MANGO AND CITRUS TRESS GROWN AS CASHCROPS AND FOR SOIL FERTILITY IMPROVEMENT [អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ betty adoch
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ JOY TUKAHIRWA, Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Drake Mubiru, Nicole Harari, Stephanie Jaquet, Udo Höggel
Gwoko nyig yen igang
technologies_2319 - អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Okello Vincent
0782954875
okellovincent7@gmail.com
Pagwari Fruit Farmers Association
Pader district, Acoro Sub-County , Acoro parish, Pagwari East village
អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
09/05/2017
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
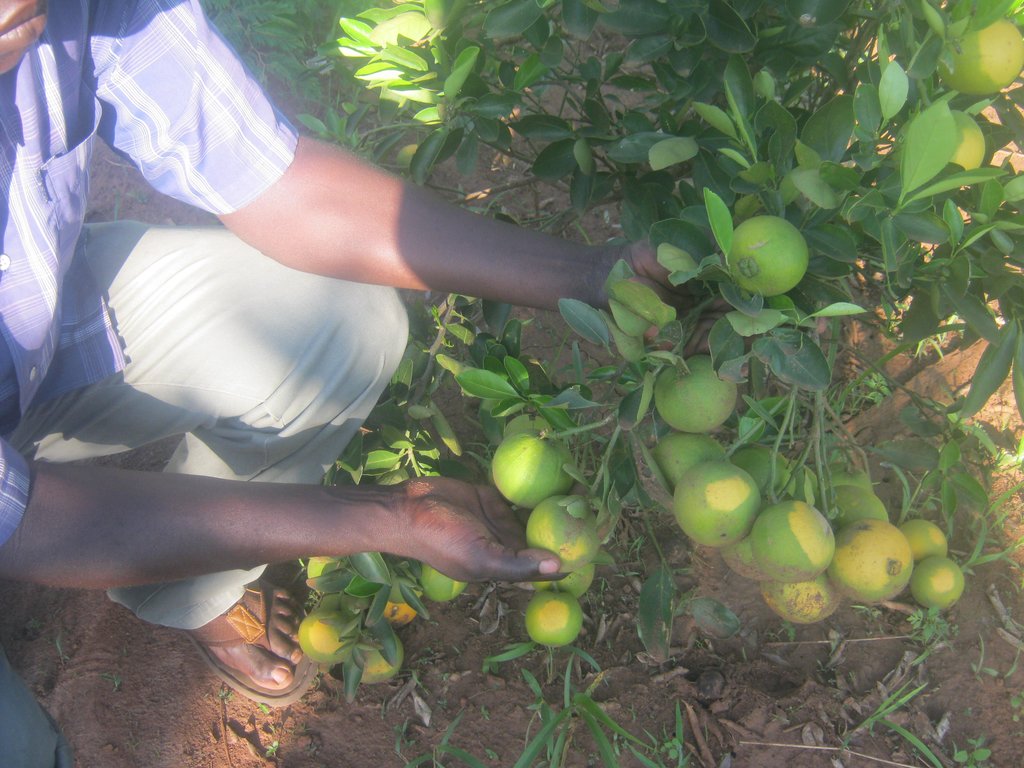
Different varieties of mangoes such as Banganapalle, Alphonso, Kesar, Haden, Bombay, Kent, Keitt, oranges such as Washington Navel, Valencies, Tangarine, jack fruits and avacados are grown for purposes of household income and soil fertility improvement.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
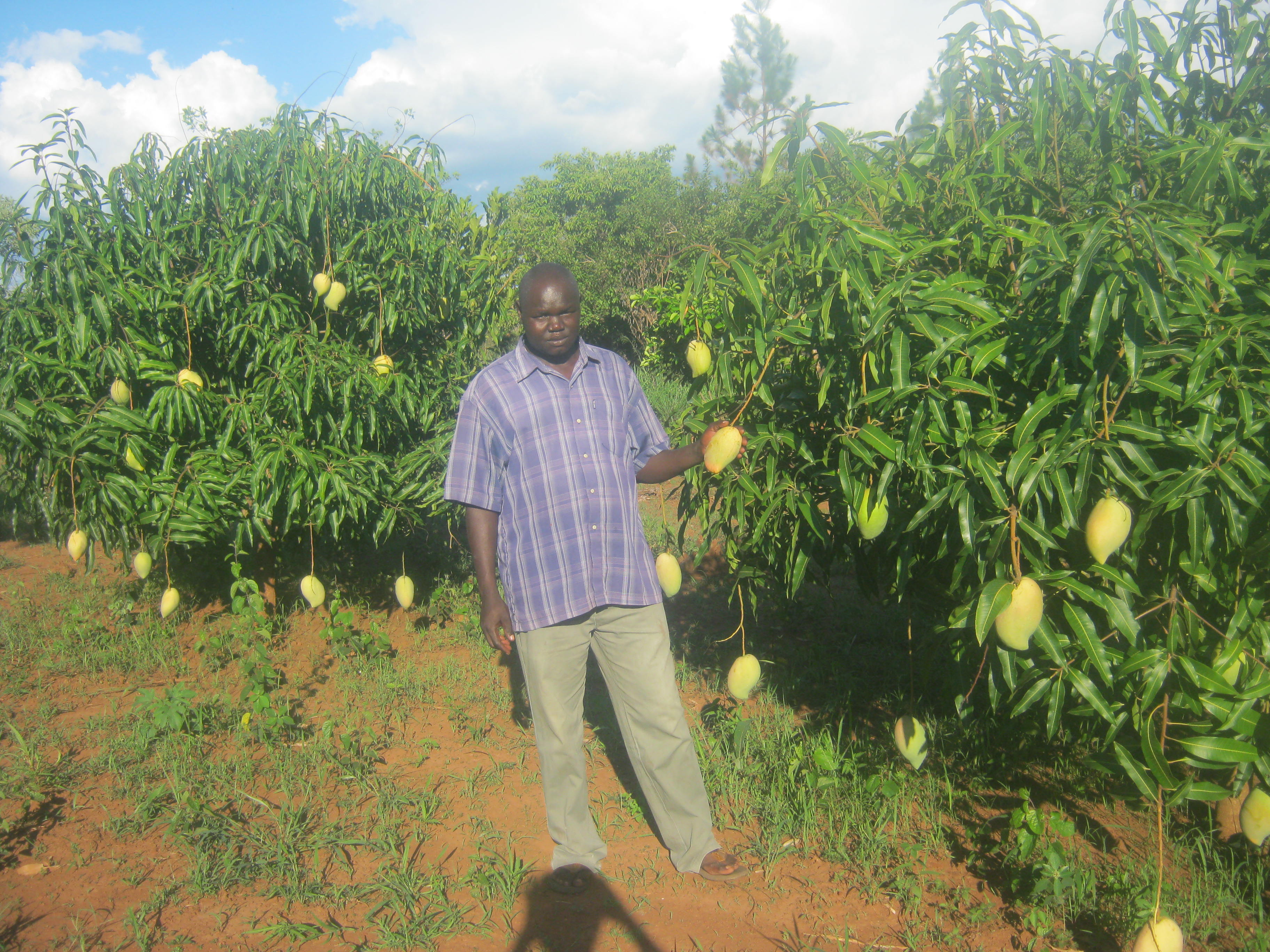
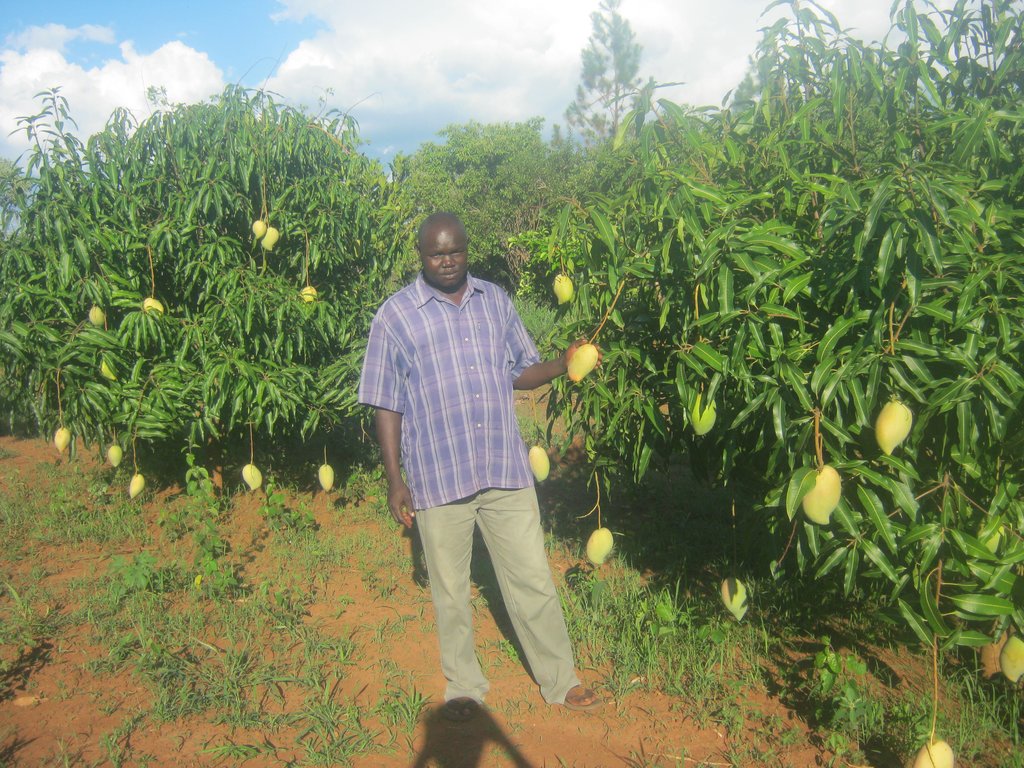
Home fruit tree groves of grafted mango (mangifera indica) and citrus (citrus aurantium) is a farming practice that farmers practice in Northern Uganda to diversify their economic activity, for soil fertility improvement and household income.
Northern Uganda has tropical savanna climate which receives moderate amount of rainfall ranging from 750-1000mm per annum. The soils are moderately fertile with less organic matters coupled with soil erosion, which leads to low crop productions hence low incomes. The moderate rainfall is also unreliable which makes the region to experience drought. Farmers grow fruits as an alternative source of income.
This land user generates over 90% of his household income from fruit growing. The planted fruit trees increase the organic matter content in the soil when dry leaves decompose, rooting prevents soil erosion, pruned brunches are a source of fuel wood and trees acts as wind breaks. Major fruits grown include jack fruits, grafted mangoes, oranges and avocados.
For all these fruits, seeds are first planted in a nursery bed for a period for about two months with the following required inputs: hoes, pangas, spades, wheelbarrows, and shovels. Afterwards, transplanting into the gardens is done. Selection and clearing of the field is done and the planting holes are marked. Excavation is done in accordance to the slope direction: the top soil is put on the hillward side of the planting hole then the sub-soil is put on the downward side of the planting hole. The planting holes are dug in a square shape at 60*60 cm. Composite manure is mixed with top soil and applied into the hole to speed up the seedling establishment and to enhance growth. When planting, the hole is not fully filled but ends 5 cm below the surface so to enable water harvesting, moisture retentions and infiltration. This ensures ample soil moisture and water supply to plants.
The spacing for avocados is 8 × 8 m (65 seedlings/acre), jack fruits is 10 × 10 m (44 seedlings/acre), mangoes 10 × 10 m (44 seedlings/acre) and oranges 4 × 5 m (200 seedlings/acre). After planting, mulching is done by saw dust, kitchen waste like groundnut husks, vegetables and so on. 75 mangoes, 150 oranges, 20 avocados, 20 jack fruits and 4 grapes trees are spread evenly over the planting area. To realize maximum production, the land user needs to have constant water for irrigation.
On the other side, fruit tree growing has brought negative feelings from neighbors who don't promote this practice. Fruit farmers' lifestyle has changed due to revenues realised from growing fruit trees. To maintain this technology, weeding, pruning and creating fire lines during dry seasons to protect the farm is very critical . The technology is highly susceptible to pests and diseases that may require support from the local extension worker from time to time to be able to obtain high yields.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់សម្គាល់ទូទៅនៃរូបថត/រូភាព:
Fruit trees protect the soil from environmental degradation and its effects such as soil erosion and landslides.
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
19/05/2017
ទីតាំង:
Pader District, Acoro parish, Pagwari East village.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
Betty Adoch
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Northern Uganda.
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Pader District, Acoro parish,Pagwari East village.
មតិយោបល់:
GPS point indicating the land user fruits garden
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2013
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Land user needs to generate income.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- បន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំព្រៃឡើងវិញ:
- ពូជបញ្ចូលគ្នា
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- ផ្លែឈើ និងគ្រាប់ធញ្ញជាតិ
ប្រសិនបើដីមានការប្រែប្រួលបន្ទាប់ពីការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការប្រើប្រាស់ដីមុនពេលអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេស:
The land was use for brick making
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
មតិយោបល់:
Drip irrigation is done during dry seasons
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
ដង់ស៊ីតេនៃសត្វចិញ្ចឹម (បើពាក់ព័ន្ធ):
Cows: 5, Goats:7. Improved breeds of goat and cattle which are high yielding
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវការបង្កាត់ពូជរុក្ខជាតិ/ សត្វ
- គេហសួន
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ សូមកំណត់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍:
- < 0.1 គម2 (10 ហិកតា)
មតិយោបល់:
The fruits gardens covers 2 acres of land.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M1: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់
មតិយោបល់:
Fruit growing promotes soil conversation.
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)
មតិយោបល់:
Fruit growing conserves the environment by preventing tree cutting.
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
The area initially was severly degraded by brick making work but after putting it under fruit growing, it became very fertile.
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Betty Adoch
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
19/05/2017
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
The fruit trees are planted on a generally flat average land size of 2 acres of land with following spacing: mangoes 10X10msq, jack fruits 10X10msq because it forms a big canopy, oranges 5X5 msq.
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
2 acres
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
UGX
កំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (បើទាក់ទង)៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
3500,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
3000 UGX
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site clearing for nursery bed | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | dry season |
| 2. | Raising the nursery | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | dry season |
| 3. | Digging planting holes | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | dry season |
| 4. | Applying composite manure | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | dry season |
| 5. | Transplanting at 15 to 30cm seedling high | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | onset of rain |
មតិយោបល់:
Different fruit species have different nursery beds
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Site clearing for nursery bed | Meters | 2,0 | 10000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Raising the nursery | Meters | 2,0 | 10000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Transplanting | Acres | 2,0 | 50000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Pitting for fruit tree planting | Acres | 2,0 | 50000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Pangas | Pieces | 10,0 | 5000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Hoes | Pieces | 15,0 | 10000,0 | 150000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Axes | Pieces | 5,0 | 10000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Wheelbarrows | Pieces | 4,0 | 95000,0 | 380000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | String | Pieces | 4,0 | 5000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Dipper | Pieces | 4,0 | 45000,0 | 180000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Watering can | Pieces | 2,0 | 25000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Spray pump | Pieces | 4,0 | 75000,0 | 300000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Bamboo | Pieces | 10,0 | 10000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Dry grass | Bundles | 5,0 | 3000,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 1535000,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The technology is technically easy to maintain once established and can be replicated by other land users.
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | after every 3 months |
| 2. | Pest control | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | dry season use cow dung and driny use season pesticide |
| 3. | Stray animal control | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | dry season |
| 4. | Thieves control | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | rainy season |
| 5. | Prunning branches | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | rainy season |
| 6. | Buying pesticides | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | rainy season |
| 7. | Transportation to market | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | season of harvest |
| 8. | Buying mulching materials | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | onset of rain |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Hired labour | Man day | 4,0 | 3000,0 | 12000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Spray pump | Piece | 4,0 | 75000,0 | 300000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Irrigation during dry season | Litres | 10000,0 | 200,0 | 2000000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Syringe pipe | Piece | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Seedings | Pieces | 269,0 | 3500,0 | 941500,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Composite manures | Wheelbarrows | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Stringes for making holes in a stright line | Rolls | 4,0 | 5000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Peg for setting holes | Boundle | 1,0 | 10000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Pesticides (dythen m45) | kg | 1,0 | 40000,0 | 40000,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 3331000,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The land user has knowledge on agronomic practices.
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
High costs of labor
High transportation cost
Purchase of pesticides
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
950,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Heavy rains in April, May, August and September
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Pader weather station
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Savanna climate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Loamy, silty soil at the top and deep down there is gravel. Soil pH is neutral and less saline.
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Very low water table
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ខ្ពស់
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
The land user is a typical farmer who is contented with his lifestyle as a fruit grower due to the income derived from sale of fruits.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
មតិយោបល់:
The land user bought the land from the community members.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
មតិយោបល់:
The land user has fenced his land and put marked stones.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to the litter from the leaves, increased soil fertility leading to increased production.
គុណភាពដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to the nutrients from the soil.
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Especially from the jack fruits wastes
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increased level of nutrients in the soil.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃផលិតផល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Because of the different fruit trees species planted.
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The land user recently acquired additional plot of land (0.5 acres) from the sale of fruit trees.
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Fruit trees reduce soil erosion and increase soil fertility due to leaves litter.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Fruit trees dont require alot of inputs once established; minimal costs for reducing pests and diseases; minimized by the role of extension workers during trainings.
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
From the sale of fruits and reduced expenses on farm in puts
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
From the sale of diverse fruit types (mangoes, oranges, jack fruits and others)
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Only labour for maintenance and monitoring against thieves
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Income from sale of fruits is used to buy other household income.
ស្ថានភាពសុខភាព
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Daily portion of fruits within diet.
កម្មសិទ្ធដីប្រើប្រាស់/ ទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Community bye-laws on controlled grazing and encroachment were put in place.
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Local bye-law committee (LBC) was put in place and supported by the Sub-County and District Council.
Bye-law on controlled grazing and encroachment passed at Sub-County Level.
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Trainings conducted by extension workers and fellow champion farmers, also integrating exposure learning events.
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The presence of the local bye-law committee and bye-laws reduced conflicts: no encroachment, no grazing on fruit gardens and no thieves.
ស្ថានភាពក្រុមដែលមានបញ្ហាក្នុងសង្គម និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Integrating people with disabilities (PWDs) in fruit tree growing trainings and exposure learning events.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Planted fruit trees control soil run off/soil erosion.
ដី
គម្របដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees.
ការបាត់បង់ដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees.
ការកើនឡើងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
ដីហាប់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ដីបាក់/ លំហូរកំទិចកំទី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to planted fruit trees and soil&water conservation bye-law on tree planting.
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Planted trees reduce drought.
ហានិភ័យនៃភ្លើងឆេះព្រៃ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to firelines to control bush burning during dry season.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to presence of strict community bye-laws.
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមការវាយតម្លៃផលប៉ះពាល់:
The technology is rewarding in the short, medium and long term and can be replicated by any farmer in any climatic region especially tropical regions.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ថយចុះ | ល្អណាស់ | |
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | សើម/រដូវភ្លៀង | ថយចុះ | ល្អណាស់ |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | សើម/រដូវភ្លៀង | កើនឡើង | ល្អណាស់ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អណាស់ |
| ភ្លើងឆេះព្រៃ | ល្អណាស់ |
| ភ្លើងឆេះ | មធ្យម |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ដីបាក់ | ល្អណាស់ |
មតិយោបល់:
This technology is drought resistant and manageable by any farmer who has the interest to practice it.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
The fruits are locally sold expensively at 1000 UGX@ and raise much income to the farmer.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 10-50%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
20 household
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 90-100%
មតិយោបល់:
The land user uses the little resources he has to establish the technology.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Constant supply of fruits provides high income to the land user. To realize maximum production, there is need for irrigation to have a constant fruit supply with support from extension workers who are readily available with the extension workers for technical advice. |
| The fruit trees modify the micro-environment making it conducive. |
| The technology is very rewarding, cost effective once established and can easily be replicated by other land users. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| The technology is good for small , medium and large scale farmers due to its ability to improve soil fertility, increase production and household income. |
| Can easily be replicated by other land users. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Before establishment the technology requires some knowledge and skills on fruit growing which can be extended by the extension worker who are located far from the land user. Associated with high costs in terms of transport and allowances to the land user. |
Training and capacity building of local land users / experts. Training champion farmers. Establishment of learning sites / demonstrations. |
| Prone to climate change | Irrigation during the dry season |
| Requires water supply | Irrigation during dry seasons |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| High establishment costs associated with reduced maintenance costs both in the short, medium and long term. | Adapt low cost practices for those starting and integrate with time and for those with low incomes. |
| Associated with high prevalence of pests and diseases. Risky to spray during flowering season. |
Close monitoring of the field all the time. Seek technical advice from the extension worker. |
| Labour intensive at the time of establishment. | Supplement with family labour. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
1
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
1
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
1
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Do Trees on Farms Improve Household Well-Being? Evidence From National Panel Data in Uganda, Daniel, C.Miller,September 2020.2020.0010
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
On-line. Free of cost.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល