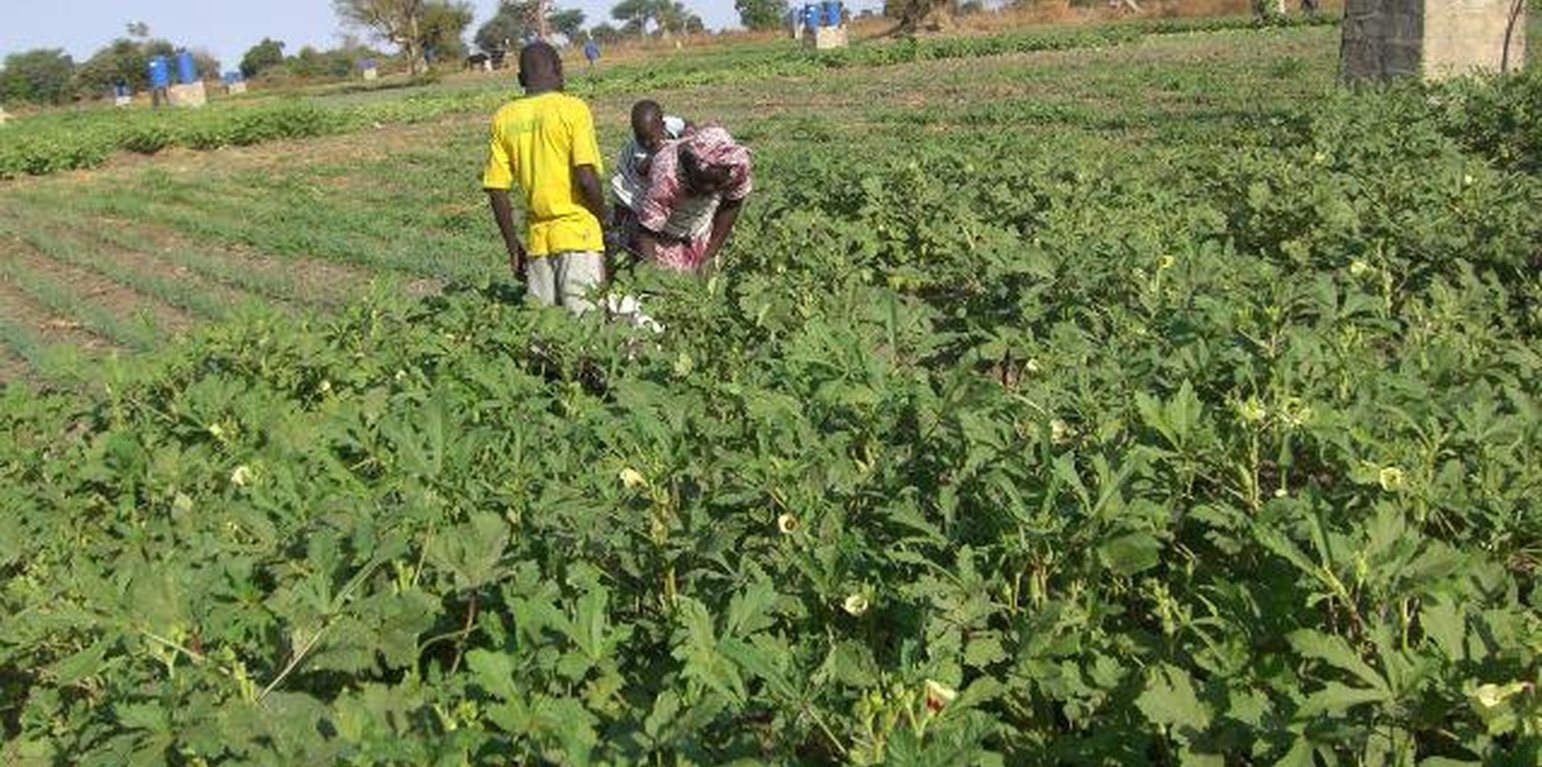




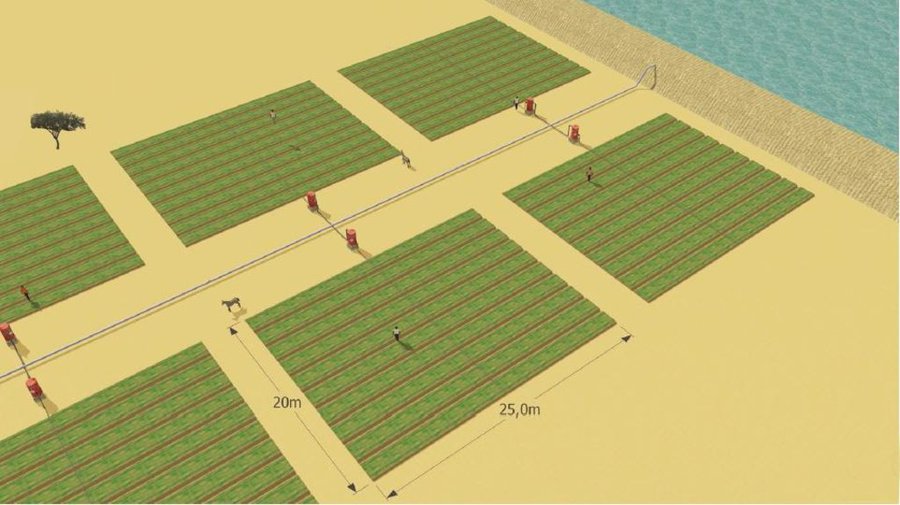
According to the level of experience, market orientation or social structure of the land users, four different AMG models have been developed. This case study focuses on the “Cluster System” which is suitable for an organized group of independent vegetable producers sharing a common water delivery system. From a central source, water is distributed through a pipe network to a cluster of plots. Each farmer operates a 1,000 m2 unit, and each is equipped with an elevated 200 litre barrel and a standard irrigation kit, including a tap, filter and thick-tube drip laterals. Minimal size of an AMG unit should be 500 m2. Affordable high-quality material is used and the design and operation is simple. The barrel also serves as a fertilizer tank. A float ensures a constant pressure head. Water supply is calculated by the time needed for delivery of the daily water dosage, or through the use of water dosing valves. Producers have individual control of water use. Since the AMG requires only 1 meter pressure for operation, it can draw on low-capacity renewable energy sources such as elevated dams, solar pumps or reservoirs. To supply an area of 50,000 m2 with 8 mm/day in the hot season a 400 m3-reservoir is required. The crops are planted on elevated beds. Water mixed with urea as fertilizer is applied daily. Drip irrigation improves growing conditions for crops while at the same time saving labor, water and other inputs. AMG is promoted as a holistic management package, integrating all aspects of production, post-harvest and marketing in one system. This includes the use of improved vegetable varieties, improved crop husbandry, integrated pest management, as well as improved storage, processing and marketing of products, and improved access to inputs.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The following establishment activities are connected to this technology: 1. Build concrete reservoir. 2. Drill borehole (110 mm diameter; 12 m deep, hand drilled). 3. Install motor pump and tubes to connect well with reservoir. 4. Install drip kit with tap, filter and drip laterals (8-16 mm in diameter). 5. Establish a fence to protect the garden.
For maintenance the following activities are required: 1. Prepare elevated beds with a basic dressing of 4 kg/m2 manure and 0.1 kg/m2 NPK fertilizer biannually. 2.Add urea to irrigation water (concentration: 50-100 ppm N). 3. Operate water supply system.
Natural / human environment: AMG is spreading fast in Senegal and Burkina Faso. Up-scaling of AMG in dry West Africa will depend on access to technology, inputs, knowledge and organization, and a conducive institutional environment.
ສະຖານທີ່: Ngoyé Ndioffogor and Mbassis Tadadem, ຊີນີໂກ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ:
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?:
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ




| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (n.a.) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (n.a.) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ອຸປະກອນ | |||||
| Tools | Unit | 1.0 | 65.0 | 65.0 | |
| Drip system | Unit | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | |
| Oil drum | Unit | 1.0 | 56.0 | 56.0 | |
| Well/borehole | Unit | 1.0 | 16.0 | 16.0 | |
| Motor pump | Unit | 1.0 | 34.0 | 34.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | |||||
| Fence | Unit | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| PVC connections | Unit | 1.0 | 79.0 | 79.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 575.0 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 575.0 | ||||
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (n.a.) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (n.a.) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ແຮງງານ | |||||
| Labour | Unit | 1.0 | 510.0 | 510.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 510.0 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 510.0 | ||||
Effective application of fertilizer with the water
Due to doubled profits from vegetable production (compared to traditional irrigation methods)
Reduced workload: total workload for AMG is 11.5 man-days compared to 30 man-days in traditional irrigation system (allows people to engage in other activities or education)
Costs for drip irrigated gardens are 50% lower than for traditional irrigated gardens due to savings in labour, water and consequently in fuel
Improved organisation (farmer associations, user groups)
Improved knowledge on irrigation techniques /horticulture
Water availability / reduced pressure on water resources
Effective use of water due to accurate and equal distribution of water at optimal rates