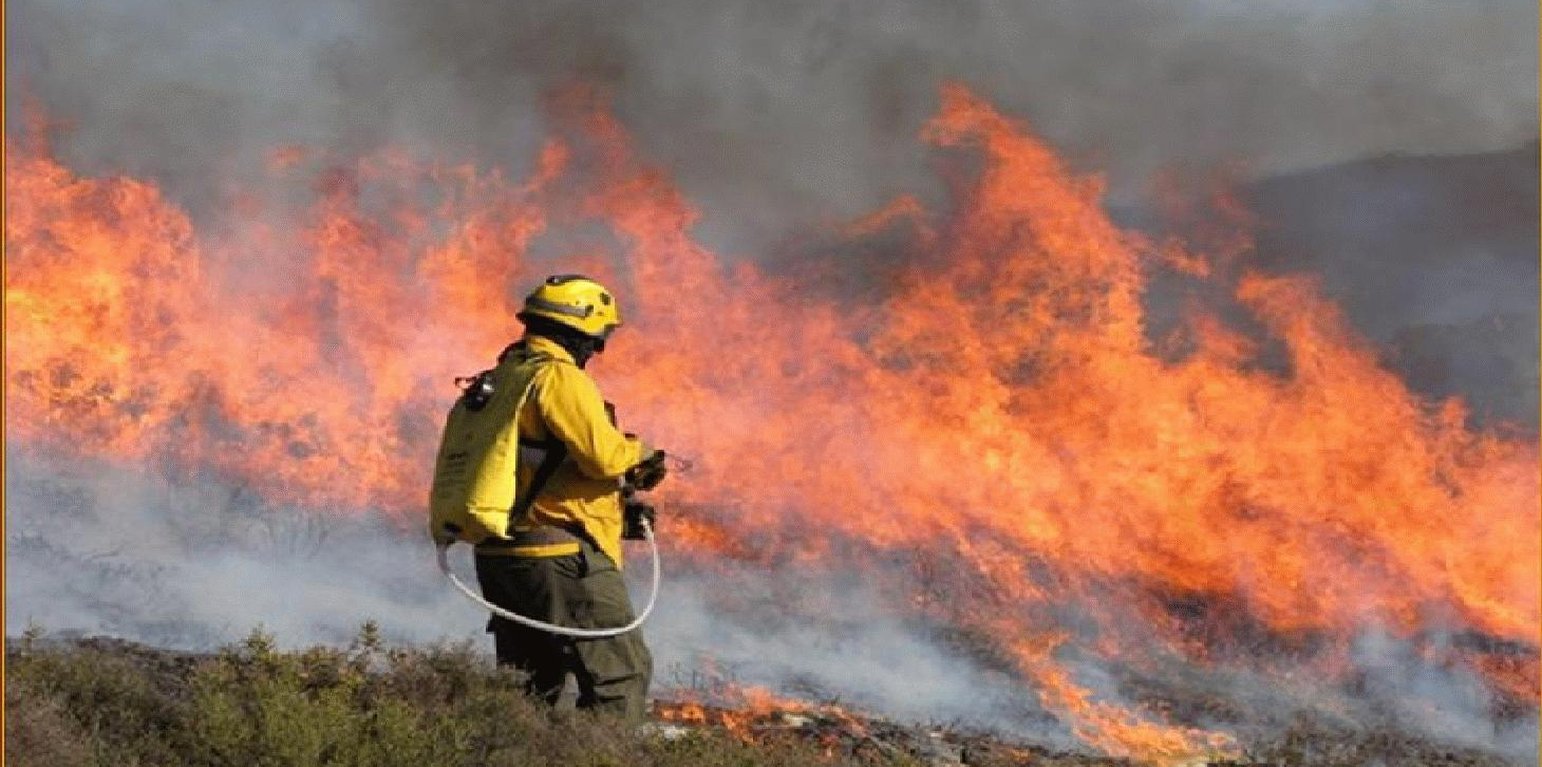




This technique is an essential management tool that applies fire to control the quantity of forest or scrubland fuels. The type of fire depends on the specific goals and on the weather conditions. Firstly, it is important to consider slope angle and the kind of fuels to be burned. Weather conditions include temperature, wind direction and air humidity. Another important aspect is the ability to control the speed of flame spread. In order to carry out the controlled fire, a plan has to be drawn up and approved and a fully-trained, authorised technician must be present in addition to the appropriate support teams (fire fighters, forest management teams). These teams use water or other means of combating the fire in the event of it possibly getting out of control and are in charge of the burning process.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purposes are enhancement of grazing areas and the creation of the so-called primary network for wildfire defence, which is a national network to limit the spread of wildfire. It involves strategically burning key sites (e.g. mountain ridges) to restrict the spread of the wildfire.
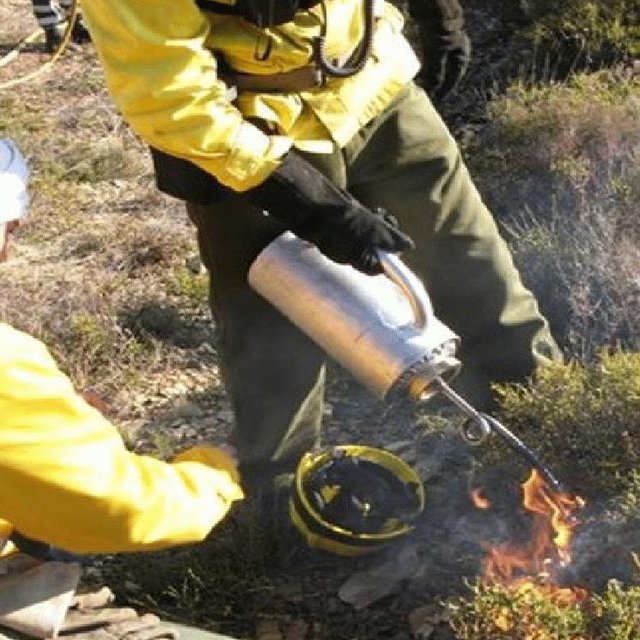
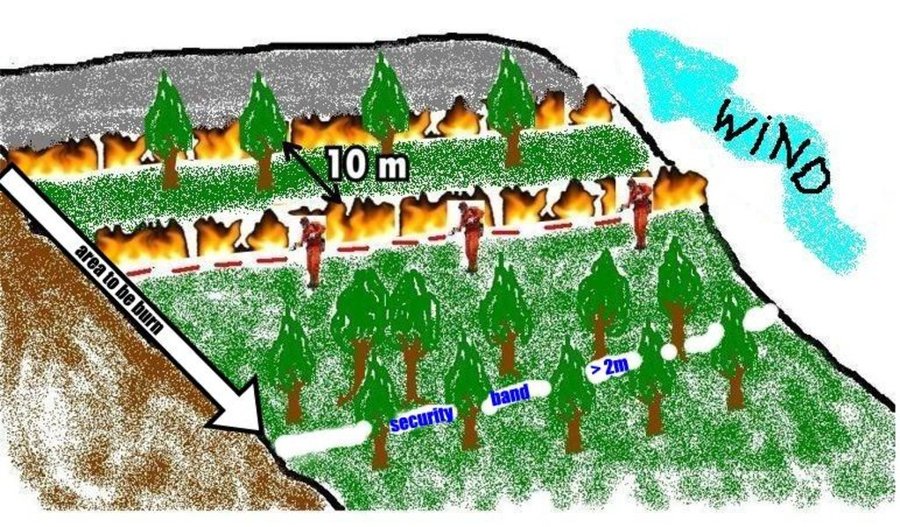
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: An analysis of weather conditions is made prior to carry out the prescribed fire. On the day of the prescribed fire itself, safety checks are made and the specific tasks of all the team members are defined. Wind direction and strength need to be minimal and are strictly controlled during burning. The size of the team depends on the specific problems of the area to be treated. Team size needed for about 10 ha is around 10 persons. The team members start along a line working from the top on the mountain along the contour and move downwards. Gentle breeze should be against the direction of the spreading of the fire. Workers use a drip-feed fuel can. There is also a strategy for prescribed fires by burning a strip along ridges of the mountains to avoid spreading of accidental wildfires and to burn in catchments the lowest point from which fire can spread to different areas and spread in different directions on the slopes.
Natural / human environment: Improved grazing management might also reduce the fuel load. Abandoning grazing in the forest can increase the fuel load and aggravate the occurrence and impact of wildfires. The creation or maintenance of grazing areas is determined by the size of the herd. Prescribed fire used as a means of improving grazing enables the local population needs to be addressed while considering environmental concerns. The prescribed fire also helps to protect the local population and their property by reducing the likelihood of devastating wildfire.
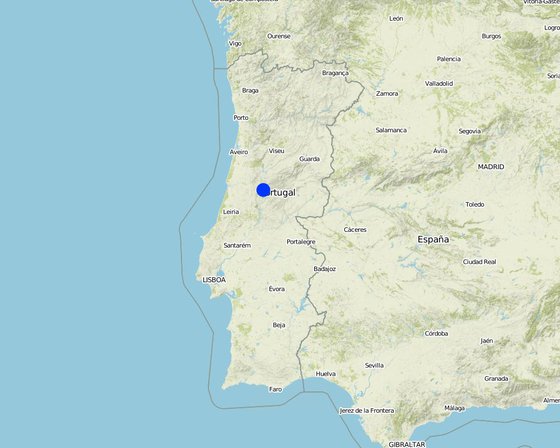
ສະຖານທີ່: Leiria, Castanheira de Pêra, ປໍຕູໂກລ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ:
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່ (0.57 km²)
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?:
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: ຫຼາຍກ່ອນ 50 ປີຜ່ານມາ (ແບບພື້ນບ້ານ)
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ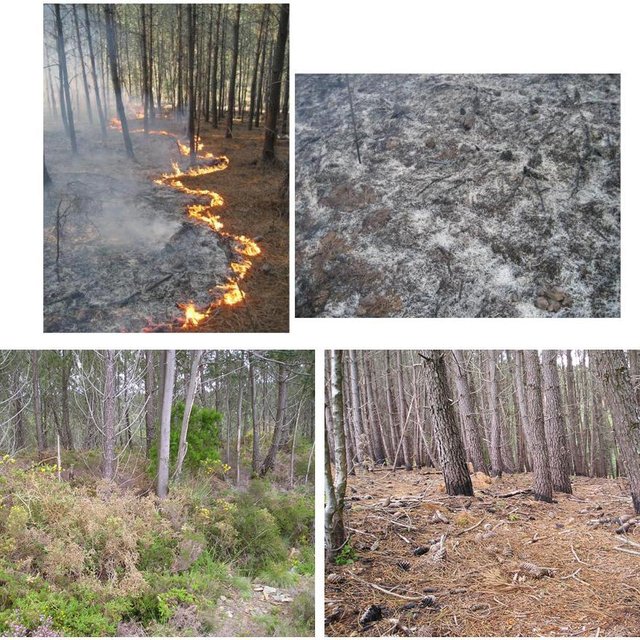





| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (EURO) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (EURO) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ແຮງງານ | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| ອຸປະກອນ | |||||
| Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 50.0 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 0.37 | ||||
Under investigation.
There are not direct improves on livelihoods, they are the results of the prevention of forest fires.
if decreased: Resulting from rainfall infiltration that will carry out pollutants and contaminate water recharge.
Avoid extreme/catastrophic events of hot fires