



The Rajshahi, Chapai Nawabganj and Naogaon regions of Bangladesh geographically belong to High Barind Tract (HBT) of Bangladesh under Agro Ecological Zone (AEZ) 26. This region is the hottest region of the country where water scarcity is a common problem. The annual precipitation is 1410 mm and the farmer is habituated to use deep tubewell underground water for their crops operated by Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA). Rice is the common crop in this region and in Boro season (from November to March) rice consumed the lion share of underground water through flood irrigation. And this flood irrigation system is very traditional cultivation method resulting the underground water table is consistently going down for heavy extraction by shallow or deep tube-well.
It is not always necessary to keep standing water in rice fields for its maximum production like aquatic plant. To address these problems ‘Alternate Wetting and Drying’ is a good choice, because it is not necessary to keep the water standing throughout the whole growing season of Boro rice (wet rice). In this method 20-25% less water is consumed, which may save approximately USD 30 per hectare.
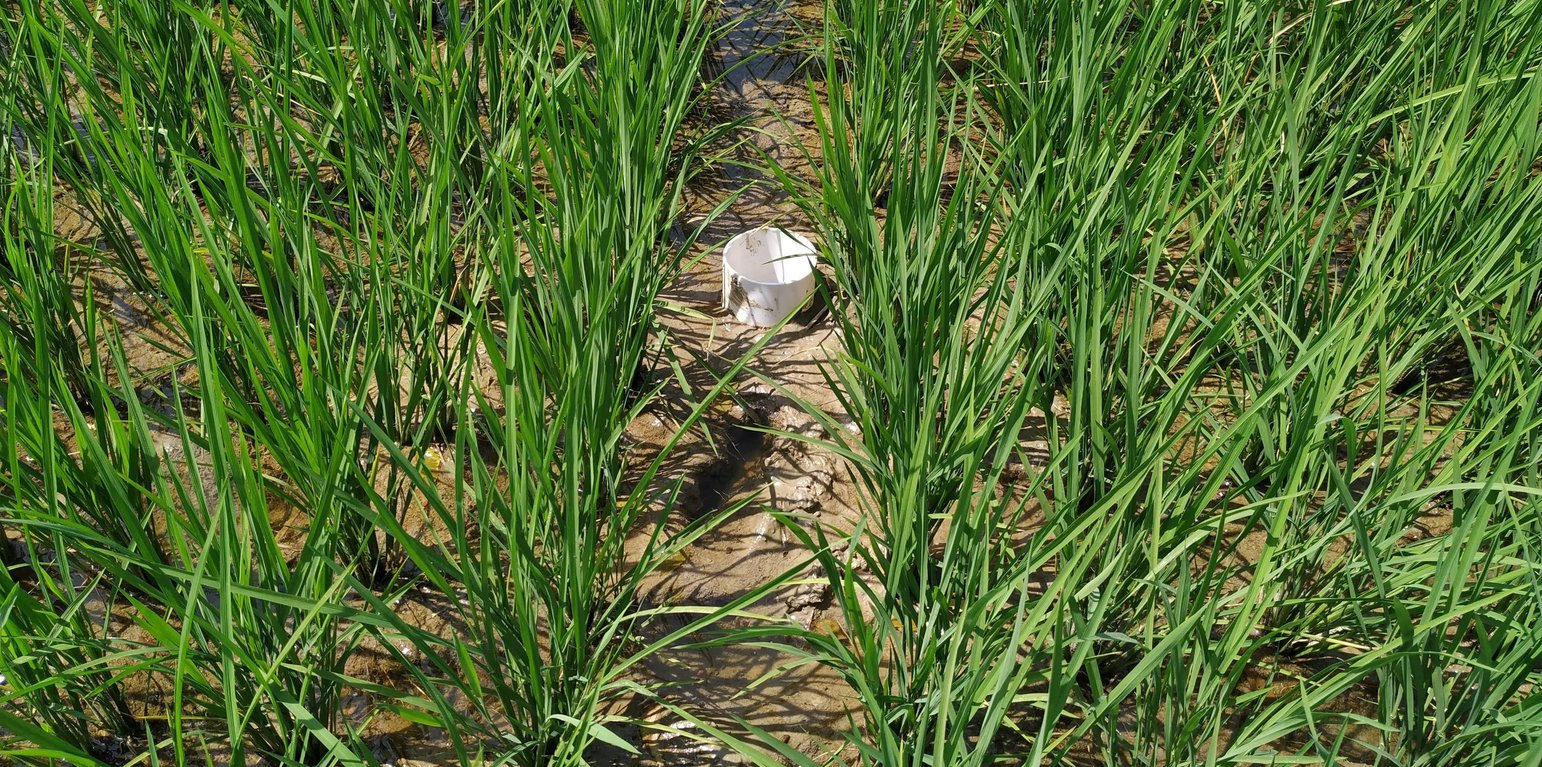
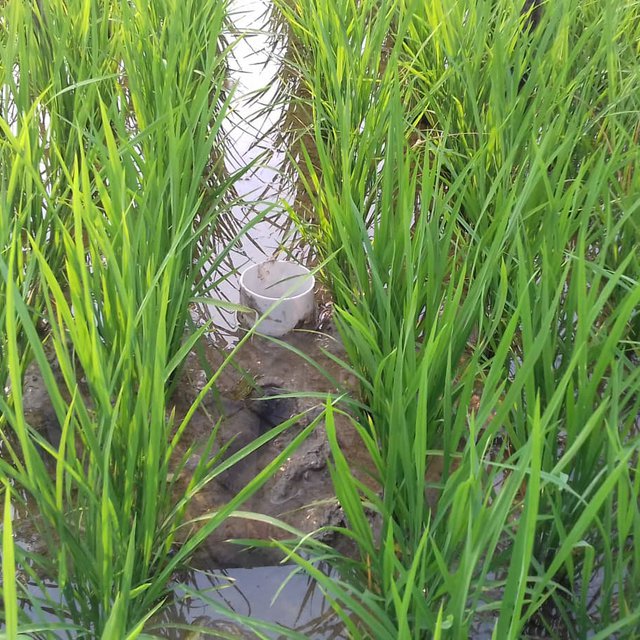
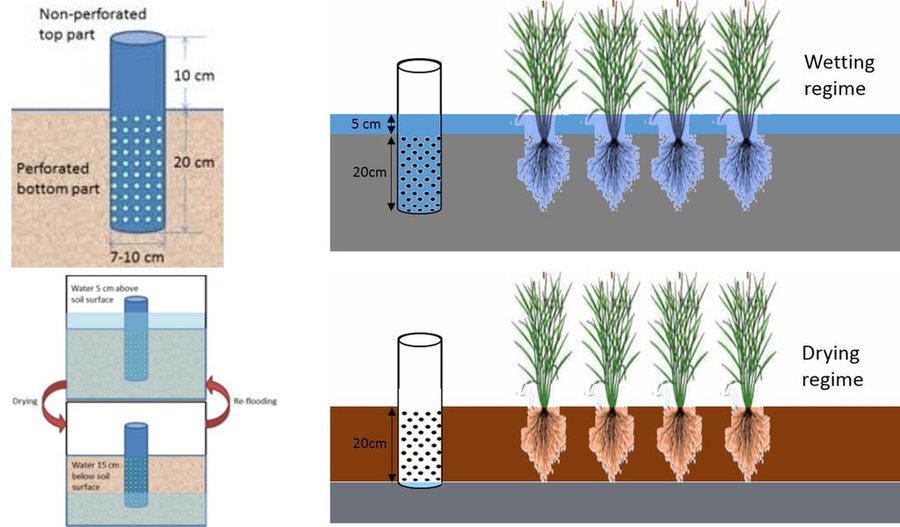
After 10-15 days of transplanting of rice seedling shallow standing water can be allowed and then the field can be drained and wetted alternately. To implement this method, first a perforated plastic pipe is installed to examine the water level and irrigate the rice field when necessary. The 25 cm long and 7-10 cm diameter perforated pipe is installed vertically. Only the lower 15 cm of the pipe should be perforated so that water can enter and exit, and then the pipe should be installed so that the non-perforated portion remains above the ground to protect it from debris.
In a leveled rice field of one hectare, seven to eight pipes are enough to monitor water depth. 10-15 days after seedling transplanting the AWD method can start. In each irrigation, the water level should reach 5-7 cm from the above the soil in wetting regime, and when the water level goes down to the soil level in drying regime, then the field can be irrigated again. This can continue until the panicle initiation stage. Then from panicle initiation to the milking stage, the field should be irrigated with 2-4 cm of water (also wetting regime). After the milking stage, the AWD can be continued until two weeks before harvesting from April to May (depending on rice variety).
Promotion of AWD in Bangladesh has been piloted and tested by different organisations like Bangladesh Rice Research Institute (BRRI), Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) and Department of Agricultural Extension (DAE) during 2008 to 2010. In HBT, the quantity of groundwater is continuously decreasing, so farmers applied AWD without installing the pipe. The farmers are experienced with this technology long-ago and know that the cracks appeared when the groundwater goes down to 18-20 cm below soil surface. When the farmers saw the "hair like crack" in their rice field, they irrigated. BMDA introduced the pre-paid card for irrigation, so the farmer irrigated his rice field several times when he saw the field cracks. The aim is to save money as well as to save groundwater.
ສະຖານທີ່: Amnura, Chapainawabganj, ບັງລາເດດ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ: 2-10 ພຶ້ນທີ່
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?: ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ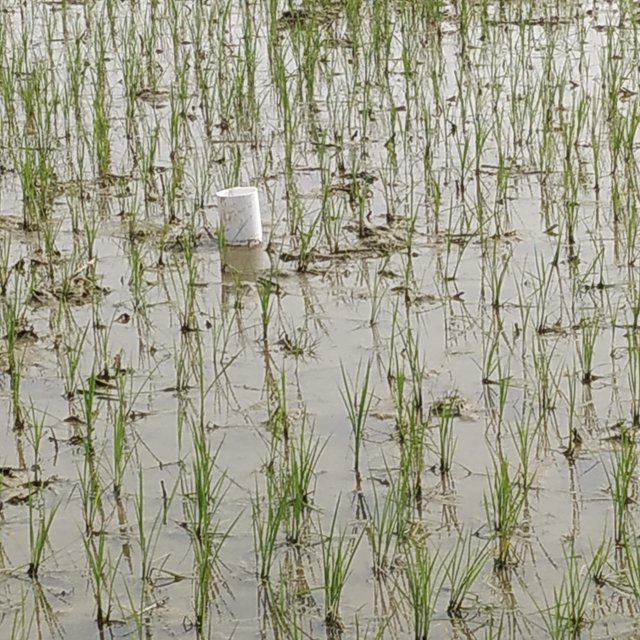






| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (USA) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (USA) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ແຮງງານ | |||||
| Labour for plastic tube installation | Person-day | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | |||||
| Plastic tube | Number | 20.0 | 0.64 | 12.8 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 17.8 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 17.8 | ||||
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (USA) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (USA) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ແຮງງານ | |||||
| Land preparation | Person-day | 6.0 | 5.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Seedling transplanting | Person-day | 37.0 | 5.0 | 185.0 | 100.0 |
| Herbicide and pesticide application | Person-day | 8.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| Irrigation | Person-day | 18.0 | 5.0 | 90.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | |||||
| Power tiller rent for plowing | Machine-hour | 16.0 | 2.0 | 32.0 | 100.0 |
| Sprayer | Machine-hour | 24.0 | 1.0 | 24.0 | 100.0 |
| Cost for irrigation | Machine-hour | 22.0 | 2.5 | 55.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | |||||
| Seed | kg | 15.0 | 1.3 | 19.5 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | |||||
| Chemical fertilizer | Kg | 70.0 | 0.35 | 24.5 | 100.0 |
| Manure | Kg | 1500.0 | 0.05 | 75.0 | 100.0 |
| Herbicide and pesticide | Kg | 18.0 | 2.4 | 43.2 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | |||||
| Labour for harvesting | Person-day | 24.0 | 5.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour for threshing | Person-day | 10.0 | 5.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour for drying | Person-day | 4.0 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour for repairing spray machine | Person-day | 2.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour for cleaning plastic tube | Person-day | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 823.2 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 823.2 | ||||
AWD increases the crop production (yield) than traditional method. So, more crop yield increases the socio-economic condition of farmer. Moreover, this method reduces the input cost for crop production.
AWD method decreases the production cost for irrigation. So, the land area under this method is increasing gradually.
The irrigation water and the drinking water come from same underground source by deep tube-well. So, when the water extraction is reduce for irrigation, the availability for drinking water is increase.
In dry regime of AWD method, the evaporation is decrease on land
Some plant nutrient like Zinc (Zn) is much available when the soil going from wet to dry regime. Constant wet condition inhibit some other plant nutrient also.