Participatory monitoring and evaluation of long-term changes in ecosystems
(ມາດາກັສກາ)
ຄຳອະທິບາຍ
Establishing a knowledge base and communication platform in collaboration with para-ecologists for monitoring changes in ecosystems, to aid decision-making in forest management.
Aims / objectives: This approach strengthens knowledge about the response of biodiversity to environmental changes – namely land conversion, climate change induced impacts and climate-related extreme events, such as droughts and cyclones. Information generated can be used to inform regional authorities. They are then able to adapt management to current conditions, in order to better preserve biodiversity within the National Park. An important component of this approach is the integration of people from the local population as 'para-ecologists' who are trained in survey techniques for biodiversity monitoring. They directly observe changes in biodiversity, and share their knowledge with others in the area. The approach, thus, includes the sensitization of the local population to impacts of environmental change on biodiversity.
Methods: Under this approach, local assistants were trained in biodiversity monitoring techniques by researchers during their regular research activities. Part of the process comprised skills in species identification. Because the researchers had a limited period available for field work, training of these para-ecologists was a pre-requisite for implementation of long-term monitoring activities based on surveying at regular intervals. The surveys initiated by the researchers were plant phenology monitoring, regular capture, marking and recapture of Galidictis grandidieri (the giant striped mongoose) which is a flagship species in the Tsimanampesotse National Park, as well as reptile occurrence monitoring along transects. Monitoring procedures were established, and then continued by para-ecologists under the guidance of a Malagasy researcher who is familiar with ecological field work and acted as a ‘scientific coordinator’. The task of the scientific coordinator was data control and storage, planning of monitoring activities, as well as communication between national authorities, ecologists and para-ecologists. All survey data are available for scientific purposes and can be used to inform Malagasy authorities, or can be directly demanded by Malagasy authorities.
Stages of implementation: A basic research camp for monitoring was established within the Tsimanampesotse National Park in collaboration with Madagascar National Parks and WWF Toliara with third party funding. Four para-ecologists, two cooks and a guard constitute the team. The camp is maintained by a manager who is responsible for maintenance of buildings and electric facilities as well as provision of food. Surveying equipment is stored at the base camp. Computers and other necessary equipment were provided under the SuLaMa project. There are two para-ecologists trained on flora and a further two on fauna. Survey sites for monitoring of animal diversity and plant phenology were established by plant and animal ecologists in cooperation with the para-ecologists. Infrastructure for data acquisition and storage was established. This included the installation of electrical facilities as well as the provisioning of field books and computers. Technicians received language courses and learned computer operation. Regular exchange between the research camp and the national park authority, MNP, was established through a permanently employed scientific coordinator. This exercise resulted in a first workshop on survey techniques, in which staff of Madagascar National Park learned from researchers and para-ecologists.
Role of stakeholders: All survey data are available for scientific purposes and can be used to inform Malagasy authorities, or can be directly demanded from Malagasy authorities.
ສະຖານທີ່
ສະຖານທີ່: Beheloke, Atsimo-Andrefana (South-West Madagascar), ມາດາກັສກາ
ການຄັດເລືອກພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ອີງໃສ່ຂໍ້ມູນທາງພູມີສາດ
ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ: 2011
ປີຂອງການສິ້ນສຸດ: 2016
ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
-
ພື້ນເມືອງ / ທ້ອງຖີ່ນ
-
ການລິເລີ່ມ ພາຍໃນປະເທດ ທີ່ຜ່ານມາ / ນະວັດຕະກໍາ
-
ພາຍໃຕ້ໂຄງການ / ແຜນງານ
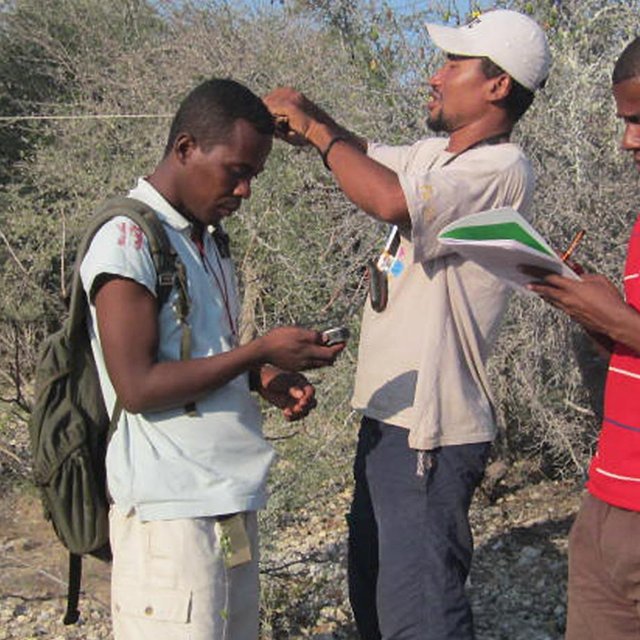

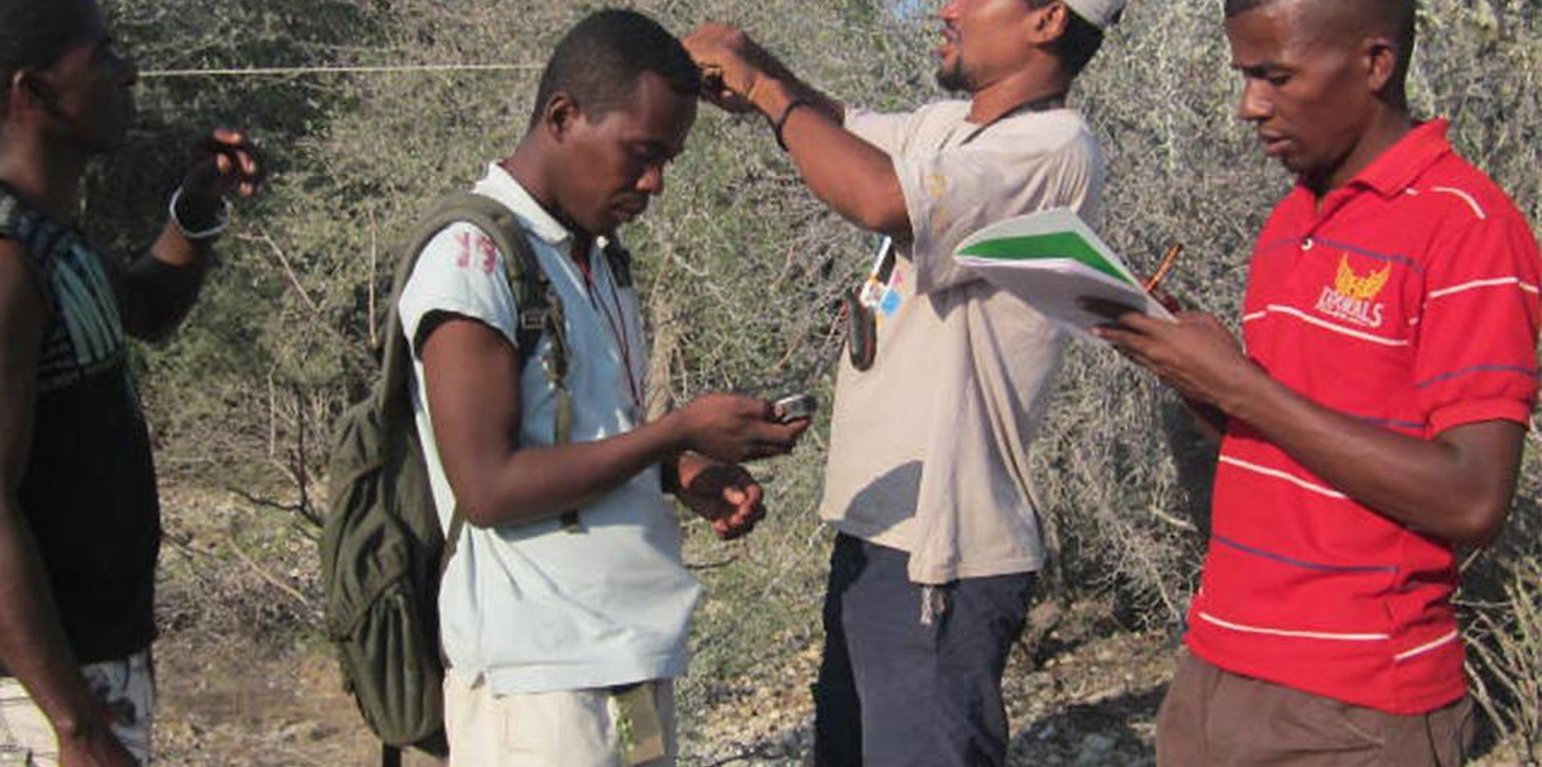
Staff of Madagascar National Parks during a workshop on survey techniques that can be used in biodiversity monitoring programs. (Yedidya R. Ratovonamana)
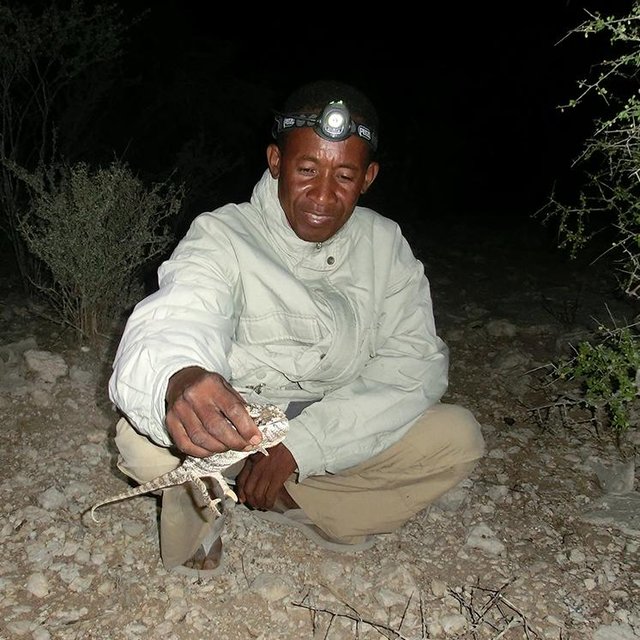

Paraecologists during a reptile survey at night holding a warty chameleon (Joachim Nopper)
ເປົ້າໝາຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ການປົກປັກຮັກສາສິ່ງແວດລ້ອມ
ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດແນວທາງ
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (raising environmental awareness, environmental education)
Collect data on biodiversity to increase understanding of environmental change impacts. Use of this data to inform conservation managers. Involve the local population in this process to raise awareness and create ownership.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Lack of knowledge about the changes in biodiversity within the national park; inadequate expertise in animal and plant identification; lack of knowledge about standardized sampling methods; data storage and dissemination not established.
ເງື່ອນໄຂທີ່ສະໜັບສະໜູນໃຫ້ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ບົນພື້ນຖານແນວທາງ
ເງື່ອນໄຂທີ່ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນໃຫ້ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ບົນພື້ນຖານແນວທາງ
-
ສັງຄົມ / ວັດທະນະທໍາ / ມາດຕະຖານ ແລະ ຄຸນຄ່າທາງສາສະໜາ: language barrier
Treatment through the SLM Approach: employment of a French teacher
-
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ: No housing and facilities for para-ecologists, no infrastructure for data entry and storage as well as storage of equipment
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Establishment of a research camp as the base for all monitoring activities; Establishment of a database for storage of survey data. Keeping of a copy by the scientific coordinator who is able to distribute the data to researchers.
-
ວຽກ, ມີກໍາລັງຄົນ: Due to different reasons surveys were occasionally cancelled.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Data quality of monitoring programs suffers if
surveys are not conducted at regular intervals. To avoid the cancellation of surveys, two persons were trained in the same survey techniques, so that a replacement is available. Nevertheless, occasional cancellations could not be avoided.
ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
ພາລະບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດແນວທາງ
| ແມ່ນໃຜ / ພາກສ່ວນໃດ ທີ່ເປັນເຈົ້າການ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີການ? |
ລະບຸ ພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ |
ພັນລະນາ ບົດບາດ ໜ້າທີ່ ຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ |
| ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ |
members of local population that gain knowledge on biodiversity |
|
| ນັກຄົ້ນຄວ້າ |
|
Para-ecologists are all men. Camp staff are equally divided between women and men. No woman occupied a top position however. |
| ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ບໍ່ຂື້ນກັບລັດຖະບານ |
MNP, WWF |
|
| ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ) |
MEEF |
access to monitoring data and knowledge on status of biodiversity conservation effectiveness. |
| ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ສາກົນ |
BMBF |
|
ອົງການທີ່ເປັນຕົວແທນໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
Researchers from different disciplines were involved. Scientific coordination was conducted by a Malagasy botanist.
ການລວບລວມເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ/ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດແນວທາງ ແຕ່ລະໄລຍະ
ບໍ່ມີ
ການບໍ່ປະຕິບັດ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ການຮ່ວມມື
ການນໍາໃໍຊ້ເອງ
ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ
Training, identification of places for monitoring activities
ການປະຕິບັດ
Monitoring within the National Park, giving results of research to National Park staff
ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ
ແຜ່ນວາດສະແດງ
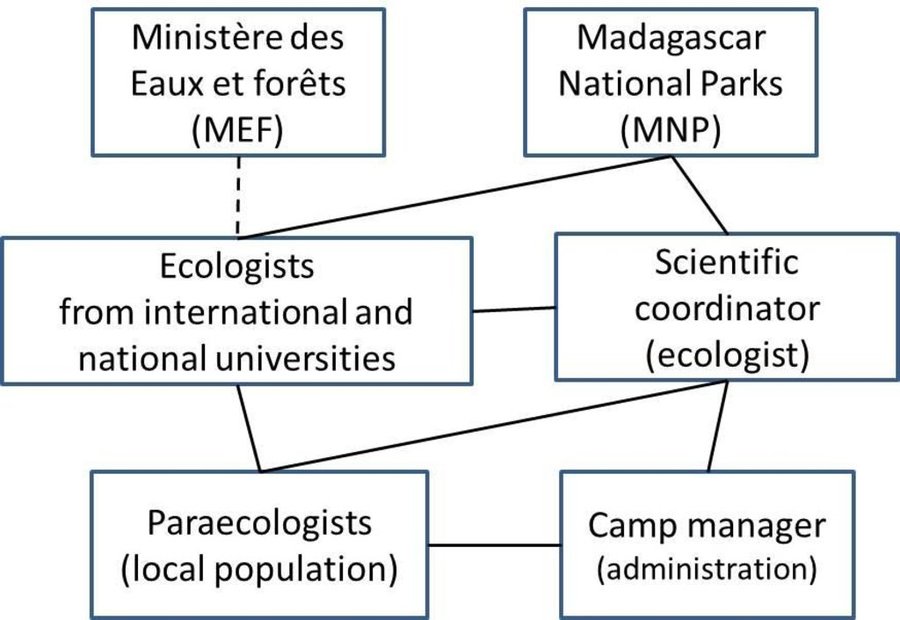
Key partners for a biodiversity monitoring programme in southwestern
Madagascar. Collaborative research is focussed in and around Tsimanampesotse National Park. Ecologists train para-ecologists and develop long term monitoring programs. Scientific coordinator collects data and communicates results to MNP. Para-ecologists conduct surveys, a camp manager ensures research equipment is available and coordinates maintenance.
ການຕັດສິນໃຈໃນການເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ການຕັດສິນໃຈໂດຍ
-
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນຜູ້ດຽວ (ການລິເລີ່ມດ້ວຍຕົນເອງ)
-
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນຫຼັກ, ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ໂດຍຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທັງໝົດ, ເປັນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ຂອງວິທີທາງແບບມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
-
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ຫຼັກດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ມີການຕິດຕາມປຶກສາຫາລືກັບຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
ຊຽ່ວຊານ ສະເພາະດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງຜູ້ດຽວ
-
ນັກການເມືອງ / ຜູ້ນໍາ
-
by researchers
ການຕັດສິນໃຈບົນພື້ນຖານ
-
ປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ (ຫຼັກຖານທີ່ຊ່ວຍໃນການຕັດສິນໃຈ)
-
ຜົນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບ ຈາກການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
-
ປະສົບການສ່ວນບຸກຄົນ ແລະ ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ທີ່ບໍ່ເປັນເອກກະສານ)
ການສະໜັບສະໜູນເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ ແລະ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຄວາມຮູ້
ກິດຈະກຳ ດັ່ງລຸ່ມນີ້ ແມ່ນເປັນພາກໜຶ່ງຂອງແນວທາງ
-
ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
-
ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
-
ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
-
ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ / ຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ໄດ້ສະໜັບສະໜູນຝຶກອົບຮົມໃຫ້ແກ່ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງດັ່ງລຸ່ມນີ້
-
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
-
ພະນັກງານພາກສະໜາມ / ທີ່ປຶກສາ
-
local population
ຮູບແບບການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
-
ການເຮັດຕົວຈິງ
-
ຕົວຕໍ່ຕົວ
-
ເນື້ອທີ່ສວນທົດລອງ
-
ກອງປະຊຸມ
-
ຫຼັກສູດ
ກວມເອົາຫົວຂໍ້
Local men who were trained in animal and plant identification and survey techniques. They became specialists in their area of work and due to regular surveys, better understand the effects of environmental changes on plant phenology and the occurrence and behaviour of animals. They share their knowledge in their villages, thus contributing to raising awareness about the environment.
ການບໍລິການທາງດ້ານການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ໄດ້ຮັບການບໍລິການທາງດ້ານການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
-
ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
-
ສູນຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
Advisory service is inadequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
ການຕິດຕາມ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through observations; indicators: data collection by paraecologists was observed by researchers during training phase
Control of data quality aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations
Regular data collection aspects were regular monitored by project staff through
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: n/a
ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ການວິໄຈໄດ້ຮັບການຮັກສາຫົວຂໍ້ຕໍ່ໄປນີ້
-
ສັງຄົມ
-
ເສດຖະສາດ / ການຕະຫຼາດ
-
ລະບົບນິເວດ
-
ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
Research was exclusively undertaken within the national park. Extension of research activities into non-protected areas is aspired in collaboration with the local communities.
Research was carried out on station
ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
ງົບປະມານປະຈຳປີ ໃນກິດຈະກຳ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ທີ່ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນໂດລາ
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
100,000-1,000,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: n.a.
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (German Ministry of Education and Research, BMBF): 100.0%
ການບໍລິການ ຫຼື ສິ່ງກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ ດັ່ງລຸ່ມນີ້ ແມ່ນໄດ້ສະໜອງໂດຍຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນເອງ
-
ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
-
ຫຼຸດປັດໃຈນໍາເຂົ້າ
-
ສິນເຊື່ອ
-
ສິ່ງຈູງໃຈ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອງມືອື່ນໆ
ເງິນສະໜັບສະໜູນອຸປະກອນ / ສະໜອງໃຫ້ຜູ້ຊົມໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ
ງົບປະມານເຕັມສ່ວນ
electric facilities and research equipment
construction & maintenance of research camp
ແຮງງານຂອງຜູ້ນໍ້າໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
ການອາສາ
-
ລ້ຽງເຂົ້າ - ອາຫານ
-
ຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນສົດ
-
ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ອຸປະກອນດ້ານອື່ນ
ການວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສະຫຼຸບລວມ
ຜົນກະທົບຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ແນວທາງ
ບໍ່
ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
This approach is to evaluate long-term impacts of land conversions, gradual climate change and climate-related extremes (disasters) on biodiversity. Due to insufficient data because of the short time since implementation, impacts have not yet been assessed.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ທາງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ເສດຖະກິດບໍ່?
By providing employment for some local people.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
Community-based monitoring is on the rise in Madagascar.
ສິ່ງກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ໃຫ້ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການປະຕິບັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
ການຜະລິດເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ
-
ກໍາໄລເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ (ຄວາມສາມາດ), ການປັບປຸງຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ, ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ, ອັດຕາສ່ວນ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງຂອງໄພພິບັດ
-
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນພາລະວຽກ
-
ການຊໍາລະເງິນ / ເງິນອຸດໜູນ
-
ກົດລະບຽບແລະລະບຽບການ (ລະອຽດ) / ການບັງຄັບໃຊ້
-
ກຽດສັກສີ, ຄວາມກົດດັນທາງສັງຄົມ / ການຕິດຕໍ່ກັນທາງສັງຄົມ
-
ລວມເຂົ້ານໍາກັນກັບການເຄື່ອນໄຫວ / ໂຄງການ / ກຸ່ມ / ເຄືອຂ່າຍ
-
ຄວາມຮັບຮູ້ ທາງສີ່ງແວດລ້ອມ
-
ພາສີ ແລະ ຄວາມເຊື່ອຖື, ສົມບັດສິນທໍາ
-
ການປັບປຸງ ຄວາມຮູ້ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
ການປັບປຸງຄວາມງົດງາມ
-
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ
-
well-being and livelihoods improvement
ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດກິດຈະກໍາຂອງແນວທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຕາມແນວທາງໄດ້ເອງບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກການສະໜັບສະໜູນຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ແລະ ບົດຮຽນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບ
ຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ: ທັດສະນະມູມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ: ທັດສະນະມຸມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນເອງ
-
By employing people from villages surrounding the national Park in regular research activities as well as biodiversity monitoring, knowledge on dynamics of natural systems is experienced firsthand and can be transmitted to other members of the local population. This can be seen as an informal knowledge hub from which communities learn more about the ecosystem they live in. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Creating owenership might lead to a more sustainable resource use practice.)
-
Collecting data and knowledge to support evidence based decision making for biodiversity conservation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Maintain and carry forward the knowledge base and communication platform by ensuring funding )
ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ: ທັດສະນະມູມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນວິທີການແກ້ໄຂແນວໃດ
ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ: ທັດສະນະມຸມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນເອງວິທີການແກ້ໄຂແນວໃດ
-
Monitoring activities depend on continuous funding. Funding was provided by SuLaMa/BMBF. Efforts for a continuation of funding need to be undertaken throughout project implementation as well as after project has terminated.
The situation could be stabilized by mainstreaming monitoring activities in programs of in-country authorities, which is planned but has not yet been implemented.
ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ
ການທົບທວນຄືນ
-
Fabian Ottiger
-
Deborah Niggli
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: Feb. 8, 2016
ປັບປຸງລ່າສຸດ: April 4, 2018
ບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ
-
Joachim Nopper (joachim.nopper@uni-hamburg.de) - ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Yedidya R. Ratovonamana - ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Jörg U. Ganzhorn - ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ການບັນຍາຍລາຍລະອຽດ ໃນຖານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງຂໍ້ມູນການຄຸ້ມຄອງການນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ເອກກະສານ ແມ່ນໄດ້ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກໂດຍ
ສະຖາບັນ
- Universität Hamburg (UHH) - ເຢຍລະມັນ
- University of Antananarivo - ມາດາກັສກາ
ໂຄງການ
- Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)
- Sustainable Landmanagement in south-western Madagascar (SuLaMa / GLUES)