



The Itaparica reservoir was completed in 1988 to generate hydropower. About 40'000 people were compulsorily relocated. The construction of the reservoir lead to a shortage of fish, making aquaculture a viavle and profitable alternative. However excess feed and excreta of fish add nutrients and pollute water.
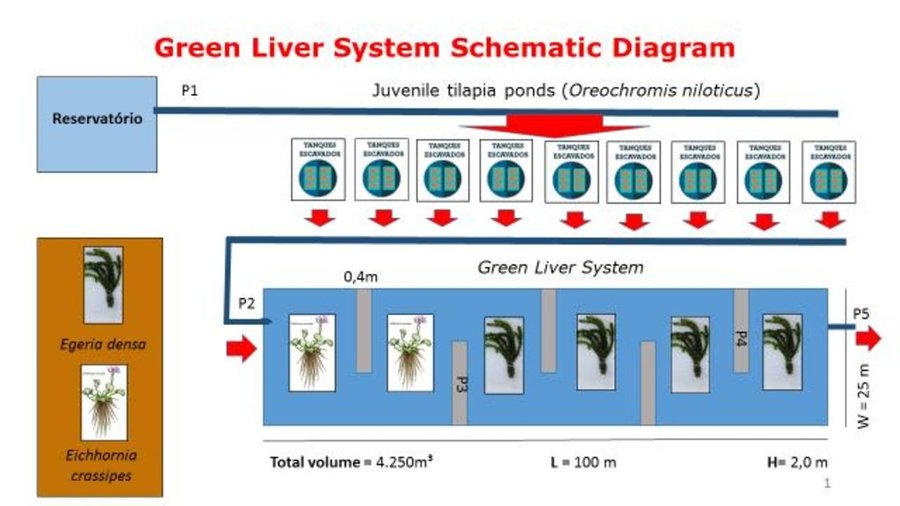
The “Green Liver System” uses aquatic plants, established in artificial wetlands, to remove, transfer, stabilize or eliminate pollutants in wastewater from fish farms. The use of large quantities of feed in aquaculture, along with the application of antibiotics, hormones and probiotics, has negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems due to the introduction of nitrogen, phosphorous and drug residues into the system. The Green Liver System is a form of phytoremediation (phyto = plant and remediate = correct) that uses a range of plants to decompose, extract, or hold contaminants present in soils and waters. This technology has been considered as an innovative alternative and a low cost option compared to others used in contaminated sites - like membrane bioreactors, upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB), and others.
The plants selected for use in Green Liver System artificial wetlands depend on the pollutant to be removed. Research shows physiological differences between species, which need to be taken into account when planning wastewater treatments. Ideal plants for phytoremediation need: a) a fast growth rate; b) high biomass production; c) long rooting systems; d) easy maintenance/pruning; e) to be able to persists, and f) to have the ability to store trace metals within specific parts which can be later removed.
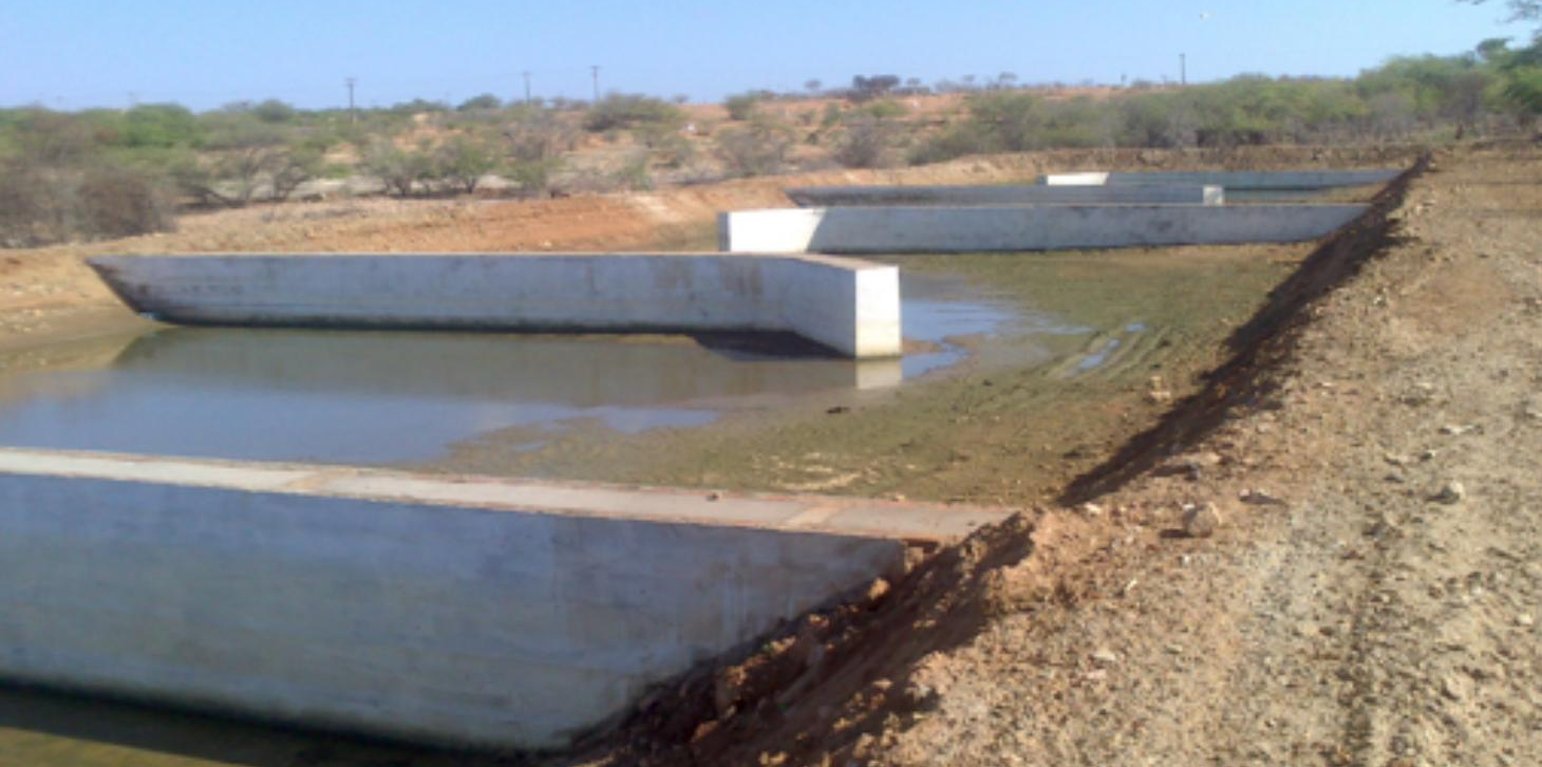
The Green Liver System uses aquatic macrophytes, which extract contaminants from the water, store them, or even metabolize them - transforming them into less toxic or harmless products. In the case of Eichhornia crassipes, most of the solids in suspension are removed by sedimentation or by adsorption in the root system. The dense coverage of these plants reduces the mixing effect of the wind, as well as minimizing thermal mixture. Shading by the plants restricts algal growth and the root system prevents horizontal movement of particulate material. In this way, particles are removed from the wastewater and microorganisms associated with the plants’ rhizosphere slowly decompose. Many organisms can be used in biodegradation: these include bacteria and fungi as well as plants, and the efficiency of one or the other depend, in many cases, on the molecule structure and of the presence of enzymes that are effective in degrading the pollutant.
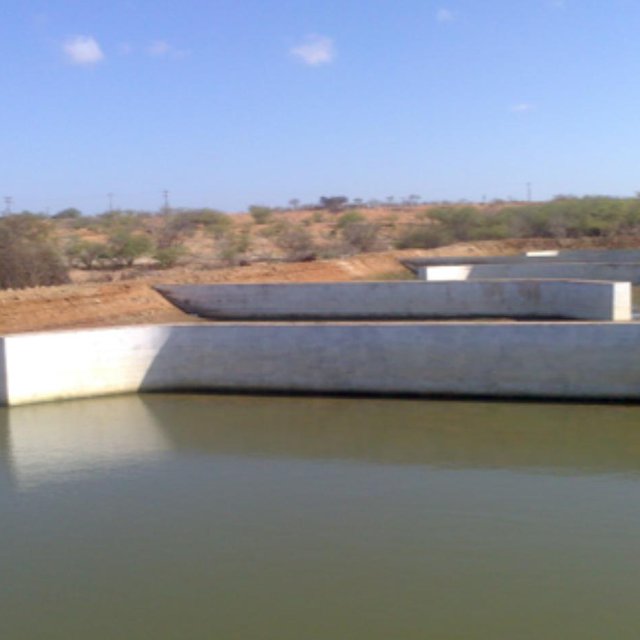
The fish farm used as an example here is located on the margins of the Itaparica reservoir in Brazil. There are dozens of excavated tanks used to produce tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and “tambaqui” (Colossoma macropomum) fingerlings and juvenile fish. As well as these tanks, there are many net enclosures installed in the reservoir where the fishes are reared to maturity. Part of the wastewater from the excavated tanks is released into a stabilization lagoon, and the remainder goes to the Green Liver System. The effluent is enriched with spare feed, and excreta from the fish, which includes drug residues. If not treated, this may cause eutrophication because of its mineral richness. The Green Liver System consists of an excavated tank of 100m x 20m x 2m in size. The tank is subdivided into six parts: two planted to Eichhornia crassipes and four to Egeria densa. A mesh barrier stops fish from being flushed into the tank. Regular monitoring of the physical, chemical and biological parameters is required to control environmental fluctuations.
ສະຖານທີ່: Vila do Coité, Itacuruba, Pernambuco, ບາຊິວ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ:
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?:
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ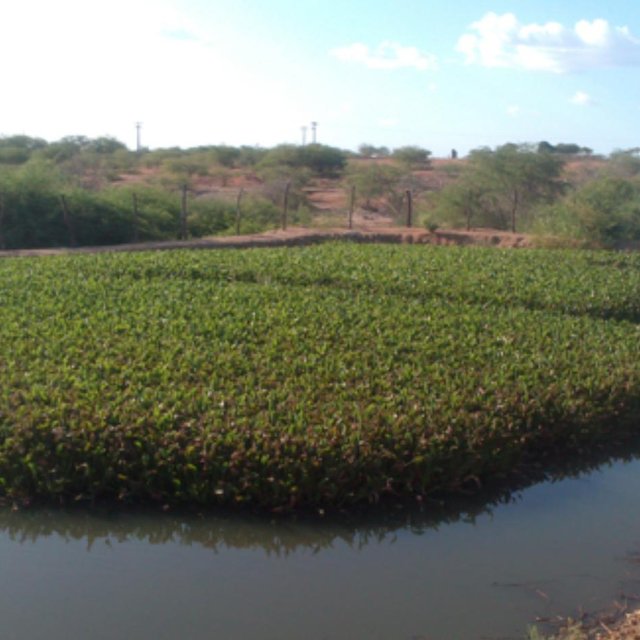






| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (USA) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (USA) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ແຮງງານ | |||||
| Construction | 1.0 | 5060.0 | 5060.0 | ||
| Supervision | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | ||
| ອຸປະກອນ | |||||
| Truck for removal of soil | 1.0 | 125.0 | 125.0 | ||
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | |||||
| Walls/baffles (cement) | 1.0 | 475.0 | 475.0 | ||
| Barbed wire | 1.0 | 315.0 | 315.0 | ||
| Earthwork | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | ||
| Tubular elements | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | ||
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 7'255.0 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 2'288.64 | ||||
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (USA) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (USA) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ແຮງງານ | |||||
| Labour | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | ||
| ອຸປະກອນ | |||||
| Nylon fabric | 1.0 | 38.41 | 38.41 | ||
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 3'038.41 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 958.49 | ||||
Biomass of macrophytes for potential ethanol production.
Increase of maintenance costs as manual labor is required for management of macrophytes.
Better water management in a setting of decreasing seasonal rainfall.
The technology contributed to improved water quality, which is directly related to people's health.
Any open water body is subjected to the very high potential evaporation in the region. Though, the surface of the system is very small as compared to the adjacent reservoir.
The vegetation had to be removed in order to construct the artificial wetland.
A nylon grid prevents the macrophytes from occasionally breaking loose into the reservoir.
The ecology of the system is sort of fragile. If the macrophytes float too much, the system can break down.
the technology contributed to improved water quality, which is directly related to people's health.