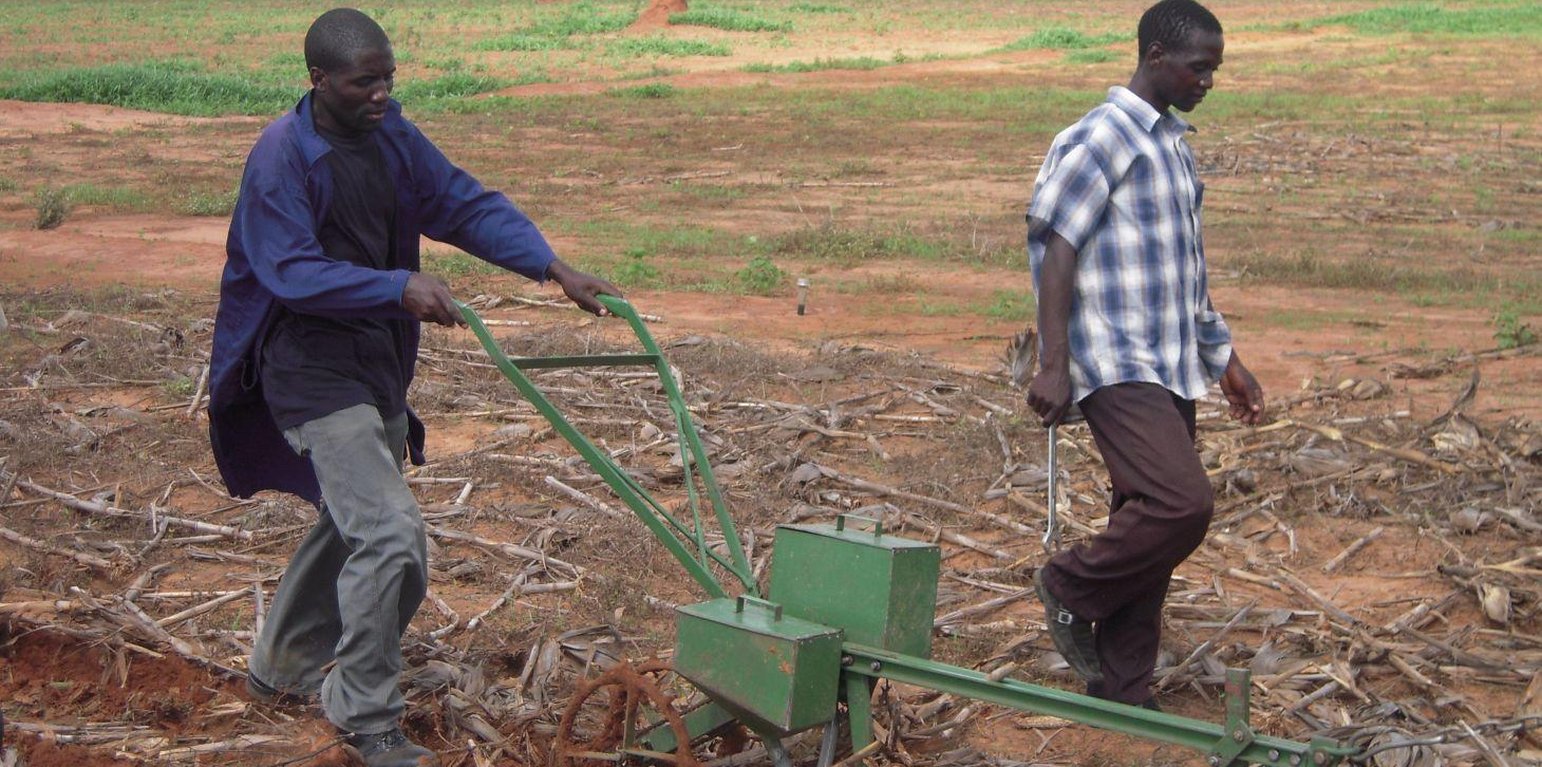
Animal Draft Zero-Tillage
(ແຊມເບຍ)
Direct Planting
ຄຳອະທິບາຍ
Animal draft zero-till involves the use of an animal drawn mechanical planter to plant directly in untilled soil to minimize soil disturbance and leave a cover of crop residues to conserve the soil and water.
Zero-tillage takes advantage of the beneficial effects of biological processes to loosen the soil and to improve fertility. The organic matter from these processes aggregate the soil while the movement of soil organisms like worms and termites loosen the soil. This is called biological tillage and replaces mechanical tillage. The untilled soil surface covered by residues will require a planter specialized to plant in these conditions. In a sense, adopting zero-till does actually require a zero-till planter. The development of the strip-planter has made zero-till a viable option for animal draft farmers, which until now was not possible due to the unavailability or high cost of zero-till planters. The new planter is both cheap and easy to manufacture locally. The planter uses a narrow tine to open a planting furrow and seed/fertilizer is metered by vertically rotating plates. The planter is pulled by oxen and can plant rows of 75cm or 90cm rows with an intra-row which is determined by the seed plate used (3, 4, 5,…… seeds/m). The planting technology needs to be complemented with sound residue cover and weeding management practices.
Purpose of the Technology: The planter enables planting and fertilizing in untilled soil so that the soil residue cover and soil structure are preserved and can be used sustainably. The protective soil cover reduces evaporation and enhances infiltration while the improved soil structure and organic matter content increases soil water storage making zero tillage an important drought mitigating strategy. The immediate benefits of adopting zero-till are the possibility to plant a bigger area quickly and in time as well as the reduced soil erosion.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The first step in establishing zero-till is to assess the soil condition and levels of degradation. Where possible tests should be carried out but where not, the farmer needs to start on a small plot to check if there will be yield reduction from not tilling the soil. Where soils are severely degraded, an establishment phase should be embarked on where reduced tillage is practiced until the soil structure has recovered sufficiently to support crop growth without tillage. Liming acidic soils followed by a final ploughing will be required in the first year to correct the soil pH which otherwise will be difficult to correct once conservation tillage has been established. The organic matter levels need to be increased by increasing the amount of residues produced by the crop (i.e. the yields) and retaining these as soil cover. The next establishment activity is the purchase of the planter unit. Maintenance activities include planting and fertilizing in the same operation and weeding. Weeding will have to involve herbicide use to handle increased weed densities implying that spraying will become a major operation. In addition to the normal conventional inputs, herbicides will also become a major input and cost.
Natural / human environment: Zero-till has been applied in a wide range of bio-physical environments but mostly by the large scale farmers. The unavailability and high cost of specialized zero-till planter for small-scale farming has resulted in low adoption rates. The development of the Magoye Planter creates new opportunities for this practice. The farmer has to have sufficient knowledge to assess the soil condition and decide if is too degraded for zero-till or how long the transitional phase should be. Literacy is essential as the farmers will have to learn new approaches on weed control, pest control and crop rotations and adapt practices to suit his/her specific conditions.
ສະຖານທີ່
ສະຖານທີ່: Mazabuka/Magoye, Zambia/Southern Province, ແຊມເບຍ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ:
ການຄັດເລືອກພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ອີງໃສ່ຂໍ້ມູນທາງພູມີສາດ
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?:
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ
-
ໂດຍຜ່ານນະວັດຕະກໍາຄິດຄົ້ນຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
-
ໃນໄລຍະການທົດລອງ / ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
-
ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
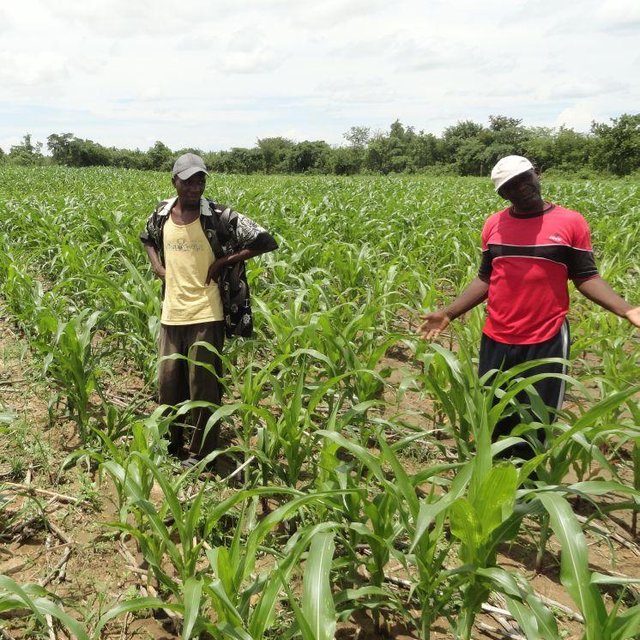

A farmer in his field planted with the Magoye CA planter (Arthur Chomba (Box 670577, Mazabuka Zambia))
ຈຸດປະສົງຕົ້ນຕໍ
-
ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
-
ປົກປັກຮັກສານໍ້າ / ນໍ້າພື້ນທີ່ - ປະສົມປະສານກັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີອື່ນໆ
-
ປົກປັກຮັກສາ / ການປັບປຸງຊີວະນາໆພັນ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງ ທາງໄພພິບັດທໍາມະຊາດ
-
ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ກັບການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ ແລະ ຜົນກະທົບ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຜົນກະທົບ ຈາກການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ
-
ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
-
ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທີ່ເປັນທາງບວກ ໃຫ້ແກ່ສັງຄົມ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
-
ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ: ທັນຍາພືດ-ສາລີ, Annual cropping is the main source of livelihood.
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ: 1
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ
-
ນໍ້າຝົນ
-
ປະສົມປະສານ ກັນລະຫວ່າງ ນໍ້າຝົນ ແລະ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
-
ນໍາໃຊ້ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ ພຽງຢ່າງດຽວ
ຈຸດປະສົງທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
-
ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
-
ບໍ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທີ່ຕ້ອງໄດ້ເອົາໃຈໃສ່
-
ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ - Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ
-
ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ - Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)
-
ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ - Pk: ການບັນເທົາ ແລະ ການປົກຄຸມຂອງເປືອກໂລກ
-
ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ - Bl: ການສູນເສຍ ຈຸລິນຊີໃນດິນ
ກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ - A1: ພືດ / ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງດິນ, A2: ອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ຫຼື ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນໃນດິນ , A3: ການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ (A 3.1: ບໍ່ມີການໄຖ), A4: ການບໍາລຸງ ປົກປັກຮັກສາ ຊັ້ນຮອງໜ້າດິນ , A5: ການຈັດການ ແລະ ການປັບປຸງແກ່ນເມັດພັນ ແລະ ແນວພັນ, A6: ການຈັດການສິ່ງເສດເຫຼືອ, A7: ອື່ນໆ
ເທັກນິກການແຕ້ມຮູບ
ຂໍກຳນົດທາງເທັກນິກ
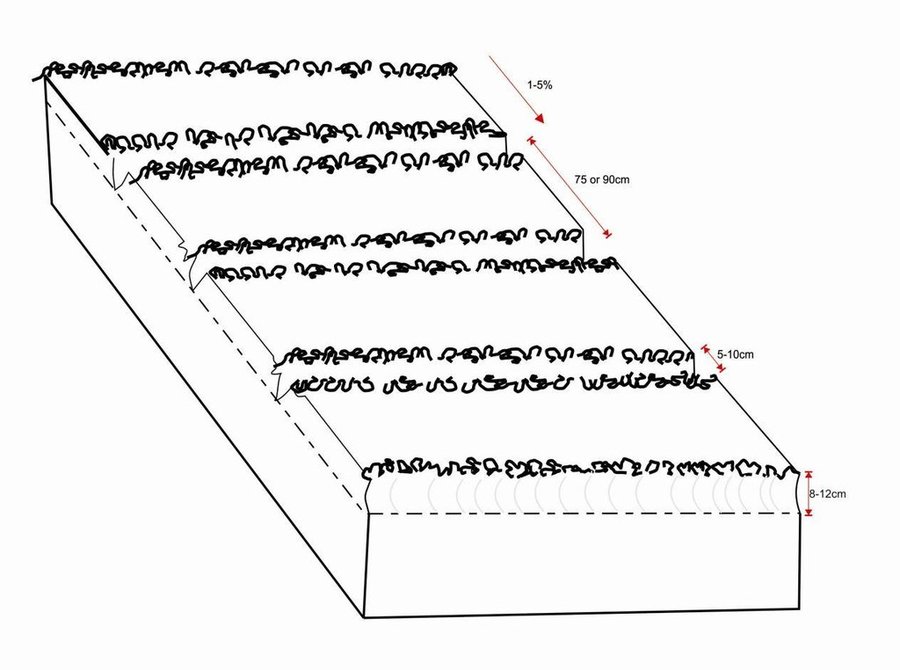
Planting lines are done at a depth of 8-12cm with inter row of 75 or 90cm. The width of the open furrow is 5-10cm wide. Planting rows are done across the slope to reduce runoff, these planting rows are done when the soil is moist during the rainy season and planting is done at the same time with land preparation. Farmers in Monze have combined ripping and zero till together. In the dry season they rip with the Magoye Ripper or GART Planter and later when the soil is moist use a zero till implement to plant.
Location: Magoye. Mazabuka/Southern Province/Zambia
Date: 2014-06-29
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (This is a new technology and the extension staff must be able to help farmers troubleshoot and adapt the technology to local conditions.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (The farmers have to adopt new soil management practices, crop rotations and adapt the weeding approaches to complement the planting technology)
Main technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Early planting
Material/ species: maize
Quantity/ density: 44,000 pla
Remarks: 25cm intra row by 75cm
Mulching
Material/ species: crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: uniformly spread
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: uniformly spread
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: basal and top dressing
Quantity/ density: 400kg/ha
Remarks: spot application
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: lime
Quantity/ density: 1ton/ha
Remarks: broadcast
Author: Silenga Wamunyima, Box 670577, Mazabuka, Zambia
ການຈັດຕັ້ງ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ: ກິດຈະກໍາ, ວັດຖຸດິບ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ການຄຳນວນ ປັດໃຈການຜະລິດ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
- ຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ: Kwacha
- ອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນ (ເປັນເງີນ ໂດລາ): 1 USD = 5.0 Kwacha
- ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຂອງການຈ້າງແຮງງານຕໍ່ມື້: 2.40
ປັດໄຈທີ່ສໍາຄັນສຸດທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
The weed control method is the main determinate factor depending on whether the farmer uses hand hoe or herbicides. Weed densities are higher in unploughed fields increasing the labour requirements/costs by a factor of about 5 if hand weeding is used instead of herbicides. Another major cost is that of fertilizer which makes up about half the cost hence the total cost will vary significantly depending on fertilizer cost.
ກິດຈະກໍາການສ້າງຕັ້ງ
-
Purchase a magoye planter (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: None)
-
Purchase a knapsack sprayer (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: None)
ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ |
ຫົວໜ່ວຍ |
ປະລິມານ |
ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (Kwacha) |
ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (Kwacha) |
% ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
|
ອຸປະກອນ
|
| Magoye Planter |
piece |
1.0 |
500.0 |
500.0 |
100.0 |
| Knapsack sprayer |
piece |
1.0 |
80.0 |
80.0 |
100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ |
580.0 |
|
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ |
116.0 |
|
ກິດຈະກໍາບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ
-
Slashing, spreading residues (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: May-June every year after harvest)
-
Liming (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: Nov - Dec every 3years)
-
Planting and fertilizing (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: Nov-Dec at onset of rain)
-
Chemical weeding (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: 3 times per growing season)
-
Harvesting (ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່: May-June)
ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ |
ຫົວໜ່ວຍ |
ປະລິມານ |
ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (Kwacha) |
ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (Kwacha) |
% ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
|
ແຮງງານ
|
| Slashing, spreading residues |
person days |
8.0 |
2.5 |
20.0 |
100.0 |
| Liming |
person days |
2.0 |
2.5 |
5.0 |
100.0 |
| Chemical weeding |
person days |
24.0 |
1.0 |
24.0 |
100.0 |
| Harvesting |
person days |
8.0 |
2.5 |
20.0 |
100.0 |
|
ອຸປະກອນ
|
| Animal traction for planting and fertilizing |
ha |
1.0 |
40.0 |
40.0 |
100.0 |
|
ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ
|
| Seeds |
kg |
20.0 |
2.5 |
50.0 |
100.0 |
| Fertilizer |
kg |
400.0 |
0.8 |
320.0 |
100.0 |
| Herbicides |
l |
5.0 |
6.0 |
30.0 |
100.0 |
| Lime |
ton |
1.0 |
42.0 |
42.0 |
100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ |
551.0 |
|
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ |
110.2 |
|
ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ
ສະເລ່ຍປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
-
< 250 ມີລິແມັດ
-
251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
-
501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
-
751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
-
1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
-
> 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ເຂດກະສິກໍາ-ສະພາບອາກາດ
-
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
-
ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
-
ເຄິ່ງແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
-
ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ຂໍ້ມູນຈໍາເພາະກ່ຽວກັບສະພາບອາກາດ
Thermal climate class: subtropics. 3 distinct seasons – summer, winter and one rainy season
ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ
-
ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
-
ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
-
ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
-
ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
-
ເນີນ(16-30%)
-
ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
-
ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ
-
ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
-
ສັນພູ
-
ເປີ້ນພູ
-
ເນີນພູ
-
ຕີນພູ
-
ຮ່ອມພູ
ລະດັບຄວາມສູງ
-
0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
-
> 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້ໃນ
-
ລັກສະນະສວດ
-
ລັກສະນະກີ່ວ
-
ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຄວາມເລິກຂອງດິນ
-
ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
-
ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
-
ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
-
ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
-
ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ໂຄງສ້າງຂອງດິນ (ເທີງໜ້າດິນ)
-
ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
-
ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
-
ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ໂຄງສ້າງຂອງດິນ (ເລິກລົງ 20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
-
ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
-
ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
-
ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ທາດອິນຊີຢູ່ເທິງໜ້າດິນ
-
ສູງ (> 3 %)
-
ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
-
ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນ
-
ເທິງຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
-
< 5 ແມັດ
-
5-50 ແມັດ
-
> 50 ແມັດ
ມີນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
-
ເກີນ
-
ດີ
-
ປານກາງ
-
ທຸກຍາກ / ບໍ່ມີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ການຮັກສາ)
-
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
-
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
-
ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາພຽງຢ່າງດຽງ (ຊົນລະປະທານ)
-
ຜິດປົກກະຕິ
ຄຸນນະພາບນ້ຳ ໝາຍເຖີງ:
ດິນເຄັມເປັນບັນຫາບໍ່?
ການເກີດນໍ້າຖ້ວມ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການວາງແນວທາງຕະຫຼາດ
-
ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
-
ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
-
ການຄ້າ / ຕະຫຼາດ
ລາຍຮັບທີ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນໆ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
-
ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
-
10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
-
> 50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ
-
ທຸກຍາກຫຼາຍ
-
ທຸກຍາກ
-
ສະເລ່ຍ
-
ຮັ່ງມີ
-
ຮັ່ງມີຫຼາຍ
ລະດັບຂອງການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ
-
ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
-
ສັດລາກແກ່
-
ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເລລ້ອນ
-
ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
-
ແບບເຄີ່ງຂັງ-ເຄີ່ງປ່ອຍ
-
ແບບປ່ອຍຕາມທຳມະຊາດ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ
-
ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
-
ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
-
ການຮ່ວມມື
-
ການຈ້າງງານ (ບໍລິສັດ, ອົງການ ລັດຖະບານ)
ອາຍຸ
-
ເດັກນ້ອຍ
-
ຊາວໜຸ່ມ
-
ໄວກາງຄົນ
-
ຜູ້ສູງອາຍຸ
ເຂດພື້ນທີ່ການນໍາໃຊ້ຕໍ່ຄົວເຮືອນ
-
<0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
-
0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
-
1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
-
2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
-
5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
-
15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
-
50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
-
100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
-
500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
-
1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
-
> 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຂະໜາດ
-
ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
-
ຂະໜາດກາງ
-
ຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່
ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ
-
ລັດ
-
ບໍລິສັດ
-
ຊຸມຊົນ / ບ້ານ
-
ກຸ່ມ
-
ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
-
ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ເຊົ່າ
-
ບຸກຄົນ
-
Land is apportioned by traditional leaders
ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
-
ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ເຊົ່າ
-
ບຸກຄົນ
-
Land is apportioned by traditional leaders
ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ)
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ
ຜົນກະທົບ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ເສດຖະກິດ
ເນື້ອທີ່ ການຜະລິດ (ທີ່ດິນໃໝ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ປູກພືດໃສ່ / ນໍາໃຊ້)
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ: 2-3ha
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ: >10
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງສັງຄົມ ວັດທະນະທໍາ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ການຂຸດຄົ້ນ / ເກັບກັກນໍ້າ (ການໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າ, ນໍ້າຄ້າງ, ຫິມະ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ)
ດິນເປັນຜົງ / ການຈັບໂຕຂອງດິນ ທີ່ມີຂະໜາດນ້ອຍຫຼາຍ ທີ່ມີການຈັບໂຕກັນເປັນກ້ອນ
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຜົນກະທົບນອກສະຖານທີ່
ມີນໍ້າ (ນໍ້າໄຕ້ດິນ, ນໍ້າພຸ)
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ (ທີ່ບໍ່ພຶງປາດຖະໜາ)
ມົນລະພິດ ທາງນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າໄຕ້ດິນ
ພື້ນທີ່ທໍາການຜະລິດ ຂອງເພື່ອນບ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນກະທົບ
ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການສ້າງຕັ້ງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບຫຼາຍ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ (ແມ່ນໍ້າ) ນໍ້າຖ້ວມ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ໄລຍະເວລາການຂະຫຍາຍຕົວຫຼຸດລົງ
ການຍອມຮັບ ແລະ ການປັບຕົວ
ອັດຕາສ່ວນຂອງຜູ້ຊົມໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບຮອງເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
-
ກໍລະນີດຽວ / ການທົດລອງ
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ມີໃຜແດ່ທີ່ສາມາດປັບຕົວຕໍ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນ?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
ໄດ້ມີການດັດແປງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອປັບໃຫ້ເຂົ້າກັບເງື່ອນໄຂການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ່?
ໄດ້ປ່ຽນແປງເງື່ອນໄຂຫຍັງແດ່?
-
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ຮ້າຍແຮງ
-
ຕະຫຼາດມີການປ່ຽນແປງ
-
ມີແຮງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ເນື່ອງຈາກການເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍແຮງງານ)
ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ແລະ ບົດຮຽນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບ
ຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ: ທັດສະນະມູມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
Enables early planting
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant in with the first rain
-
Quicker planting enables the planting of larger areas
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant the seed and fertilize in one operation
-
reduced workload
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage minimum tillage
ຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ: ທັດສະນະມຸມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນເອງ
-
Enables early planting
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant in November with the first heavy rain
-
Quicker planting enables the planting of larger areas
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use herbicides because without them, the capacity to weed will limit the production capacity
-
Preserves soil cover and reduces soil disturbance
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training in residue management and zero till
ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ: ທັດສະນະມູມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນວິທີການແກ້ໄຂແນວໃດ
-
The purchase price of the Magoye planter is quite high
Subsidize the implement
-
Excessive weeds and lack of information on herbicide use
More training on herbicide use
ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ: ທັດສະນະມຸມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນເອງວິທີການແກ້ໄຂແນວໃດ
-
The purchase price for the planter is on the higher side making it affordable only to the larger small-scale farmers
the price is likely to go down when the planter is mass produced
-
difficult to control weeds in the absence of herbicides
use herbicides
ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ
ການທົບທວນຄືນ
-
Alexandra Gavilano
-
Fabian Ottiger
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: Jan. 15, 2013
ປັບປຸງລ່າສຸດ: Aug. 14, 2019
ບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ
-
Silenga Wamunyima - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Alfred Katoweji - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Sharon Ndandula - ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ການບັນຍາຍລາຍລະອຽດ ໃນຖານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງຂໍ້ມູນການຄຸ້ມຄອງການນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ເອກກະສານ ແມ່ນໄດ້ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກໂດຍ
ສະຖາບັນ
- Golden Valley agricultural research trust (Golden Valley agricultural research trust) - ແຊມເບຍ
ໂຄງການ
ການອ້າງອີງທີ່ສໍາຄັນ
-
Social-economic analysis of conservation agriculture in southern Africa, FAO, 2011: FAO
-
Conservation farming in Zambia, Steven Haggblade, Gelson Tembo, October 2003: Indaba project, Michigan state university
-
Conservation farming in Zambia, Conservation farming unit (CFU), 2011: cfu@zamnet.zm













