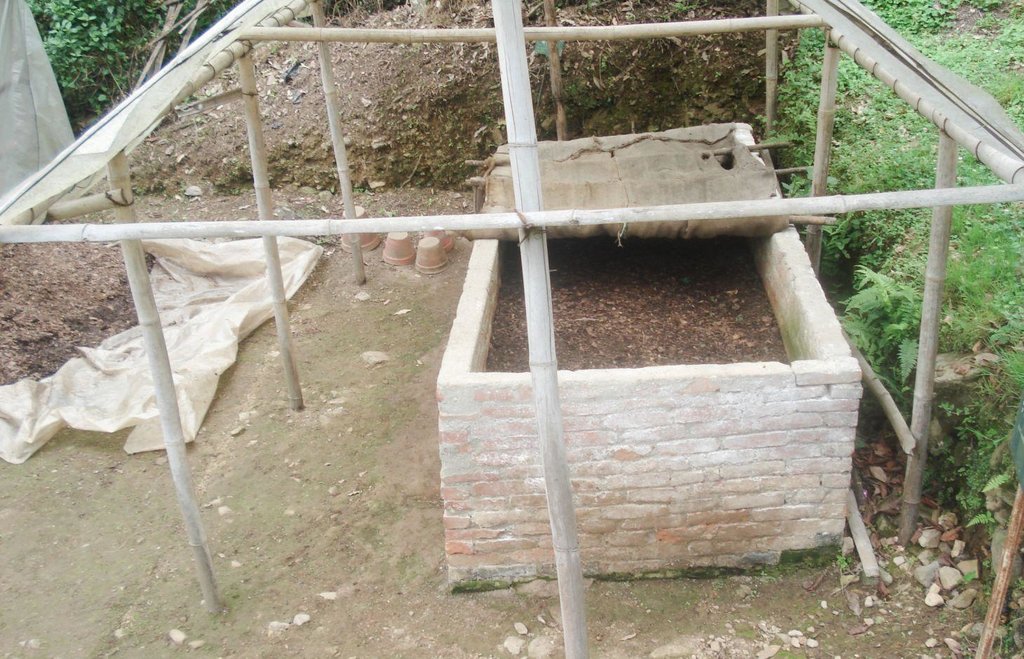
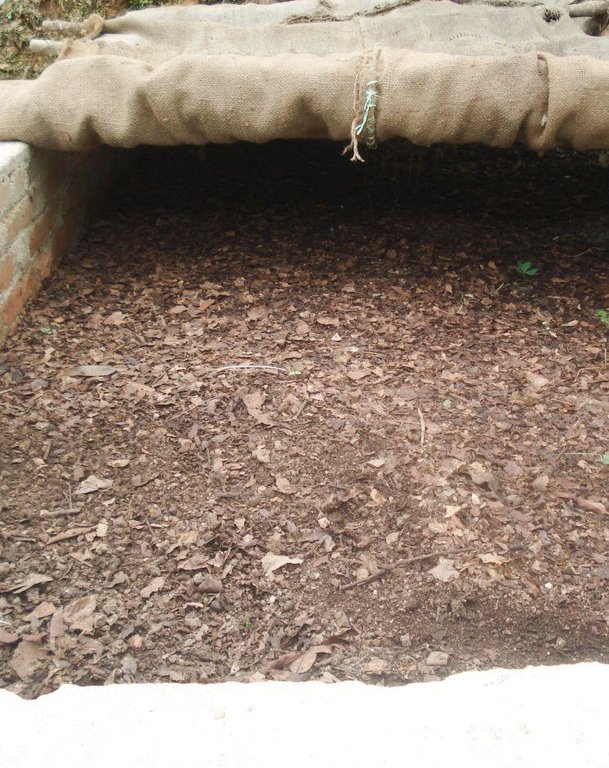
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Vermicomposting can be carried out in different types of containers. There are only a few requirements for a good worm pit, the most important being good ventilation; the pit needs to have more surface area than depth (wide and shallow) and it needs to have relatively low sides. The base of the worm pit is prepared with a layer of sand then alternating layers of shredded dry cow dung and degradable dry biomass and soil are added. Under ideal conditions, 1,000 earthworms can covert 45 kg of wet biomass per week into about 25 kg of vermicompost.
Natural / human environment: Worm castings contain five times more nitrogen, seven times more phosphorous, and eleven times more potassium than ordinary soil, the main minerals needed for plant growth. The vermicompost is so rich in nutrients that it should be mixed 1:4 with soil for plants to be grown in pots and containers. Vermicompost should not be allowed to dry out before using.
Note: This type of vermicomposting is sometimes referred to as 'Pusa' vermicomposting because it was popularized in South Asia by the Rajendra Agricultural University located in Pusa, Bihar, India.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Godavari, Lalitpur District
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- Improve fertilizer
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ)

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- អុស
- វាលស្មៅ
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Crop productivity is limited by poor soil fertility, intense cropping, and a scarcity of irrigation water. Farmers notice a marked decrease in the health of their crops and degraded soil conditions when chemical fertilizers are overused. Vermicomposting is a low input response to this problem.
Forest products and services: fuelwood
Other forest products and services: fodder
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងជីជាតិដីតាមបែបចម្រុះ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់/ ការគ្រប់គ្រងទឹកកង្វក់
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: soil management
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
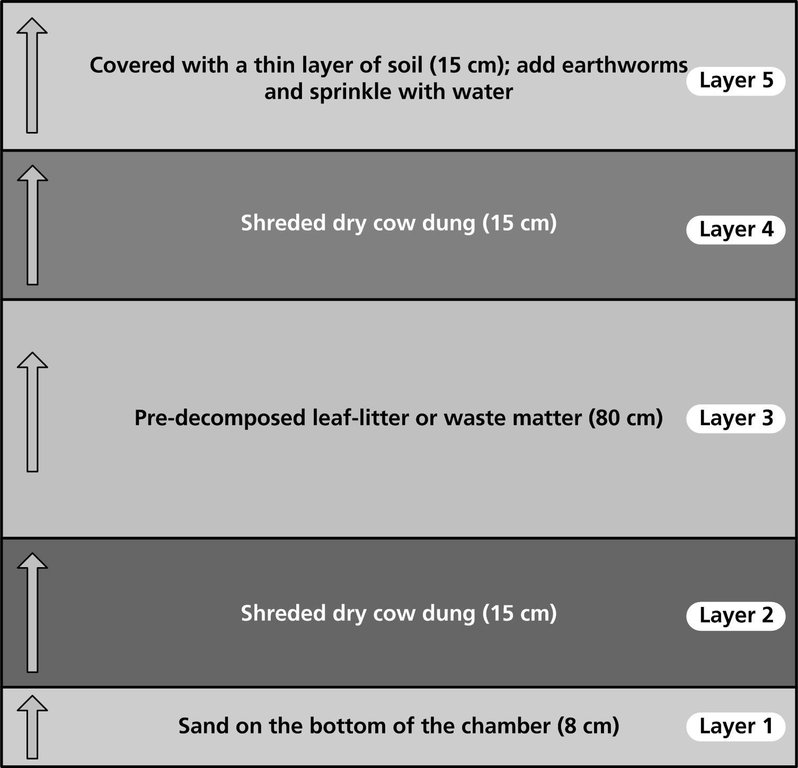
Establishing a vermicompost pit
Diagram showing the layers needed to set up a vermicompost pit. Note that the middle layer is the thickest; the worms start here and eat both upwards and downwards. It is best to house the pit under a thatched or plastic roof in order to shield it from excessive sunshine and rain.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), Improve Soil Fertility
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), Stabilizes that soil
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
AK Thaku
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងឯកតាបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ឯកតា:
worm pit
បញ្ជាក់ពីទំហំនៃឯកតា (បើពាក់ព័ន្ធ):
A typical outdoor pit can measure 4 m long, 1 m wide and 0.75 m high
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | A low cost pit can be constructed with bricks on a moist or shaded site | |
| 2. | If bricks are not available, stones can be used for the pit construction; | |
| 3. | alternatively, a wooden or bamboo box or a plastic tray can also be used. | |
| 4. | Vermicompost pits are best started during the summer months. | |
| 5. | A thatched roof was built over the pit to help retain moisture in the heap | |
| 6. | at a level of approximately 40–50%, as well as to maintain an optimal temperature of about 20–30oC. | |
| 7. | Sand, soil, cow dung, and leaf litter are piled up as shown in the diagram. | |
| 8. | Material Used are Bricks and cement, dry cow dung, plastic sheet/bamboo, earthworm (around 2000) |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Construction of pit | persons/day/unit | 10,0 | 5,0 | 50,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Brick and cement | unit | 1,0 | 70,0 | 70,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Dry cow dung | unit | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Plastic sheet/bamboo | unit | 1,0 | 70,0 | 70,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Earthworm (2000) | unit | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 260,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 260,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Water regularly and collect, harvest vermicompost | |
| 2. | The pit is watered regularly. After five to six weeks, the top layer is removed and piled in one corner of the pit. After a few days, the worms will have borrowed down to the bottom of this pile and the compost can be harvested. The compost prepared in the pit should be harvested within 6 months and the pit refurbished as for the first set as discussed above. |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Watering pit | persons/day/unit | 5,0 | 5,0 | 25,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Dry cow dung | unit | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Water pipe | unit | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 40,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 40,0 | |||||
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
All costs and amounts are rough estimates by the technicians and authors. This was a demonstration project conducted by ICIMOD.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
< 5 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Water quality (untreated): Also for agricultural use (irrigation)
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ខ្ពស់
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
695 species of flora and 230 species of fauna have been documented within the Park's 30 ha area
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- ច្រើនជាង 50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
- Governement
- ICIMOD
- ICIMOD
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
labour:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The vermicompost pit needs to be watered and maintained regularly
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
Earthworms need to be purchased from outside
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
livelihood and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Provides employment opportunities. Quality compost helps to improve the soil and increases crop production
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ីផ្សេងៗ
soil fertility
can be used to produce organic crops
use of chemical fertilizer
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
dependency on external inputs
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| active in warm climate | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Vermicomposting training was provided to farmers in Nuwakot, Rasuwa, Godavari, and Bishankhunarayan VDCs by ICIMOD staff in collaboration with local NGOs. More than 60% of the farmers who received training adopted vermicomposting on their own farms and they have also started selling worms to other farmers. The technology has been adopted by others who have visited the ICIMOD Knowledge Park at Godavari but most of these are just interested in introducing it on a small scale, such as, to produce vermicompost from kitchen waste for household use in their own gardens. The participants were also taught how to collect local earthworms to use for composting.
Drivers of adaptation of the technology
• A simple technology and easy to implement
• Local earthworms can be used.
• Not expensive; farmers can construct pits or uses wooden boxes or plastic trays.
• Produces high quality compost with a high concentration of nutrients
• Helps to reduce pests in the soil
• Can be scaled up to produce compost commercially
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
The use of vermicompost reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and reduces dependence on outside sources. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote the technology by disseminating it to a large number of farmers on both small and big farms |
|
Vermicomposting does not require keeping livestock. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It is considered to be a low-cost alternative that uses local earthworms and materials to produce compost. |
| On-farm composting saves the transportation cost needed to deliver compost to the farm. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Purchasing earthworms from outside may be expensive for farmers. | Farmers can be encouraged to harvest local earthworms for composting. |
| Making compost from earthworms is not very popular in rural areas. | Create greater awareness on how earthworms can be used to compost leaf-litter and other kitchen waste. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Vermicomposting: Journey to forever organic garden (no date)
វេបសាយ:
http://journeytoforever.org/compost_worm.html
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល