Improved terraces
(ເນໂປ)
GARA SUDHAR- Nepali
ຄຳອະທິບາຍ
Hillside forward-sloping terracing and stabilisation using structural and vegetative measures
This technology addresses the soil erosion and water runoff problems associated with traditional outward-sloping terraces by reshaping the land into a series of level or gently sloping platforms across the slope. This technology is a variant of sloping land agricultural technology (SALT) or contour hedgerow technology. Nitrogen-fixing hedgerow species and quality fodder grass species, which bind the soil, are cultivated along terrace riser margins to improve terrace stability. This also enhances soil fertility and increases fodder availability. The plants are grown in either single or multiple layers. The practice is applied under rainfed conditions and is culturally acceptable and affordable. After establishment, the technology also addresses the problems of fodder scarcity making it easier and less time consuming for women and girls to gather fodder.
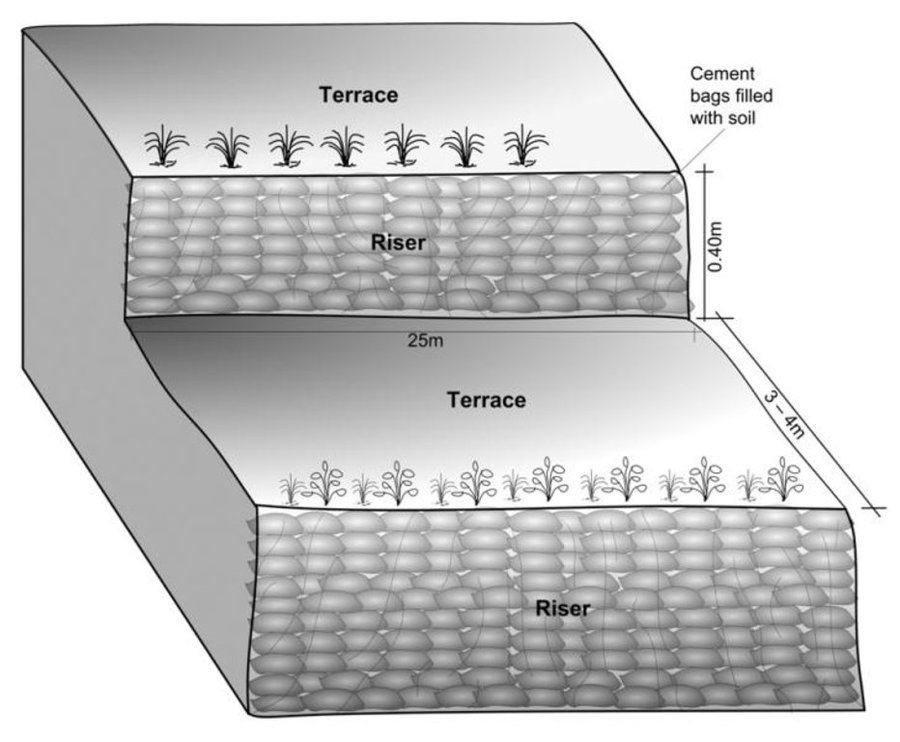
The hedgerow and grass species are established between January and June. Complete establishment of this technology may take one year. The first step in creating the terraces is to build retaining walls using cement bags filled with soil which are then supported with bamboo cuttings along the contour (= future terrace risers). This divides the land into the planned terrace sections. The length and width of the terraces depends on the size and shape of the original field. Secondly, the soil is excavated from the upper part of the terraces and is used to build up the lower part above and behind the terrace riser wall to create a level bed. The fertile top soil must be kept aside and later spread over the newly terraced fields. The final step is to plant grass and hedgerow species on the outermost margins of the terrace above the risers.
Maintenance involves slicing the terrace risers once or twice a year with a spade, and smoothing off rills that appear on the surface of terraces after the premonsoon and monsoon periods. Hedgerows should be cut regularly but not more than twice a year, normally to a height of about 50 cm. Grasses should be cut about once to twice a month depending on their rate of growth.
The technology is applied under humid subtropical climate conditions (1300 mm annual rainfall with about 80% of it falling in the monsoon months of June - September). The case study area has hill slopes of 16-30% that are mostly highly erodible red soils (FAO classification: luvisols).
ສະຖານທີ່
ສະຖານທີ່: Hokse VDC ward no2, ເນໂປ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ:
ການຄັດເລືອກພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ອີງໃສ່ຂໍ້ມູນທາງພູມີສາດ
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່ (0.0126 km²)
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?:
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: ຫຼາຍກ່ອນ 50 ປີຜ່ານມາ (ແບບພື້ນບ້ານ)
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ
-
ໂດຍຜ່ານນະວັດຕະກໍາຄິດຄົ້ນຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
-
ໃນໄລຍະການທົດລອງ / ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
-
ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຈຸດປະສົງຕົ້ນຕໍ
-
ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
-
ປົກປັກຮັກສານໍ້າ / ນໍ້າພື້ນທີ່ - ປະສົມປະສານກັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີອື່ນໆ
-
ປົກປັກຮັກສາ / ການປັບປຸງຊີວະນາໆພັນ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງ ທາງໄພພິບັດທໍາມະຊາດ
-
ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ກັບການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ ແລະ ຜົນກະທົບ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຜົນກະທົບ ຈາກການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ
-
ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
-
ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທີ່ເປັນທາງບວກ ໃຫ້ແກ່ສັງຄົມ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
-
ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ: ທັນຍາພືດ-ສາລີ, ພືດຕະກູນຖົ່ວ ແລະ ຖົ່ວປະເພດອື່ນໆ, ການປູກພືດໃຫ້ຮາກ / ຫົວ - ມັນຝລັ່ງ, wheat, chili, tomatoes
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ: 3
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ
-
ນໍ້າຝົນ
-
ປະສົມປະສານ ກັນລະຫວ່າງ ນໍ້າຝົນ ແລະ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
-
ນໍາໃຊ້ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ ພຽງຢ່າງດຽວ
ຈຸດປະສົງທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
-
ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ບໍ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທີ່ຕ້ອງໄດ້ເອົາໃຈໃສ່
-
ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ - Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ, Wg: ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຮ່ອງນ້ຳ / ຫ້ວຍ
-
ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງນໍ້າ - Ha: ສະພາບແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
ມາດຕະການ ຕັດຂວາງ ກັບຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ
-
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງນໍ້າ ແລະ ການລະບາຍ
ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ - V1: ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງໄມ້ພຸ່ມ
-
ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ - S1: ພັກຄັນໃດ
ເທັກນິກການແຕ້ມຮູບ
ຂໍກຳນົດທາງເທັກນິກ
Schematric view after intervention [terracing and vegetative measures]
Riser slope: 75 degree
Terrace slope: ~ 2 degree
Location: Kubinde
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase in soil fertility
Vegetative measure: on risers
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 2500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3 to 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Sunhemp(Crotalaria juncea),Tephrosia (Tephrosia candida) and Flemingia (Flemingia microphylla)
Grass species: Napier(Pennisetum purpureum),Molasses (Melinis minutiflora) and Stylo(Stylosanthes guianensis)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 5.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 75.00%
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3-4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10-15
Construction material (earth): Cement bag filled with soil, Bamboo nets were used to make risers.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 5%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Author: Madhav Dhakal, A. K. Thaku
ການຈັດຕັ້ງ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ: ກິດຈະກໍາ, ວັດຖຸດິບ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ການຄຳນວນ ປັດໃຈການຜະລິດ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
- ຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ: USA
- ອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນ (ເປັນເງີນ ໂດລາ): 1 USD = -1.0
- ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຂອງການຈ້າງແຮງງານຕໍ່ມື້: 1.40
ປັດໄຈທີ່ສໍາຄັນສຸດທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
In case of projects interested in promoting this technology in the region, the labour cost is the major expenditure in the initial stage.The labour charges are decided by the district soil conservation office.
ກິດຈະກໍາການສ້າງຕັ້ງ
-
Area estimation ( for vegetative measures) (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: before rainy seasonn/lean period (February))
-
Selection of fodder grass species (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: Before rainy season (Feb))
-
Planting of grasses and hedgerow species on the outward margins (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: During rainy season.)
-
Establishment of riser, using cement bags (filled with soil) and bamboo culms for terrace stabilisation (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: Beginning of rainy season(May))
-
Terrace leveling:The length and width of the terraces depends on the size and shape of the field. Excavate soil from the upper part of the terrace field and use it to build up the lower part behind the terrace riser wallt creat a level plateform/bed. (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: Beginning of rainy season(May))
ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ |
ຫົວໜ່ວຍ |
ປະລິມານ |
ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (USA) |
ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (USA) |
% ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
|
ແຮງງານ
|
| Labour |
ha |
1.0 |
970.0 |
970.0 |
50.0 |
|
ອຸປະກອນ
|
| Total costs |
ha |
1.0 |
92.0 |
92.0 |
100.0 |
|
ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ
|
| Seeds |
ha |
1.0 |
25.0 |
25.0 |
|
| Seedlings |
ha |
1.0 |
30.0 |
30.0 |
|
| Bamboo |
culms |
80.0 |
1.0 |
80.0 |
50.0 |
|
ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ
|
| Cement bags |
ha |
1.0 |
80.0 |
80.0 |
50.0 |
|
ອື່ນໆ
|
| Supervision charge |
ha |
1.0 |
10.5 |
10.5 |
|
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ |
1'287.5 |
|
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ |
-1'287.5 |
|
ກິດຈະກໍາບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ
-
Hedgerow/grass maintenance: Hedgerows are cut regularly but not (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: Grass is cut once or twice a month.)
-
(Re)plantation of hedge species if necessary (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: Before monsoon /1*/year)
-
Surface and riser maintenance: smooth the surface/rills on the (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: after pre monsoon and after monsoon/2 */ year ,Jun)
ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ |
ຫົວໜ່ວຍ |
ປະລິມານ |
ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (USA) |
ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (USA) |
% ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
|
ແຮງງານ
|
| Labour |
ha |
1.0 |
310.0 |
310.0 |
100.0 |
|
ອຸປະກອນ
|
| Tools total costs |
ha |
1.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
100.0 |
|
ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ
|
| Seeds |
ha |
1.0 |
6.0 |
6.0 |
100.0 |
| Seedlings |
ha |
1.0 |
6.0 |
6.0 |
100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ |
342.0 |
|
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ |
-342.0 |
|
ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ
ສະເລ່ຍປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
-
< 250 ມີລິແມັດ
-
251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
-
501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
-
751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
-
1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
> 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ເຂດກະສິກໍາ-ສະພາບອາກາດ
-
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
-
ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
-
ເຄິ່ງແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
-
ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ຂໍ້ມູນຈໍາເພາະກ່ຽວກັບສະພາບອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນສະເລ່ຍຕໍ່ປີເປັນມິລິແມັດ: 1304.0
Thermal climate class: subtropics
ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ
-
ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
-
ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
-
ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
-
ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
-
ເນີນ(16-30%)
-
ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
-
ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ
-
ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
-
ສັນພູ
-
ເປີ້ນພູ
-
ເນີນພູ
-
ຕີນພູ
-
ຮ່ອມພູ
ລະດັບຄວາມສູງ
-
0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
> 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້ໃນ
-
ລັກສະນະສວດ
-
ລັກສະນະກີ່ວ
-
ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຄວາມເລິກຂອງດິນ
-
ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
-
ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
-
ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
-
ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
-
ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ໂຄງສ້າງຂອງດິນ (ເທີງໜ້າດິນ)
-
ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
-
ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
-
ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ໂຄງສ້າງຂອງດິນ (ເລິກລົງ 20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
-
ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
-
ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
-
ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ທາດອິນຊີຢູ່ເທິງໜ້າດິນ
-
ສູງ (> 3 %)
-
ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
-
ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນ
-
ເທິງຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
-
< 5 ແມັດ
-
5-50 ແມັດ
-
> 50 ແມັດ
ມີນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
-
ເກີນ
-
ດີ
-
ປານກາງ
-
ທຸກຍາກ / ບໍ່ມີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ການຮັກສາ)
-
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
-
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
-
ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາພຽງຢ່າງດຽງ (ຊົນລະປະທານ)
-
ຜິດປົກກະຕິ
ຄຸນນະພາບນ້ຳ ໝາຍເຖີງ:
ດິນເຄັມເປັນບັນຫາບໍ່?
ການເກີດນໍ້າຖ້ວມ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການວາງແນວທາງຕະຫຼາດ
-
ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
-
ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
-
ການຄ້າ / ຕະຫຼາດ
ລາຍຮັບທີ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນໆ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
-
ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
-
10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
-
> 50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ
-
ທຸກຍາກຫຼາຍ
-
ທຸກຍາກ
-
ສະເລ່ຍ
-
ຮັ່ງມີ
-
ຮັ່ງມີຫຼາຍ
ລະດັບຂອງການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ
-
ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
-
ສັດລາກແກ່
-
ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເລລ້ອນ
-
ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
-
ແບບເຄີ່ງຂັງ-ເຄີ່ງປ່ອຍ
-
ແບບປ່ອຍຕາມທຳມະຊາດ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ
-
ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
-
ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
-
ການຮ່ວມມື
-
ການຈ້າງງານ (ບໍລິສັດ, ອົງການ ລັດຖະບານ)
ອາຍຸ
-
ເດັກນ້ອຍ
-
ຊາວໜຸ່ມ
-
ໄວກາງຄົນ
-
ຜູ້ສູງອາຍຸ
ເຂດພື້ນທີ່ການນໍາໃຊ້ຕໍ່ຄົວເຮືອນ
-
<0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
-
0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
-
1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
-
2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
-
5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
-
15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
-
50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
-
100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
-
500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
-
1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
-
> 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຂະໜາດ
-
ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
-
ຂະໜາດກາງ
-
ຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່
ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ
-
ລັດ
-
ບໍລິສັດ
-
ຊຸມຊົນ / ບ້ານ
-
ກຸ່ມ
-
ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
-
ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ເຊົ່າ
-
ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
-
ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ເຊົ່າ
-
ບຸກຄົນ
ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ຜົນກະທົບ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ເສດຖະກິດ
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
households of neighbouring village benefitted.
ເນື້ອທີ່ ການຜະລິດ (ທີ່ດິນໃໝ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ປູກພືດໃສ່ / ນໍາໃຊ້)
ຜົນກະທົບທາງສັງຄົມ ວັດທະນະທໍາ
ສະຖາບັນ ການຈັດຕັ້ງຊຸມຊົນ
terrace improvement group was formed
Livelihood and human well-being
Cropping pattern changed due to which, land users were able to produce more. Farm income and price of land increased.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
due to levelled surface and hedgerow barrier
Appearance of pests like rats due to introduction of planted
ຜົນກະທົບນອກສະຖານທີ່
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ (ທີ່ບໍ່ພຶງປາດຖະໜາ)
Bigger area needs swc measures
ການທັບຖົມ ຂອງດິນຕະກອນ ຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
Fodder grass seed distribution
through farmer to farmer dissemination
Nutrients downstream
due to reduced nutrients leaching on-site
ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການສ້າງຕັ້ງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ (ແມ່ນໍ້າ) ນໍ້າຖ້ວມ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ໄລຍະເວລາການຂະຫຍາຍຕົວຫຼຸດລົງ
ການຍອມຮັບ ແລະ ການປັບຕົວ
ອັດຕາສ່ວນຂອງຜູ້ຊົມໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບຮອງເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
-
ກໍລະນີດຽວ / ການທົດລອງ
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ມີໃຜແດ່ທີ່ສາມາດປັບຕົວຕໍ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນ?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
ຈໍານວນຄົວເຮືອນ ແລະ / ຫຼືບໍລິເວນກວມເອົາ
16 households in an area of 0.0126 sq km
ໄດ້ມີການດັດແປງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອປັບໃຫ້ເຂົ້າກັບເງື່ອນໄຂການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ່?
ໄດ້ປ່ຽນແປງເງື່ອນໄຂຫຍັງແດ່?
-
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ຮ້າຍແຮງ
-
ຕະຫຼາດມີການປ່ຽນແປງ
-
ມີແຮງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ເນື່ອງຈາກການເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍແຮງງານ)
ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ແລະ ບົດຮຽນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບ
ຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ: ທັດສະນະມູມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
The price of land increased considerably from NRs 30,000 in 2001 (for 1 ropani – 508.5 sq. m) to between NRs 100, 000 and NRs 150,000 per ropani after the technology was established
How can they be sustained / enhanced? The price would increase further if irrigation facilities were installed
-
Pedicels of Tephosia and Sunhemp can be used for firewood.
-
Instead of planting only maize a farmer started planting rice (primary crop) and cash crops like potato / tomato (secondary crops).
ຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ: ທັດສະນະມຸມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນເອງ
-
The area of levelled terraces nearly doubled in Kubinde village from 2001 to 2003, which is an indicator of increased awareness of the benefi ts of soil and water conservation.
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Experience sharing would help expand the area
under improved terraces.
-
Land productivity increased, maize, potato and bean production increased, vegetables and rice production started.
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Irrigation facility could increase the production capacity of the terraces.
-
Availability of grass/fodder (nitrogen fixing) increased.
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting horticultural
fruits could increase farm incomes and so it should be promoted and more nitrogen fi xing species (preferably local) should be tried out
ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ: ທັດສະນະມູມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນວິທີການແກ້ໄຂແນວໃດ
-
In the fi rst year of implementation, maize production was reduced due to soil amendment
a phenomenon which is likely to occur with new
terrace formation
ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ: ທັດສະນະມຸມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນເອງວິທີການແກ້ໄຂແນວໃດ
-
Presently the vegetative technology is confined to terrace margins
it should be extended to the risers also.
ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ
ການທົບທວນຄືນ
-
David Streiff
-
Alexandra Gavilano
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: June 7, 2011
ປັບປຸງລ່າສຸດ: Sept. 5, 2019
ບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ
-
Madhav Dhakal - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Roger White - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Bhubhan Shreshta - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Gopal Nakarmi - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Juerg Merz - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Smriti Shrestha - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Krishna.Raj Adhikari - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
P.B. Shah - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Sanjeev Bhuchar - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Bijendra K Singh - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Kalpana Thapa - ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
Gore Thapa - ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
Leela Thapa - ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
Indra Tamang - ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
Isabelle Providoli - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ການບັນຍາຍລາຍລະອຽດ ໃນຖານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງຂໍ້ມູນການຄຸ້ມຄອງການນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ເອກກະສານ ແມ່ນໄດ້ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກໂດຍ
ສະຖາບັນ
- District Soil Conservation Office (DSCO) - ເນໂປ
- ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - ເນໂປ
ໂຄງການ
- People and Resource Dynamics Project, Nepal (PARDYP)
ການອ້າງອີງທີ່ສໍາຄັນ
-
ICIMOD (2002) Hydro-meteorological Year Book of Jhikhu Khola Watershed. Kathmandu: ICIMOD: ICIMOD
-
Mathema, P.; Singh, B.K. (2003) Soil ErosionStudies in Nepal: Results and Implications. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management:
-
Mathema, P. (2003) Watershed Managementin South Asia. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management:










