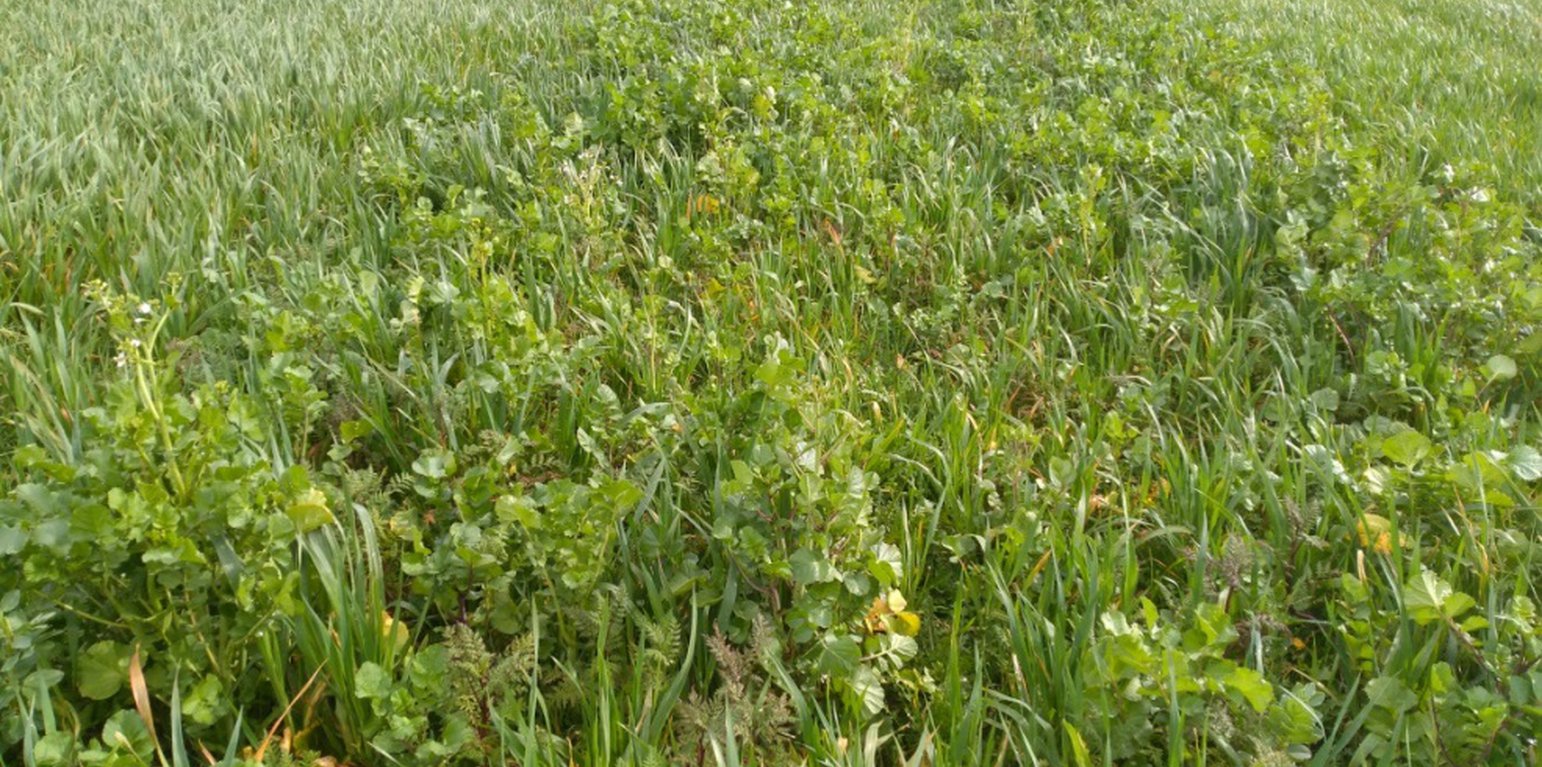




Agriculture in Brittany, in the north-west of France, is known for fish, beef, pork, poultry, vegetables and milk. Cover crops are used by farmers of Mauron, and the example described here is from a farm located in Morbihan in the basin known as Ploërmel. In this warm temperate area the average annual rainfall is 650-700 mm with an annual temperature of around 11°C.
There are three types of cover crops included in the rotation. These are selected on the basis of their benefits in relation to soil fertility and fodder production, in order to improve the farm's food self-sufficiency. There are three basic types of cover crops, as follows.
1) “Protein mixes” are composed of 35% faba (broad) beans, 26% oats, 17.5% peas, 17.5% vetch, and 4% clover. These are sown in early October after grass or maize are made into silage at the end of April.
2) "Green manure" cover crops are sown at the beginning of September after cereals, and are composed of various complementary species with the main objective of preserving and strengthening soil life (i.e. worm abundance), and winter feeding of heifers. For example, the commercial "Biomax" mix contains seeds of broad bean, vetch, clover, phacelia and radish. These cover crops are enriched by the presence of approximately 50% ryegrass regrowth, supporting the development of soil life.
3) Rapeseed is sown after cereals as a crop rotation feedstock and are made into silage.
Cover crops are either broadcast and rolled, or direct seeded depending on the conditions of the post-harvest plots. The seed drill used is equipped with discs to minimise soil disturbance as a reduced tillage technique, but more important in this respect is the presence of crop residues (i.e. straw). The seed drill is also equipped with tines.
The cover crops are grazed by heifers in a rotational 2-day paddock set-up. After grazing and regrowth of the ryegrass present, the fields may be left to develop into pasture, or seeded to crops using a minimum tillage drill.
The purposes are:
•Improved production
•Countered land degradation
•Protected watersheds
•Preserved biodiversity
•Adaptation to climate change/extreme events
The benefits are:
•Sustained ecosystem health: no pest and disease problems, good herd health
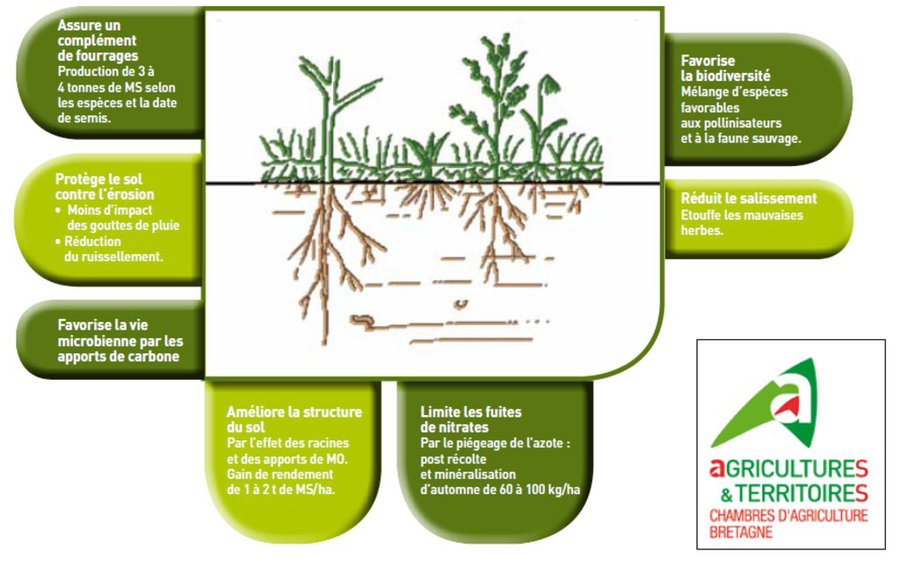
•Enrichment of the soil by the addition of carbon in organic matter and by the work of earthworms - favouring ecosystem functioning
•Protection of the soil and surface biodiversity because of maintained plant cover
•Increased weed control due to plant canopies and fertilisation effect of green manure
•Planted cover crops used as livestock feed during winter
The challenges are:
•Potential difficulties in establishing plant cover (especially in dry areas)
•Late sowing of cover crops reduces beneficial effects
•High costs of seed mixtures with high protein cover crops
ສະຖານທີ່: Mauron, Brittany, ຝຣັ່ງ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ: ພື້ນທີ່ດຽວ
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່ (approx. 10-100 ກມ 2)
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?: ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: 2019; ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ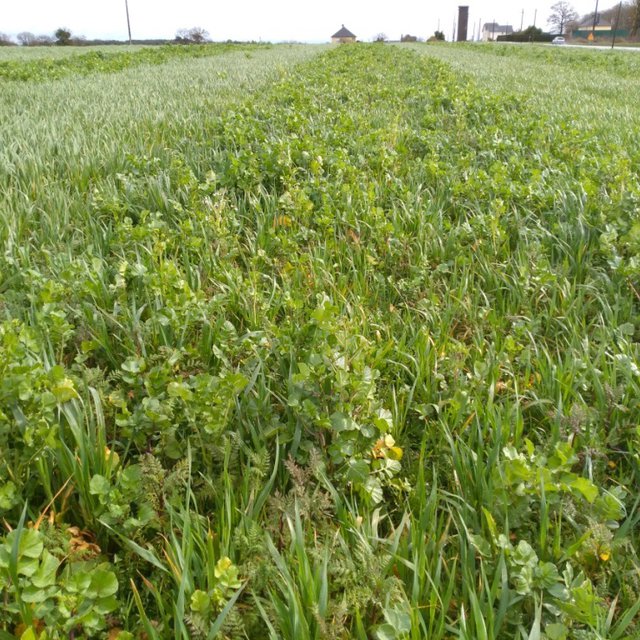



| ສາຍພັນ | ນັບ |
| ສັດໃຫ່ຍ-ງົວພັນນົມ | 115 |
| ສັດປີກ | 4500 |






| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (€) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (€) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ອຸປະກອນ | |||||
| Direct seeding (compil) | ha | 40.0 | 60.0 | 2400.0 | 100.0 |
| Broadcast sowing | ha | 72.0 | 15.0 | 1080.0 | 100.0 |
| Roller spade before sowing (1 pass) | ha | 72.0 | 23.0 | 1656.0 | 100.0 |
| Maceration by a roller with blades | ha | 224.0 | 23.0 | 5152.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | |||||
| Seeds - protein blend | ha | 60.0 | 394.0 | 23640.0 | 100.0 |
| Seeds - forage rapeseed | ha | 17.0 | 28.0 | 476.0 | 100.0 |
| Seeds - green manure "biomax" fertilizer | ha | 18.0 | 60.0 | 1080.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 35'484.0 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 39'426.67 | ||||
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
Better diversity of fodder available is producing healthier and better quality animals
Sward mix in cover crop is very diverse
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water related loss impacts
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
Improved crop and animal production
Greater workload to rotationally graze and manage crop effectively in an organic system (i.e. can't rely on spraying to solve problems). Yet, benefits outweigh extra workload.
Vastly improved understanding through SLM expert advice and practical learning from doing SLM technology.
Cover crops help maintain soil moisture and reduce runoff through root system, improving water quantity held in field.
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
Cover crops help maintain soil moisture and reduce runoff through root system, improving water quantity held in field.
Cover crops help maintain soil moisture and reduce runoff through root system, improving water quantity held in field.
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil loss
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil loss
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil crusting
Reduced tillage techniques and less passes across fields with machinery as no spraying due to organic system reduces compaction.
Selected species of cover crops help recharge nutrient availability in the soil
Cover crop rooting system & waste inversion as green manure increases the soil organic matter below ground.
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil crusting
Greater crop cover and thus more biomass above ground
Well designed mixed cover crop seed mixes, although more expensive, provide a specialised plant diversity ideal for the farm system requirements.
Certain cover crops can attract beneficial species and help control pests and diseases
A diverse vegetation supports greater habitat diversity
Certain cover crops can attract beneficial species and help control pests and diseases
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing flood risk and impact
Cover crops slow surface run off and can hold a greater water capacity reducing potential for debris flows in storm events
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing drought impacts
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing flood risk and impact
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing potential for debris flows and nutrient leaching downstream
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing potential for debris flows and nutrient leaching downstream