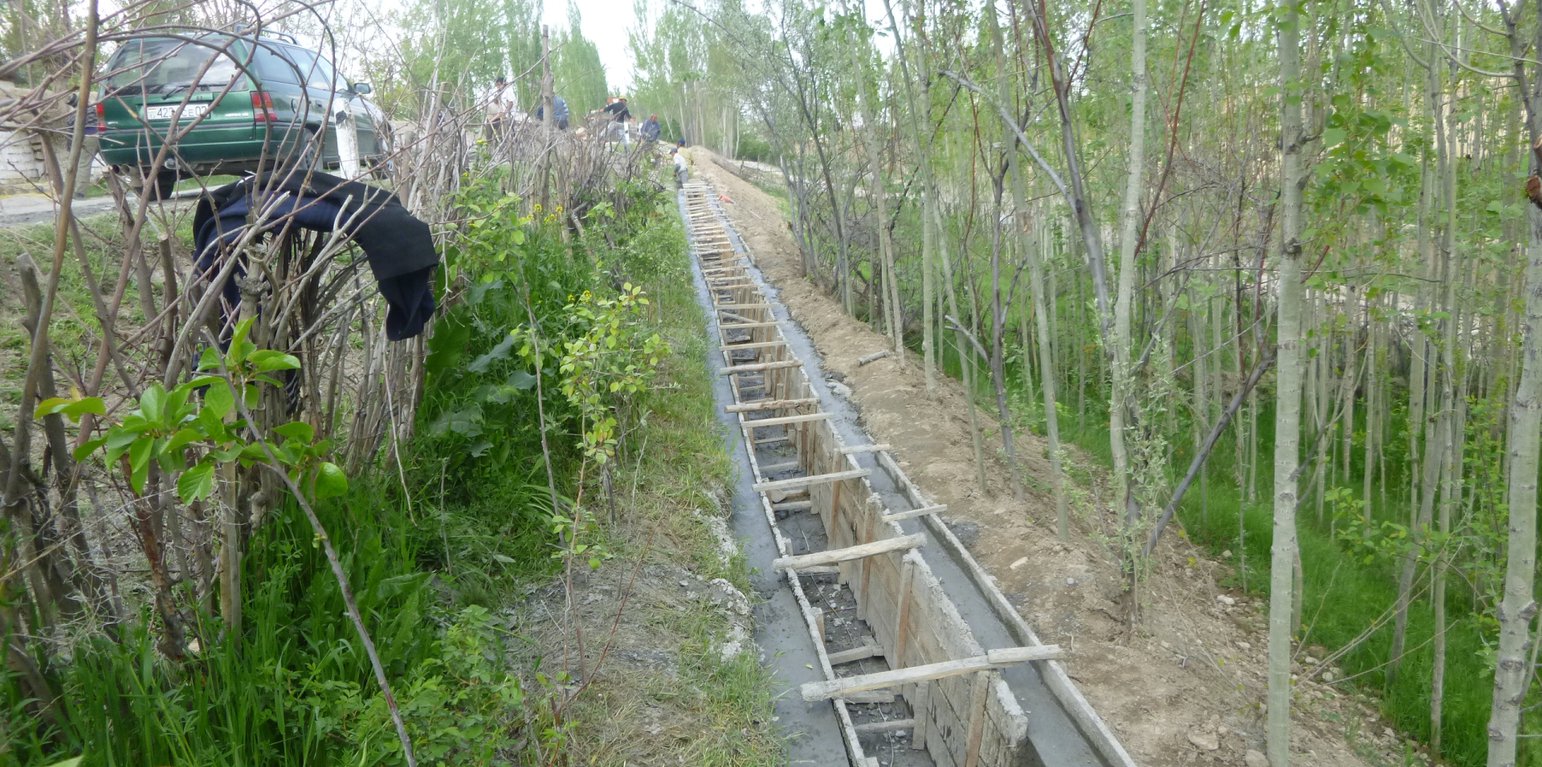




Irrigated agriculture is in many areas limited by the availability of irrigation water. In many irrigated areas the canals delivering water to villages, distributing it between farms and the on-farm irrigation systems are in poor shape, which causes substantial water losses. The human population growth further contributes to shortages of irrigation water.
These problems are increasingly exacerbated by the impact of climate change. The already visible trends and predictions show higher levels of aridity, higher temperatures during the vegetation season, reduced overall precipitation in catchment areas, more irregular rainfall patterns, reduced snow packs and accelerated snow melt as well as the loss of glaciers as buffers of water flow. These factors all cause a reduction of available irrigation water, while higher temperatures and expansion of irrigated agriculture – partly also caused by increasing aridity and reduced feasibility of rain-fed farming – lead to higher irrigation water demand.
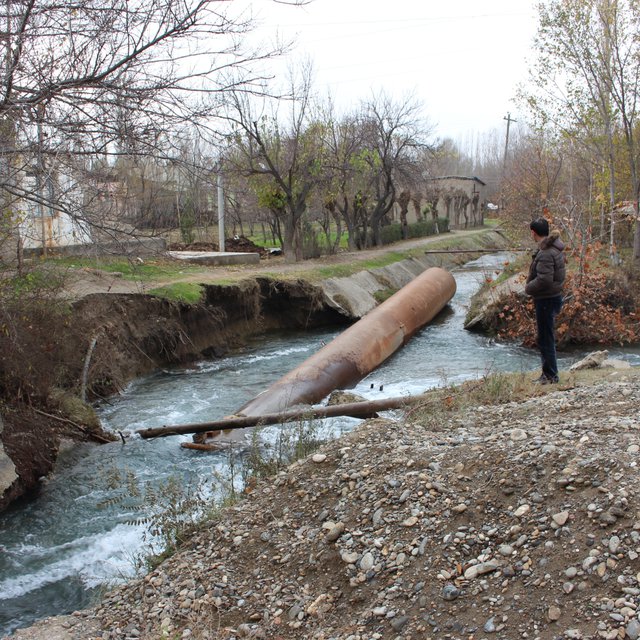
Additionally the increasing frequency and intensity of flashfloods, debris flows and landslides poses substantial risks to the stability and functioning of irrigation canals and thus to the livelihoods of farmers and food security.
The approach therefore aims at reducing the substantial losses of irrigation water caused be seepage from delivery and distribution canals, structural problems in irrigation systems (diversion weirs) and on-farm irrigation. It also addresses risks caused by flashfloods, debris flows and landslides. The structures between major canals, which are managed by the Water Management Departments, and the individual farms are managed by the administrative communities, the mahalla committees, which represent the inhabitants of one village or a section of a larger village. These institutions are called communal self-governance structures, but are subordinated to the government as they are reporting to te sub-district or jamoat.
For the lining of water delivery and distribution canals, the rehabilitation of associated structures and the proofing against disaster events the project conducted a participatory assessment and planning process in the local communities, but with involvement of the district water and irrigation management authorities. In the result of this process key sections for lining and repair were selected and the project further assisted with technical planning and assistance in form of purchase of materials. The communities would contribute about 28% to 39% of the overall costs, mainly in form of voluntary communal work, the so called hashar as well as in form of construction materials.
The community is also in charge of future operation and maintenance of the rehabilitated and disaster and climate proofed irrigation structures.
ສະຖານທີ່: Shahriston district, Sughdiyon village and J. Rasulov district, Dehmoi village, Sughd region, ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ: 2015
ປີຂອງການສິ້ນສຸດ: n.a.
ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ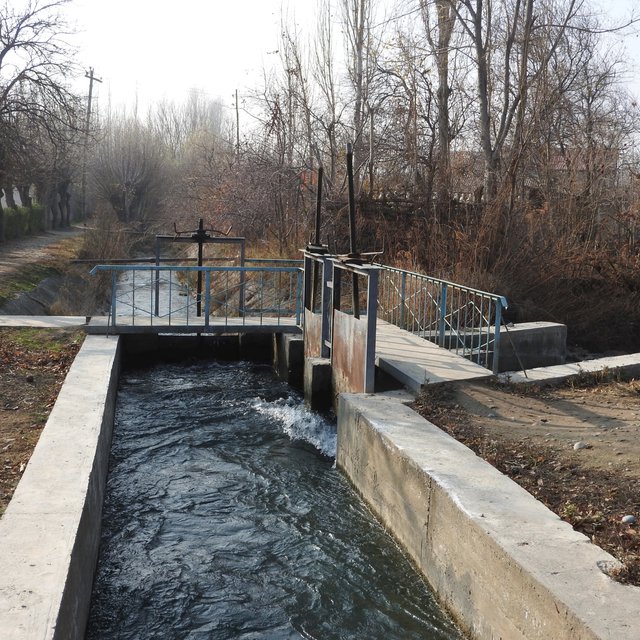

| ແມ່ນໃຜ / ພາກສ່ວນໃດ ທີ່ເປັນເຈົ້າການ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີການ? | ລະບຸ ພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ | ພັນລະນາ ບົດບາດ ໜ້າທີ່ ຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ |
| ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | Local community members | Participation in identification of sections for rehabilitation/improvement; Carrying out construction works. |
| ອໍານາດ ການປົກຄອງທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | Water management department at district level Mahalla committee | Identification of sections for rehabilitation/improvement Participation in planning Organization of community work |
| ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ສາກົນ | Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) | Overall project implementation; Technical planning and oversight; Procurement of construction materials via competitive bidding process |
ການຕັດສິນໃຈໂດຍ
ການຕັດສິນໃຈບົນພື້ນຖານ
Mobilization for joint work ti address problems affecting all farmers/community members
Construction and maintenance of irrigation systems of higher efficiency with reduced water losses and risk of disaster impact.
Coordination between donor, district level water management department, community leadership and community members
Mobilization of own resources in the community and of donor funding.
Improved technical knowledge on construction of irrigation systems minimizing water losses and reducing disaster risk.
Community leadership and district level water management department - improved technical knowledge on construction of irrigation systems minimizing water losses and reducing disaster risk.
Coordination between donor, district level water management department, community leadership and community members
More efficient water delivery and distribution reduces conflict about access to irrigation water within the community and between villages.
Mobilization of all community members to contribute to activities with common benefits.
Mobilization of all community members to contribute to activities with common benefits.
Reduced shortage of irrigation water and reduced risk of failure of irrigation systems due to disasters led to secure yields in irrigated agriculture and improved food security.
Water from irrigation canals is partly also used for household needs.
Increased resilience to climate change related irrigation water shortage by improved efficiency of water delivery and distribution; Reduced proneness of irrigation system to natural disaster, the frequency and intensity of which is increasing due to climate change.
Indirectly by providing secure access to sufficient irrigation water for farming.
Maintenance of irrigation systems through contributions of all water users and join voluntary work ("hashar").