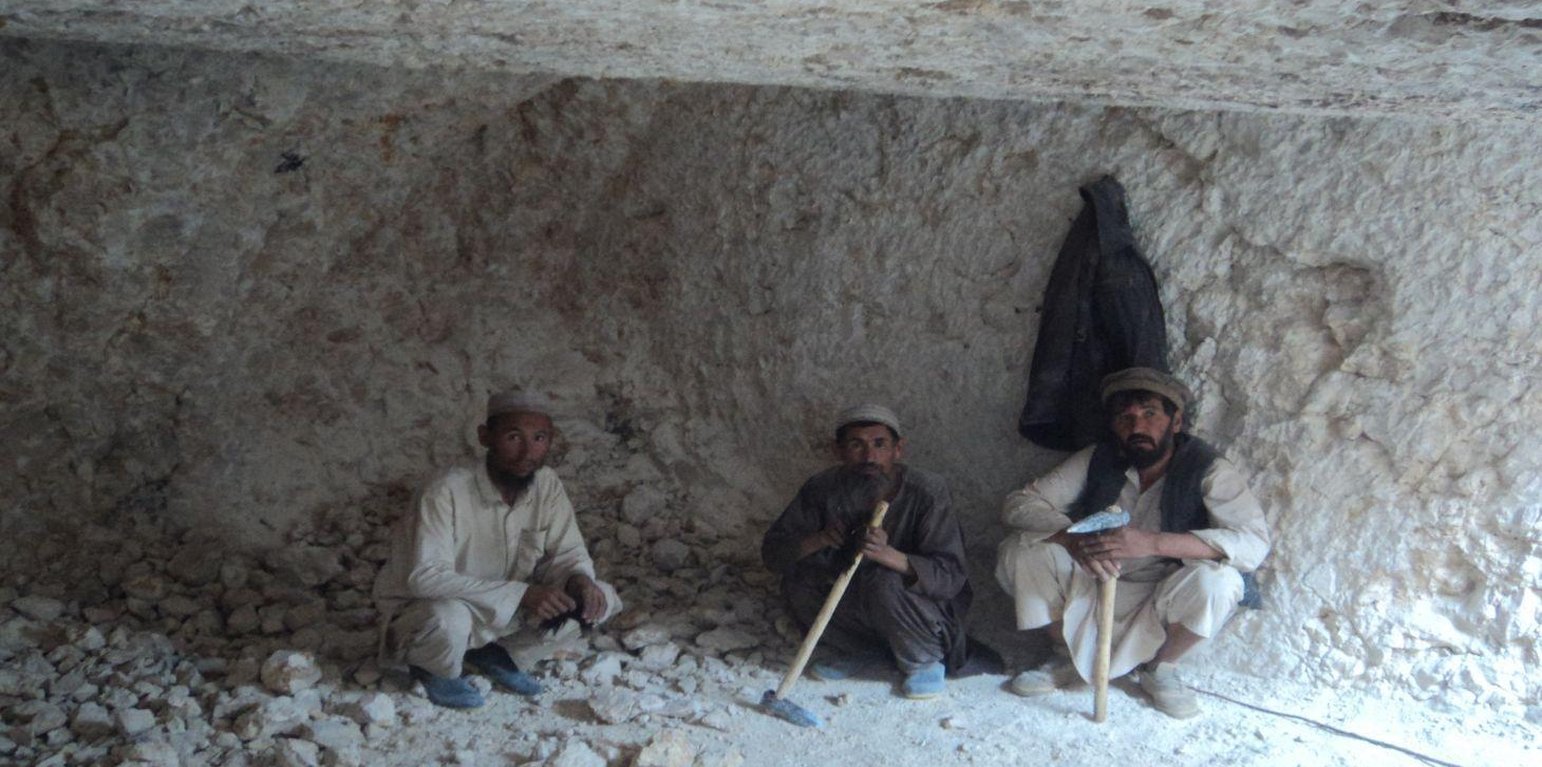




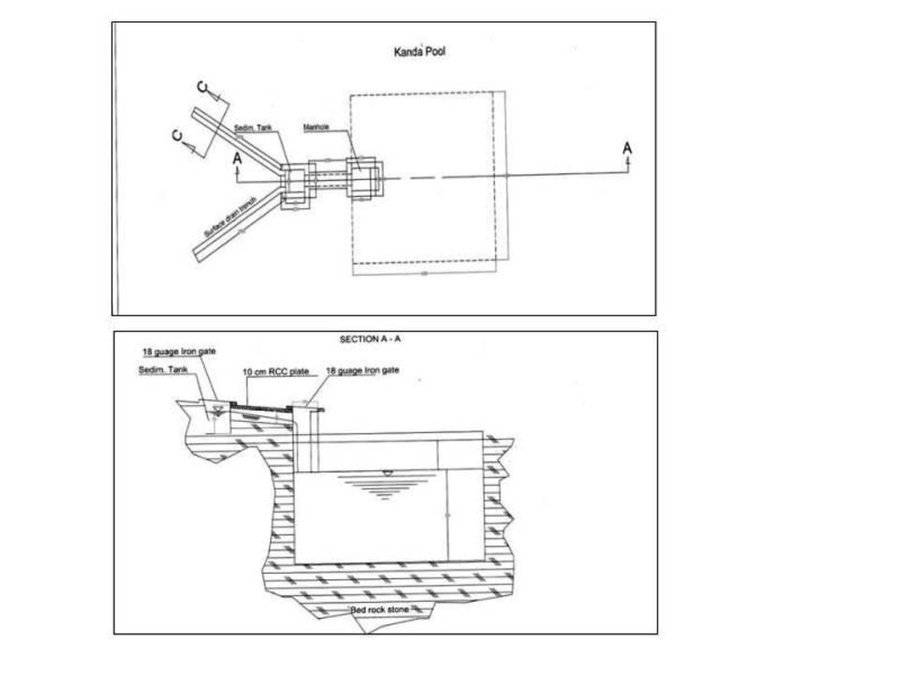
Kanda is an indigenous technology for collecting rain and snow melt. The technology comprises an underground tank carved out of rock (limestone), channels to convey the runoff into the underground tank or kanda and a rocky catchment from where runoff is collected. Kanda technology is applied in Afghanistan in many places, particularly in areas which experience scarcity of water for human beings, livestock and irrigation.
Purpose of the Technology: Due to high evaporation rates and low precipitation, harvesting runoff in open tanks is not an efficient way of water harvesting. HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation is implementing community based watershed management projects in Kahmard district of Bamyan province (Afghanistan) since 2008 with financial support from the International Swiss Re Award for sustainable watershed management (2009) and the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC). One of the activities for sustainable watershed management is plantation of fruit and non-fruit trees in the selected watersheds (upland areas) which were used for grazing and extraction of vegetation for domestic use. Due to water scarcity in the upland areas, irrigation of the planted saplings becomes very difficult and water has to be transported on donkey from far locations. To overcome this constraint, Kanda was identified as the most potent technology for harvesting runoff and snow melt.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For constructing Kandas, Kanda makers from Dara-e Suf district in Samangan province had to employed as there are no experts in Kahmard. Based on feasibility studies, eight kandas have been constructed including 4 kandas in Sourakhak wa-tershed and 4 in Baqa Kushta watershed. The size of each kanda is 6 m length, 6 m in width and 3 m in height. To convey the runoff into the tank, 10-20 m long graded channels were carved out of the rocks. The establishment cost of one Kan-da was approximately US$ 7163. Kanda making requires special skills, especially when it is carved out of rocks. A kanda maker has sound understanding of the area’s geology, and this wisdom is gained through learning by doing and ances-tors.. In Kahmard, 2-3 experts worked for 4-5 months for one Kanda.
Natural / human environment: In 2012, due to sufficient rains, 2 Kandas which did not have leakage problems in Sourakhak watershed got full with runoff water, which was then used for irrigating 6500 saplings seven times during the year. Kahmard district has a semi-arid cli-mate. Some years are dry with rainfall of about 190 mm. Considering this context, it becomes very necessary to tap rainwater, especially in the rainfed uplands, and use it for irrigating saplings or for livestock.
ສະຖານທີ່: Kahmard, Bamyan, ອັຟການີດສະຖານ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ:
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?:
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: ຫຼາຍກ່ອນ 50 ປີຜ່ານມາ (ແບບພື້ນບ້ານ)
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ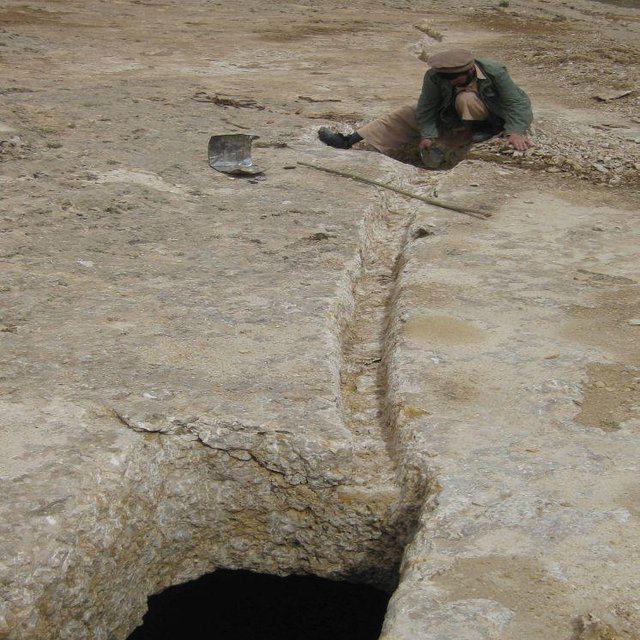




| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (USA) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (USA) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ແຮງງານ | |||||
| Labour | kanda | 1.0 | 5640.0 | 5640.0 | 15.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | |||||
| Equipement | kanda | 1.0 | 458.0 | 458.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | |||||
| Materials | kanda | 1.0 | 1065.0 | 1065.0 | 8.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 7'163.0 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 7'163.0 | ||||
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (USA) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (USA) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ແຮງງານ | |||||
| Cleaning of the canals and Kanda | persons/day/kanda | 2.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 10.0 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 10.0 | ||||
Increased availability of water for small scale irrigation such as trees, sapling and livestock and increase successful afforestation in dry land areas which in the longer term will lead to increased income, fuel wood and timber for land user and greener watersheds
due to water harvesting