



In the arid areas of Sughd region cultivation of most crops is possible with irrigation only. In many cases conventional furrow irrigation is limited or impossible due to insufficient availability of irrigation water. Furthermore, conventional furrow irrigation is often connected with problems which make irrigated farming unsustainable – high water demand causes shortages for downstream water users and ecosystems, irrigation water can flush out nutrients from soil or cause erosion, high amounts of irrigation water and insufficient drainage can lead to waterlogging and where soil and/or irrigation water contain high amounts of salt to salinization. From an economic perspective, the high amounts of irrigation water required for conventional irrigation can be costly, especially where pumping from sources to fields at higher elevation is required. Climate change impacts like increasing aridity, changing seasonality of rainfall, reduced storage of precipitation as snow and glacier ice and resulting irrigation water shortages during critical seasons require adaptation in irrigated agriculture.
The broader application of drip irrigation is one way to address economic and environmental issues of irrigated farming, while specifically addressing climate change impact. The major effect of drip irrigation is the increased irrigation water use efficiency – “More crop per drop”. This avoids or reduces the above explained impacts of conventional furrow irrigation: water demand is massively reduced allowing irrigating fields and orchards in areas where water availability would not allow for conventional irrigated agriculture; loss of soil nutrients, irrigation induced erosion and waterlogging are avoided, salinization is much less likely and occurs only in small extent in cases where highly mineralized irrigation water is applied (not an issue in the described project region). The reduced need for irrigation water avoids conflict with downstream water users and the needs of ecosystems. Under climate change impact farmers applying drip irrigation have a higher security that sufficient irrigation water is available and the drip irrigation technology allows for an adapted provision of water to the crops in accordance to their physiological demand. Drip irrigation systems can be used to apply the accurate dosages of fertilizer directly to the plants. This increases the effectiveness of fertilizing and the efficiency in terms of costs as much less fertilizer is not taken by the crops.
Drip irrigation is applied for various crops:
•perennial crops: orchards of apple, apricot, pear and other fruit trees, vineyards, lemons in greenhouses;
•corn, onions, potatoes; and
•honey melon and water melon.
The high initial investment influences on the economic profitability of the technology. The project demonstrated that drip irrigation can be used not only for orchards, where it has an advantage over field crops, because there is no need re-install pipes every season. But it can be used for crops such as melons, onion, sunflower and corn. In the case of honey melon and water melon drip irrigation is particularly efficient due to the large area covered by every single plant. Thus the distances between pipes and between drippers can be large to supply each plant, but the plants with their long tendrils and large leaves effectively use the space in between. In trials of onion cultivation the generally high investment needs, required density of tubes and drippers and the comparably low market price made the technology in not economically competitive under current circumstances.
Drip irrigation can be applied with various sources of irrigation water. Compared to conventional furrow irrigation even low amounts of irrigation water or water from comparably costly sources can be effectively used. In the frame of the documented trials the following sources of irrigation water have been used for supplying drip irrigation systems in addition to water from irrigation canals:
•spring water collection with concrete reservoir;
•water from draw well, pumped to small water tower above the well and from their running by gravitation to concrete reservoir, from where it is supplying the drip irrigation system;
•rain water collection from house roofs with concrete reservoir;
•irrigation water withdrawn by large pumps from Syrdarya river and supplied via pipelines to newly irrigated areas;
•irrigation water from household water supply system, stored in concrete reservoir during day times of low demand.
The drip irrigation systems are equipped with manual (use of local irrigation water stored in concrete reservoirs or barrels) or automatic (direct use of irrigation water from pipelines) pressure regulation valves. At the outlets of reservoirs or at the pressure regulations device fertilizer can be added and provided to the plants in exact dosage.
ສະຖານທີ່: Sughd region, ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ: 10-100 ພຶ້ນທີ່
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?: ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: 2017; ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ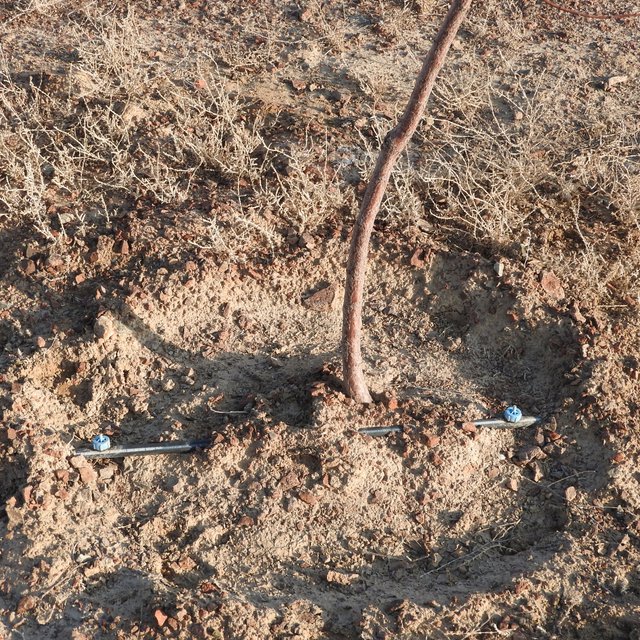





| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (TJS) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (TJS) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ແຮງງານ | |||||
| Construction of water withdrawal systems | |||||
| Construction of rainwater harvest systems | |||||
| Construction of water storage | |||||
| Installation of drip irrigation systems | ha | 5.0 | 2800.0 | 14000.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | |||||
| Water withdrawal systems | |||||
| Rainwater harvest systems | |||||
| Water storage systems | |||||
| Drip irrigation system orchard | ha | 5.0 | 7000.0 | 35000.0 | |
| Drip irrigation system onion field | ha | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 69'000.0 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 8'625.0 | ||||
Varying, depending on crop and specific situation.
Varying, depending on crop and specific situation.
Areas of several hundred hectares additionally cultivated (ongoing)
Absolute quantity of additionally available irrigation water is not high, but due to efficient use actually possible addtional irrigation is significant.
Actual consumption of irrigation water has not declined, but unsatisfied demand declined.
Expensive on-farm infrastructure required
Workload for installation and maintenance is higher than for conventional furrow irrigation.
Increase in area and productivity of irrigated lands without substantial increase of water withdrawal.
Use of water from previously not effectively used sources - rainwater from roofs, small springs, small wells.
Use of drip irrigation for establishment of tree cover at debris flow site.
Improved drought resistance by better availability, regulation and efficient use of irrigation water
Avoided reduction of water availability due to use of water efficient irrigation technology in newly irrigated areas.
Use of drip irrigation for establishment of tree cover at debris flow site.
Use of drip irrigation for establishment of tree cover at debris flow site.