Thermo insulation of walls with use of foil to decrease burden on firewood use
(ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ)
Гарминигохдории хонахо ба максади кам гардинаи истифодабарии хезум барои гарм кардани хона
ຄຳອະທິບາຍ
This technology is designed for the high altitude mountains areas, where biomass and growing trees are limited, first because of the harsh climatic conditions and secondly because of the limited arable lands for growing biomass and forests. Thermo insulation is applied in order to keep warmth inside and save using wood and biomass.
The technology is applied in the mountainous rural areas of Tajikistan, in Rasht, Khatlon and GBAO. In this mountain regions wood and biomass are usually limited because of the harsh climate, risky agricultural zone and limited arable land. In the first decade of the transition period after the collapse of the Soviet Union problems with electricity and therfore the demand for fuel and wood increased. This caused a lot of forest degradation, because people were cutting trees from government owned and community areas for their fuel needs and used animal manure for heating their houses and cooking food. The technology is specifically designed to use low cost materials so that rural households can afford it. The technology consists of material like foil and wood to build frames for some layers to keep in the heat. Depending on the altitude, which is linked to the climate condition, the number of layers is increased where the climate is cold. The layer in between contains air, which prevents outside and inside air to move out/in. The technology was intended for saving up to 30% fuel. The technology includes support of entrepreneurs to make foil available in the market and provides training for local masters and labourers in designing and constructing of the technology. The main benefit is to contribute to biomass savings and forest preservation through reduced use of wood for heating and cooking. Land users are in favour because through this technology they are using less wood and save forest. They also burn less manure and can use it as fertilizers for their land. The technology brings comfort for longer periods of time by keeping heat inside the room. In addition it contribute also to hygine and sanitation, as less fire making prevents smoke emission and therefore keeps the rooms clean. On first sight the technology seems expensive, becasue of the material costs but in the long run when the cost effectiveness is explained land users accepted it.
ສະຖານທີ່
ສະຖານທີ່: Khorog city, GBAO, ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ: 100-1000 ພຶ້ນທີ່
ການຄັດເລືອກພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ອີງໃສ່ຂໍ້ມູນທາງພູມີສາດ
-
71.667, 37.53314
-
71.71871, 37.56897
-
71.7551, 37.61268
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?:
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ
-
ໂດຍຜ່ານນະວັດຕະກໍາຄິດຄົ້ນຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
-
ໃນໄລຍະການທົດລອງ / ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
-
ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
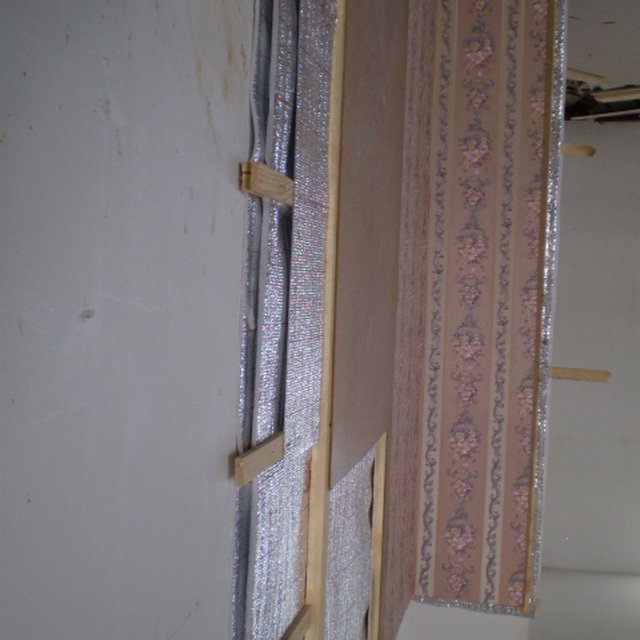

Thermo insulation of room by using foil (Zevarshoev Askarsho)
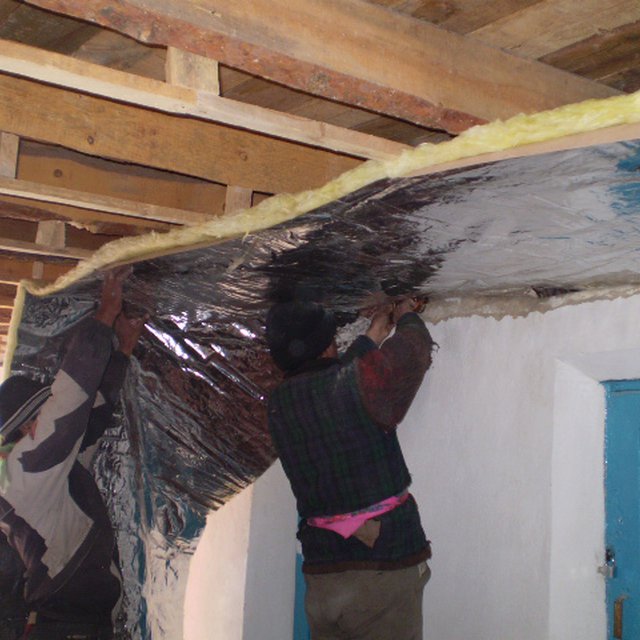

Training for local masters on thermo-insulation of ceiling (Khujamyor Khumorikov)
ຈຸດປະສົງຕົ້ນຕໍ
-
ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
-
ປົກປັກຮັກສານໍ້າ / ນໍ້າພື້ນທີ່ - ປະສົມປະສານກັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີອື່ນໆ
-
ປົກປັກຮັກສາ / ການປັບປຸງຊີວະນາໆພັນ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງ ທາງໄພພິບັດທໍາມະຊາດ
-
ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ກັບການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ ແລະ ຜົນກະທົບ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຜົນກະທົບ ຈາກການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ
-
ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
-
ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທີ່ເປັນທາງບວກ ໃຫ້ແກ່ສັງຄົມ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
-
ປ່າໄມ້ / ປ່າ
- (ເຄິ່ງ) ປ່າໄມ້ທໍາມະຊາດ / ປ່າປູກໄມ້. ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ: ການຄັດເລືອກຕັດ
- ການປູກຕົ້ນໄມ້, ການປູກປ່າ. ແນວພັນ: ແນວພັນປະສົມ
ຜົນຜະລິດ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ: ໄມ້ຟືນ
-
ການຕັ້ງຖິ່ນຖານ, ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ - ການຕັ້ງຖິ່ນຖານ, ອາຄານ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ
-
ນໍ້າຝົນ
-
ປະສົມປະສານ ກັນລະຫວ່າງ ນໍ້າຝົນ ແລະ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
-
ນໍາໃຊ້ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ ພຽງຢ່າງດຽວ
ຈຸດປະສົງທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
-
ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ບໍ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທີ່ຕ້ອງໄດ້ເອົາໃຈໃສ່
-
ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍລົມ - ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
-
ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ - Pc: ການອັດແໜ້ນ
ກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ປ່າໄມ້ ທຳມະຊາດ ແລະ ເຄີ່ງທຳມະຊາດ
-
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງການປູກປ່າ
-
ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ - S10: ມາດຕະການ ປະຢັດພະລັງງານ
-
ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ - M1: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ປະເພດ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, M2: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ / ລະດັບຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ
ເທັກນິກການແຕ້ມຮູບ
ຂໍກຳນົດທາງເທັກນິກ
A wooden frames is installed on the wall to cover the whole area. Foil will be stretched and will be fixed on the wooden frame on the wall. Based on the need number of layers is selected, which depend on the min/max outside temperature. If required according to the climate and wether of the area and based on altitude another frame from wood will be constructed on the foil and then again another layer of foil will be fixed. The scheme show the frame on the wall with thermo-insulation materials attached to it. The distance between two part of the foil should be an average 2-3sm.
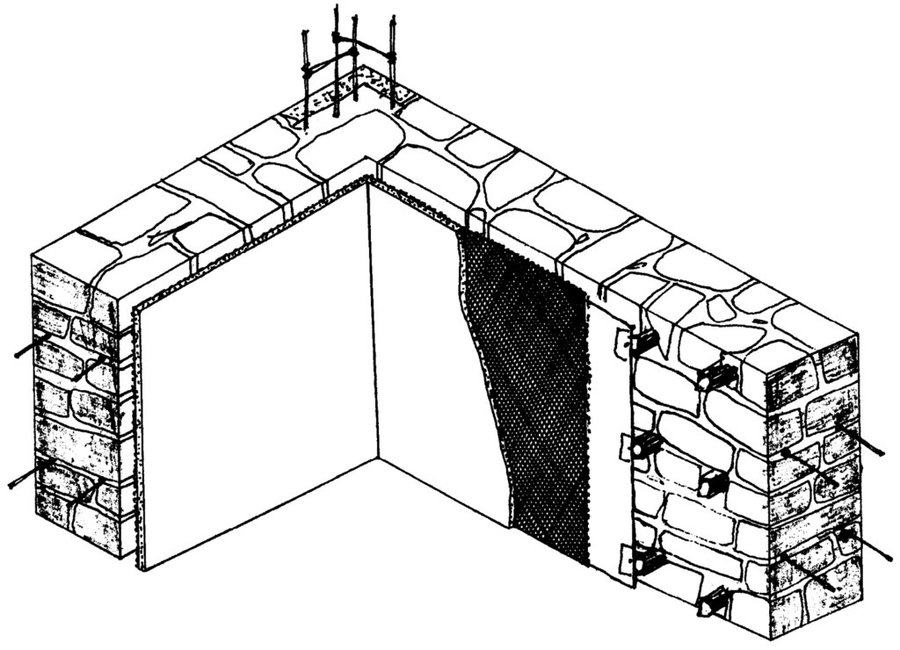
Author: Khujamyor Khumorikov
ການຈັດຕັ້ງ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ: ກິດຈະກໍາ, ວັດຖຸດິບ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ການຄຳນວນ ປັດໃຈການຜະລິດ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
- ຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ: ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂອງພື້ນທີ່:1 square meter cost 75)
- ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ: USA
- ອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນ (ເປັນເງີນ ໂດລາ): 1 USD = ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນ
- ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຂອງການຈ້າງແຮງງານຕໍ່ມື້: per sequare meter around 2.5 USD
ປັດໄຈທີ່ສໍາຄັນສຸດທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
the cost for the constuction materials in the beginning, because as new technology was introduced foil, as the main product for the technology was difficult to find in the market, which is now commonly sold
ກິດຈະກໍາການສ້າງຕັ້ງ
-
Installing of the wood frame (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: 1 day)
-
attaching/fixing the foil with nail on the wooden frame (add frame and foil layer per need) (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: 1 day)
-
Cover the structure with clay (mixture of soil and water) as construction material (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: 2-4 days)
ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ (per 1 square meter cost 75)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ |
ຫົວໜ່ວຍ |
ປະລິມານ |
ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (USA) |
ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (USA) |
% ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
|
ແຮງງານ
|
| Local master |
person |
1.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
30.0 |
|
ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ
|
| wood |
pe sq meter |
0.5 |
100.0 |
50.0 |
|
| nail |
piece |
20.0 |
0.1 |
2.0 |
|
| foil |
squire meter |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
|
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ |
55.0 |
|
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ |
55.0 |
|
ກິດຈະກໍາບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ
n.a.
ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ
ສະເລ່ຍປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
-
< 250 ມີລິແມັດ
-
251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
-
501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
-
751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
-
1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
> 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ເຂດກະສິກໍາ-ສະພາບອາກາດ
-
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
-
ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
-
ເຄິ່ງແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
-
ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ຂໍ້ມູນຈໍາເພາະກ່ຽວກັບສະພາບອາກາດ
The technology is applied in high mountain regions of Tajikistan, which are arid and semi-arid zones where some area have less than 100 mm rainfall and in some could be 200-300
ຊື່ຂອງສະຖານີອຸຕຸນິຍົມ: Regional meteorological station GBAO
the whole area of Tajikistan, where the technology is applied is classified as arid or semi-arid agro-climatic zone
ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ
-
ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
-
ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
-
ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
-
ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
-
ເນີນ(16-30%)
-
ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
-
ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ
-
ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
-
ສັນພູ
-
ເປີ້ນພູ
-
ເນີນພູ
-
ຕີນພູ
-
ຮ່ອມພູ
ລະດັບຄວາມສູງ
-
0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
> 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້ໃນ
-
ລັກສະນະສວດ
-
ລັກສະນະກີ່ວ
-
ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຄວາມເລິກຂອງດິນ
-
ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
-
ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
-
ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
-
ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
-
ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ໂຄງສ້າງຂອງດິນ (ເທີງໜ້າດິນ)
-
ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
-
ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
-
ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ໂຄງສ້າງຂອງດິນ (ເລິກລົງ 20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
-
ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
-
ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
-
ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ທາດອິນຊີຢູ່ເທິງໜ້າດິນ
-
ສູງ (> 3 %)
-
ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
-
ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນ
-
ເທິງຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
-
< 5 ແມັດ
-
5-50 ແມັດ
-
> 50 ແມັດ
ມີນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
-
ເກີນ
-
ດີ
-
ປານກາງ
-
ທຸກຍາກ / ບໍ່ມີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ການຮັກສາ)
-
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
-
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
-
ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາພຽງຢ່າງດຽງ (ຊົນລະປະທານ)
-
ຜິດປົກກະຕິ
ຄຸນນະພາບນ້ຳ ໝາຍເຖີງ:
ດິນເຄັມເປັນບັນຫາບໍ່?
ການເກີດນໍ້າຖ້ວມ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການວາງແນວທາງຕະຫຼາດ
-
ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
-
ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
-
ການຄ້າ / ຕະຫຼາດ
ລາຍຮັບທີ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນໆ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
-
ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
-
10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
-
> 50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ
-
ທຸກຍາກຫຼາຍ
-
ທຸກຍາກ
-
ສະເລ່ຍ
-
ຮັ່ງມີ
-
ຮັ່ງມີຫຼາຍ
ລະດັບຂອງການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ
-
ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
-
ສັດລາກແກ່
-
ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເລລ້ອນ
-
ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
-
ແບບເຄີ່ງຂັງ-ເຄີ່ງປ່ອຍ
-
ແບບປ່ອຍຕາມທຳມະຊາດ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ
-
ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
-
ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
-
ການຮ່ວມມື
-
ການຈ້າງງານ (ບໍລິສັດ, ອົງການ ລັດຖະບານ)
ອາຍຸ
-
ເດັກນ້ອຍ
-
ຊາວໜຸ່ມ
-
ໄວກາງຄົນ
-
ຜູ້ສູງອາຍຸ
ເຂດພື້ນທີ່ການນໍາໃຊ້ຕໍ່ຄົວເຮືອນ
-
<0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
-
0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
-
1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
-
2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
-
5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
-
15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
-
50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
-
100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
-
500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
-
1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
-
> 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຂະໜາດ
-
ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
-
ຂະໜາດກາງ
-
ຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່
ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ
-
ລັດ
-
ບໍລິສັດ
-
ຊຸມຊົນ / ບ້ານ
-
ກຸ່ມ
-
ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
-
ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ເຊົ່າ
-
ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
-
ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ເຊົ່າ
-
ບຸກຄົນ
ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ)
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ
ຜົນກະທົບ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ເສດຖະກິດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
After applying the technology it contributed to 30% of firewood saving, which cost money for the households and community before.
ຜົນກະທົບທາງສັງຄົມ ວັດທະນະທໍາ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
contributes to saving local trees, which are very few growing in the arid areas
ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຂອງດິນ / ຊາກສະລະຫະພັງ
after not cutting the trees and reforestation of degraded area, especially in the slope area contributed to land slide prevention
ຜົນກະທົບນອກສະຖານທີ່
ຄວາມເສຍຫາຍ ກ່ຽວກັບພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ ສາທາລະນະ / ເອກກະຊົນ
one contributing to disaster prevention, like landslide and mudflow also prevents damage to houses and public infrastructure
ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການສ້າງຕັ້ງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການຍອມຮັບ ແລະ ການປັບຕົວ
ອັດຕາສ່ວນຂອງຜູ້ຊົມໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບຮອງເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
-
ກໍລະນີດຽວ / ການທົດລອງ
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ມີໃຜແດ່ທີ່ສາມາດປັບຕົວຕໍ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນ?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
ໄດ້ມີການດັດແປງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອປັບໃຫ້ເຂົ້າກັບເງື່ອນໄຂການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ່?
ໄດ້ປ່ຽນແປງເງື່ອນໄຂຫຍັງແດ່?
-
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ຮ້າຍແຮງ
-
ຕະຫຼາດມີການປ່ຽນແປງ
-
ມີແຮງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ເນື່ອງຈາກການເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍແຮງງານ)
ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ແລະ ບົດຮຽນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບ
ຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ: ທັດສະນະມູມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
One time investment contributes to long term effects in saving forest and biodiversity, provides comfort without additional cost using for collection/buying firewood.
ຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ: ທັດສະນະມຸມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນເອງ
-
The technology contributes to habitat improvement at all, besides conservation of natural resources it also has social effects in terms of reduced smoke emissions as a result of less firewood making, comfortable condition during harsh winter weather.
ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ: ທັດສະນະມູມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນວິທີການແກ້ໄຂແນວໃດ
-
In the short term a big investment is required.
Funding mechanisms should be improved to provide access for farmers/rural population to invest in such technology. Some of the incentive mechanisms should be worked out for replicating the mechanism.
-
Specialized master skills are required to implement the technology.
More capacity building for existing local farmers should be organized at the local level for long term sustainability.
ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ: ທັດສະນະມຸມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນເອງວິທີການແກ້ໄຂແນວໃດ
-
By implementing one or two demonstrations at the household level the effect for the purpose of replication and dissemination is very low.
Demonstrations should be applied in public places like school or hospitals so everybody can have access and see the impact.
ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ
ການທົບທວນຄືນ
-
Yacime Khadraoui
-
Maximilian Knoll
-
Alexandra Gavilano
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: March 25, 2018
ປັບປຸງລ່າສຸດ: Aug. 6, 2019
ບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ
-
Askarsho Zevarshoev - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ການບັນຍາຍລາຍລະອຽດ ໃນຖານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງຂໍ້ມູນການຄຸ້ມຄອງການນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ເອກກະສານ ແມ່ນໄດ້ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກໂດຍ
ການອ້າງອີງທີ່ສໍາຄັນ
-
Wall Insulation Techniques for Buildings in High Mountain Areas: from SLM specialist, free of cost
|













