



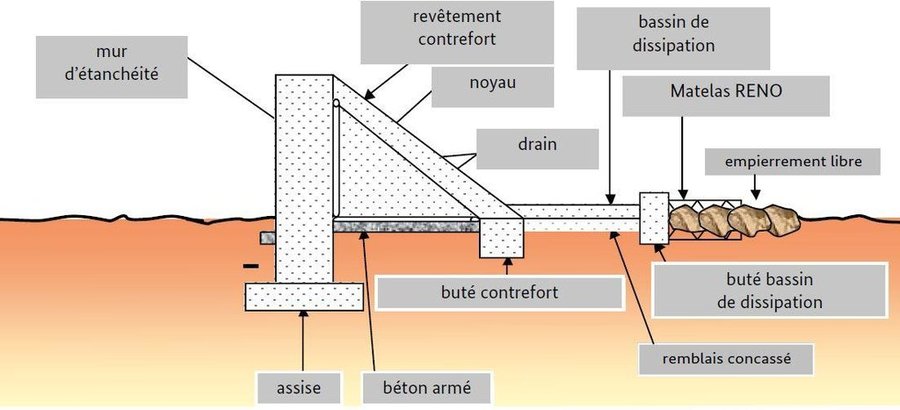
They can range in length from 100 to 200 m, and the dam wall is usually between 2 and 4 m high. Small-scale dams impound permanent or seasonal water behind them, covering areas from 5 to 15 hectares. They are built with buttresses and a stilling basin. Depending on local conditions, the dam wall can be made of quarry stone joined with mortar or concrete. The dikes are made of earth and can be reinforced with stones. Some such structures are built as bridge dams, providing a means of crossing the valley. The effect on the water table depends on the depth at which the dam is anchored. The deeper the foundation, the more groundwater is retained. Sometimes, they are fitted with geomembranes which extend down deeper to retain more groundwater.
In the rainy season, water gradually accumulates behind the dike, increasing the availability of surface water during the rainy season and groundwater in the dry season. The land is farmed upstream and downstream both in the rainy season and the dry season. During the rainy season, rice is grown, and the areas around the body of water are used for other crops (flood-recession cropping). Dams increase the area of farmable land, yields and production. The water is also used for livestock, for fish farming and sometimes for household needs. The recharged water table feeds market garden wells, enabling farmers to grow vegetables in the dry season and permitting two or three crop harvests a year which increases the availability of food, providing income for farmers and guaranteeing work all year round. This improves the stability of local communities, increases their income and raises their standard of living.
Sustainable operation and management depend directly on the participatory approach. At the planning stage, the condition of the valley upstream and downstream and all user groups must be taken into account. The question of land tenure, in particular, must be settled before construction begins. It must be determined who the owner of the bottomlands is, who will be entitled to use them once the dam has been constructed, what uses will be permitted and under what conditions. The question of project ownership and upkeep must also be clarified. Today, the role of project owner is normally assigned to the commune authorities, although management of the dam is often delegated to a management committee. In order to avoid conflicts, it is essential to take into account all the user groups, livestock keepers in particular. Watering corridors must be established to prevent animals from damaging the crops. In order to maximise the value of the investment, well-organised management committees must be set up to ensure efficient crop production and oversee maintenance work. A management committee controls the opening and closing of the gates. It organises the maintenance of the structure and the implementation of any additional measures necessary to protect the gabion structures and stone bunds. It also collects and manages funds for the maintenance of the dam and organises meetings of farmers. In dry periods, it is important to manage water resources in such a way that downstream areas have enough water. When a series of dams are built on the same watercourse, an inter-dam committee may be required to manage the distribution of water and avoid conflicts between the users of the different dams.
Well-constructed small-scale dams last at least 50 years with a certain amount of upkeep. A high standard of technical planning and construction is required for small-scale dams to avoid subsequent damage. Depending on the natural characteristics of the watershed, small-scale dams may require additional SWC/SPR measures upstream to protect them from siltation.
These small-scale dams are suitable for use in narrower valleys, as a considerable volume of water can be impounded with a relatively short structure. They are not as well suited to wide, gently sloping valleys, as very long dikes are required and this increases the cost.
ສະຖານທີ່: Mali, ມາລິ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ:
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່ (approx. 0.1-1 ກມ 2)
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?:
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: 10-50 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ






The water impounded by small-scale dams makes it possible to farm a much larger area in the valley bottoms and ensures better yields in the rainy season and also in the off-season. The production of food staples and market garden output increases significantly. More intense production ensures employment all year round, which improves the stability of local communities, increases their income and raises their standard of living.