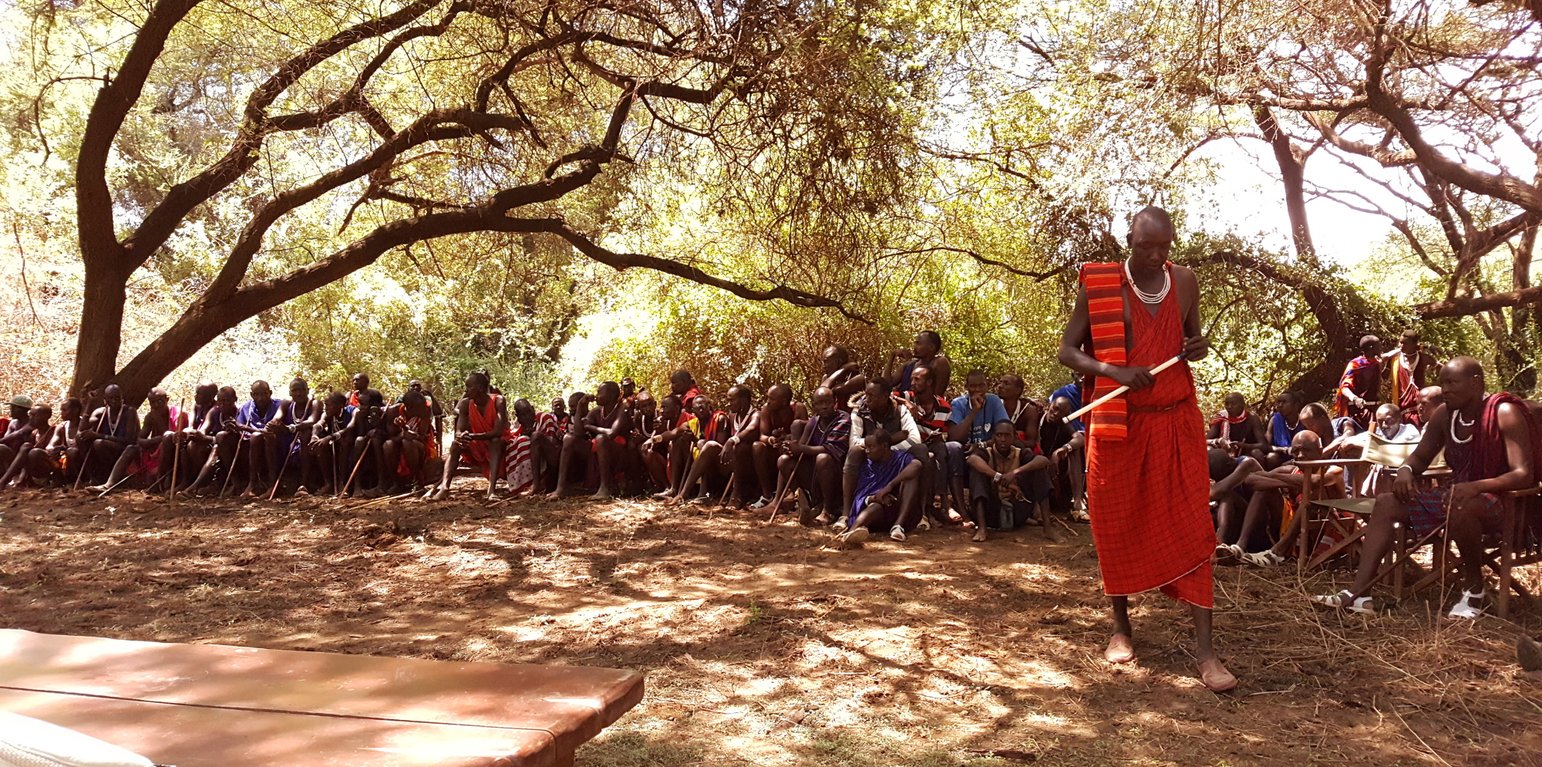
Community-based rangeland management in the southern Kenyan rangelands
(ເຄັນຢາ)
ຄຳອະທິບາຍ
Olkiramatian Group Ranch strengthened the capacity of its community governance structures and began to engage in more rigorous implementation of seasonal grazing plans. This was based on traditional ecological knowledge and rangeland management practices. The group ranch incorporated conservation, research, and joint rangeland management planning with neighboring communities.
Prior to implementation of the approach described here, rangeland management was carried out through customary institutions supported by a group ranch committee. However, many challenges hindered effective management of livestock and natural resources. These included:
• Poor financial management
• Lack of accountability from the leaders - and lack of demand for accountability from the members
• Conflicting group and individual interests
• Lack of a written constitution and grazing by-laws to reinforce traditional decision making.
To minimize and overcome some of these weaknesses, the African Conservation Centre (ACC), a conservation NGO and Southern Rift Association of Land Owners (SORALO), a Maasai land trust, worked with Olkiramatian and other communities to help them strengthen their planning and governance and to reinvigorate the traditional system of grazing management. Initially, ACC worked with the community’s governance and resource management committees to build local capacity for decision-making and resource management. Institutions previously responsible for resource management, which had existed under traditional systems, had begun to weaken from both internal and external pressures, undermining the long-term sustainability and equity of rangeland management. The group ranch emerged as the key modern institution within this community and needed to be strengthened to support traditional management. To do this several sequential steps were taken:
(i) First, the group ranch committee instituted a more objective way of identifying and electing office holders, to ensure a credible base for resource governance and building consensus among resource users;
(ii) Registration of group ranch members was re-initiated to ensure equal access and rights to resource use, and to provide clarity around membership;
(iii) Institutions responsible for rangeland management, including the group ranch committee, and the conservation and grazing subcommittees, were reinforced primarily through the strengthening of internal capacity;
(iv) ACC facilitated a process for consolidating the group ranch's governance and by-laws to help guide the implementation of the strategy, including enforcement;
(v) The group ranch implemented provisions for holding leaders accountable, allowing the group ranch members to demand their rights;
(vi) Decision-making processes were facilitated by laying down procedures for sharing information and apportioning responsibilities among the leadership - as decided at annual general meetings;
(vii) Rangeland monitoring groups and rangers, mostly local youth, were trained and positioned;
(viii) Finally, the Lale’enok Resource Centre was established, together with community enterprises based on the use of natural resources. A women’s group was included.
An important catalyst in the approach was the establishment of a community conservation area and lodge within the group ranch for the development of wildlife tourism. The conservation area capitalized on the existence of the community’s dry season reserve where wildlife such as zebra and giraffes were abundant , which is only grazed by livestock after pasture is utilized elsewhere. This creation of a conservation area, coupled with the desire to generate revenue through tourism with its semi-exclusive access rights to parts of the conservation area, worked to reaffirm the traditional grazing management strategies by preventing settlement within the conservation area and encouraging longer resting of pasture following rain. This happened alongside the development of a research program , which has helped to put community rangeland management on an evidence-based foundation.
With guidance, the community revised its grazing plan and zoned its land into four resource use areas, now embodied in the new group ranch constitution:
- Conservation or wildlife areas (which then allowed the creation of the conservancy);
- Agricultural/crop production areas;
- Livestock grazing areas (dry season and wet grazing areas);
- Human settlements.
The grazing sub-committee of the group ranch makes and implements decisions on livestock access to certain areas, with pasture rested between and across seasons. The conservancy is rested from livestock grazing as a “grass bank” during the wet seasons, which can last up to 6 months . Settlement areas are also tightly managed under this approach to preserve pasture heterogeneity and prevent local degradation. Fines are imposed on herders who break grazing regulations. On a rolling basis the communities now utilize traditional ecological knowledge, ecological monitoring and expert knowledge, to reassess these grazing regimes under changing conditions. These rangeland management activities are also nested within joint, inter-community planning such as regular meetings of the grazing committees of clusters of group ranches.
ສະຖານທີ່
ສະຖານທີ່: Kajiado West Constituency, Kajiado, ເຄັນຢາ
ການຄັດເລືອກພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ອີງໃສ່ຂໍ້ມູນທາງພູມີສາດ
ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ: 2004
ປີຂອງການສິ້ນສຸດ: n.a.
ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
-
ພື້ນເມືອງ / ທ້ອງຖີ່ນ
-
ການລິເລີ່ມ ພາຍໃນປະເທດ ທີ່ຜ່ານມາ / ນະວັດຕະກໍາ
-
ພາຍໃຕ້ໂຄງການ / ແຜນງານ
-
Hybrid traditional/project-based
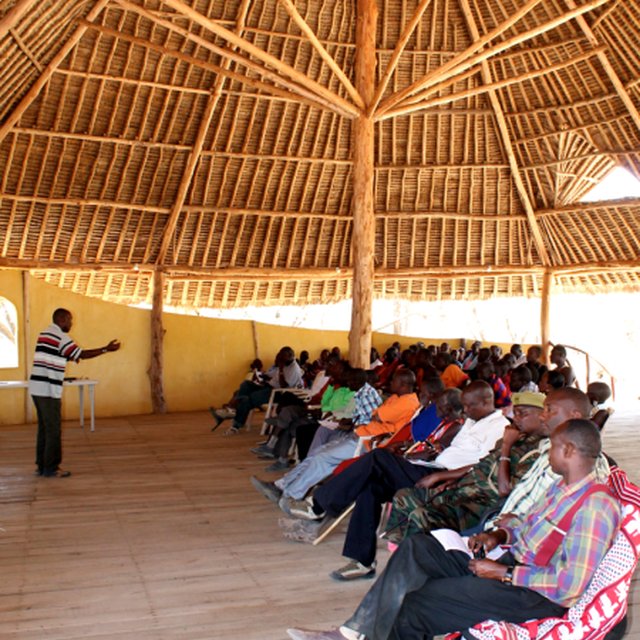

A community information feedback and management meeting at the Lale'enok Resource Centre (Lale'enok Resource Centre)
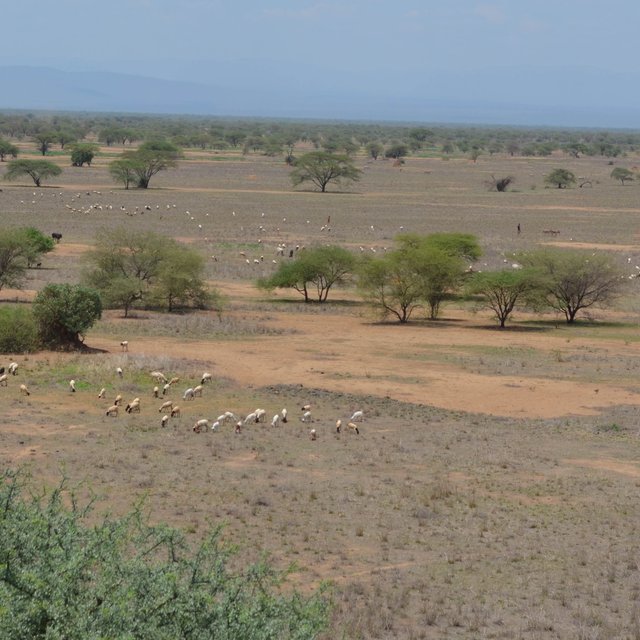

Rangeland management at Olkiramatian takes place over a large, heterogeneous landscape (Enoch Ontiri)
ເປົ້າໝາຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ການປົກປັກຮັກສາສິ່ງແວດລ້ອມ
ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດແນວທາງ
To enhance sustainable livelihoods for pastoralist community members through informed, sustainable use of their resources in an equitable manner.
ເງື່ອນໄຂທີ່ສະໜັບສະໜູນໃຫ້ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ບົນພື້ນຖານແນວທາງ
-
ສັງຄົມ / ວັດທະນະທໍາ / ມາດຕະຖານ ແລະ ຄຸນຄ່າທາງສາສະໜາ: Uniform ethnicity. Communal land tenure. The pre-existing customary institutions and the group ranch committees. The government decree on the establishment of group ranches. The strong traditional and cultural knowledge about rangeland and livestock management.
-
ການກໍ່ຕັ້ງສະຖາບັນ: The group ranch was already established and practicing planned grazing according to customary rules.
-
ກ່ຽວກັບກົດໝາຍ (ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ, ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ): There is a strong body of legislation developing in Kenya to ensure sustainable use of rangeland resources. This includes the new Community Land Act (2016), which creates local governance institutions with protection of grazing; the Wildlife Act (2012), creating community conservation areas and allowing benefits and compensation from wildlife; the Water Act (2016) and the Water Resource Users Association encourage multi-user analysis and cooperation to protect the quantity and quality of water for all users within a catchment.
-
ການປົກຄອງທີ່ດິນ (ການຕັດສິນໃຈ, ການປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ຂໍ້ບັງຄັບ): The group ranch committee is the highest decision-making body. There is a grazing sub-committee which manages the details of seasonal grazing patterns.
-
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ: The community is networked to researchers and technical experts from institutions including ACC, SORALO, Universities and TATA chemicals; through the Lale'enok Resource Centre. Mobile phones and access to internet has enhanced access to technical information. There is a wealth of traditional knowledge within the older generation who understand the requirements for sustainable management of the landscape.
-
ຕະຫຼາດ (ໃນການຊື້ວັດຖຸດິບ, ຂາຍຜະລິດຕະພັນ) ແລະ ລາຄາ: Livestock markets within reach of the community members - the Shompole crossborder livestock market is in the neighboring conservancy.
-
ວຽກ, ມີກໍາລັງຄົນ: The community members are involved in the process as part of their lifestyle. Planned grazing made it easier for them to take of their livestock and reduce the number of people required to herd their livestock.
ເງື່ອນໄຂທີ່ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນໃຫ້ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ບົນພື້ນຖານແນວທາງ
-
ສັງຄົມ / ວັດທະນະທໍາ / ມາດຕະຖານ ແລະ ຄຸນຄ່າທາງສາສະໜາ: Cultural beliefs: large numbers of livestock are seen as a status symbol; resulting in potential overstocking of livestock.
-
ມີຄວາມສາມາດ / ເຂັ້າເຖິງຊັບພະຍາກອນດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ: Financial resources are limited for the group ranch committee; they depend on small collections at local markets and some donor financing to enact projects.
-
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ: Low capacity of the many community members to tap into the existing knowledge bases. Lack of technical capacity to address specific research needs identified by the community.
-
ຕະຫຼາດ (ໃນການຊື້ວັດຖຸດິບ, ຂາຍຜະລິດຕະພັນ) ແລະ ລາຄາ: Low livestock prices at the grassroots present a challenge to the growth of the livestock value chain. A solution may be the facilitation of more direct market linkages.
ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
ພາລະບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດແນວທາງ
| ແມ່ນໃຜ / ພາກສ່ວນໃດ ທີ່ເປັນເຈົ້າການ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີການ? |
ລະບຸ ພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ |
ພັນລະນາ ບົດບາດ ໜ້າທີ່ ຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ |
| ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ |
Members and executives of the group ranch committee. |
Individual members of the group ranch, as rangeland users and through their grazing patterns according to the ranch's grazing plans, contribute to management. |
| ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ພາຍໃນຊຸມຊົນ |
Olkiramatian Group Ranch. |
The group ranch, through its democratic structures, has the ultimate responsibility for decision-making for the group ranch, including rangeland management and grazing planning, partnerships, fund raising and financial management, etc. |
| ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ທີ່ປຶກສາດ້ານກະສິກໍາ |
Personnel of SORALO and ACC. |
Provision of technical advice and support. |
| ນັກຄົ້ນຄວ້າ |
Students. |
Students, both Kenyan and international, hosted by SORALO and ACC, carry out research on conservation, ecotourism, land use, rangeland condition, etc. |
| ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ບໍ່ຂື້ນກັບລັດຖະບານ |
SORALO and ACC. |
Research guidance, and connection with other government, NGO and donor agency stakeholders. Also provision of technical advice and support (see SLM Specialists/Agricultural Advisers, above). |
ອົງການທີ່ເປັນຕົວແທນໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
Olkiramatian Group Ranch
ການລວບລວມເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ/ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດແນວທາງ ແຕ່ລະໄລຍະ
ບໍ່ມີ
ການບໍ່ປະຕິບັດ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ການຮ່ວມມື
ການນໍາໃໍຊ້ເອງ
ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ
The community invited ACC to come and support conservation work and improve ecotourism. A visiting researcher from ACC identified opportunities for reinvigorating the group ranch structure and nature-based enterprises. The work of the researcher contributed to the approach, but the ultimate push came from the community.
ການວາງແຜນ
The community evolved into an organized group and was determined to employ good resource practices to improve the rangelands and the lives of the people. They sought the help of ACC in strengthening their capacity to fundraise and improve community enterprises. SORALO was established to continue supporting the community in networking and supporting the conservation work.
ການປະຕິບັດ
The committee members, the individual members implement the approach. SORALO and to a less extent ACC, play advisory roles. The community members provide labour and time as their in-kind contribution. ACC help the community raise funds for the implementation.
ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ
With guidance from SORALO, monitoring is done by community members. The various committees have a monitoring component in their work.
Research
At the beginning, research was done by a scientist from ACC. Later on in the approach, the community youth have been trained and are actively involved in research activities.
ແຜ່ນວາດສະແດງ
Adaptation to evolving challenges through the community's governance structure -- the group ranch committee -- is at the centre of the approach.
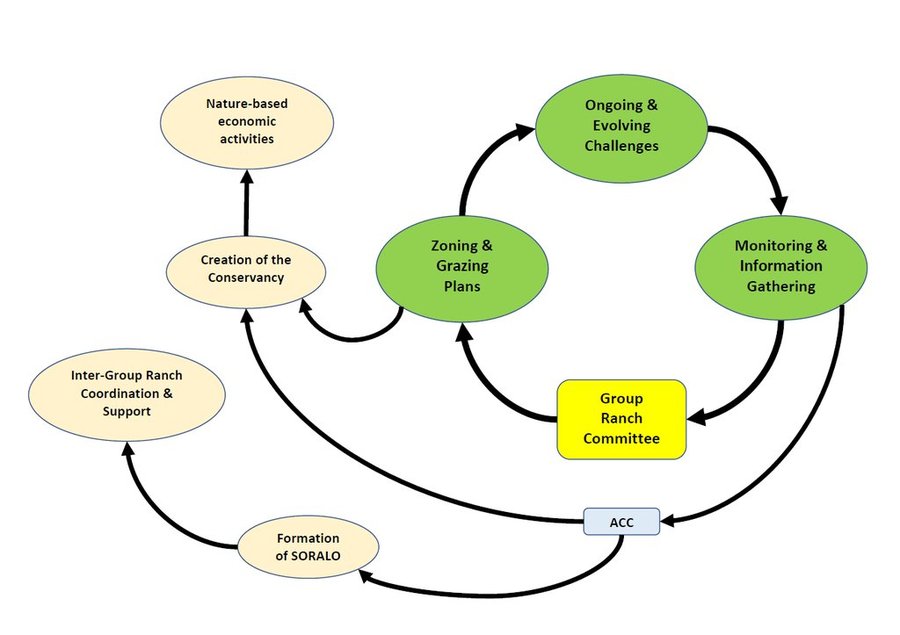
ຜູ້ຂຽນ: Enoch Ontiri and Lance Robinson
ການຕັດສິນໃຈໃນການເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ການຕັດສິນໃຈໂດຍ
-
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນຜູ້ດຽວ (ການລິເລີ່ມດ້ວຍຕົນເອງ)
-
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນຫຼັກ, ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ໂດຍຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທັງໝົດ, ເປັນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ຂອງວິທີທາງແບບມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
-
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ຫຼັກດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ມີການຕິດຕາມປຶກສາຫາລືກັບຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
ຊຽ່ວຊານ ສະເພາະດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງຜູ້ດຽວ
-
ນັກການເມືອງ / ຜູ້ນໍາ
ການຕັດສິນໃຈບົນພື້ນຖານ
-
ປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ (ຫຼັກຖານທີ່ຊ່ວຍໃນການຕັດສິນໃຈ)
-
ຜົນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບ ຈາກການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
-
ປະສົບການສ່ວນບຸກຄົນ ແລະ ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ທີ່ບໍ່ເປັນເອກກະສານ)
-
Research and evidence-based decision-making played some role, but planning of technical practices to be implemented was primarily based on traditional knowledge
ການສະໜັບສະໜູນເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ ແລະ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຄວາມຮູ້
ກິດຈະກຳ ດັ່ງລຸ່ມນີ້ ແມ່ນເປັນພາກໜຶ່ງຂອງແນວທາງ
-
ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
-
ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
-
ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
-
ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
-
ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ / ຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ໄດ້ສະໜັບສະໜູນຝຶກອົບຮົມໃຫ້ແກ່ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງດັ່ງລຸ່ມນີ້
-
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
-
ພະນັກງານພາກສະໜາມ / ທີ່ປຶກສາ
ຮູບແບບການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
-
ການເຮັດຕົວຈິງ
-
ຕົວຕໍ່ຕົວ
-
ເນື້ອທີ່ສວນທົດລອງ
-
ກອງປະຊຸມ
-
ຫຼັກສູດ
-
Training workshops
ກວມເອົາຫົວຂໍ້
The training to the women’s group was on improved bead-making and business management in order to exploit the tourism market.
Selected youth were trained as wildlife rangers and others as rangeland monitors. Species-specific teams were trained in tracking particular species such as lions.
ການບໍລິການທາງດ້ານການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ໄດ້ຮັບການບໍລິການທາງດ້ານການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
-
ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
-
ສູນຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
Advisory services provided by SORALO and ACC. A permanent resource centre, Lale'enok is present in the region.
ຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງຂອງສະຖາບັນ
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ
-
ບໍ່ມີ
-
ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
-
ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
-
ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
ໃນລະດັບດັ່ງລຸ່ມນີ້
-
ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
-
ລະດັບພາກພື້ນ
-
ແຫ່ງຊາດ
ອະທິບາຍສະຖາບັນ, ພາລະບົດບາດແລະຄວາມຮັບຜິດຊອບ, ສະມາຊິກ, ແລະອື່ນໆ.
The organizations African Conservation Centre (ACC) and Southern Rift Association of Land Owners (SORALO) have helped to strengthen the group ranch structures
ຮູບແບບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ
-
ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ
-
ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
-
ອຸປະກອນ
ລາຍລະອຽດເພີ່ມເຕີມ
Primarily support has been through capacity building and training with the group ranch committee and other committees.
Additional support has been provided by SORALO through the provision of staff and labor for hosting community meetings; writing the constitution; producing maps and other information; conducting research into pertinent management issues.
ACC with funding from various sources helped to finance establishment of the conservation area and a lodge. The lodge pays a lease fee to the group ranch. Guests at the lodge pay a bed night fee which is paid to the group ranch committee and a conservation fee which goes to the conservation committee. The conservation fee pays for scouts and also finances conservation-related development such as fences, water pipelines, and other community projects.
ການຕິດຕາມ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
The community, especially youth, are involved in assessing the ecological status of the rangeland. There are ecological monitoring units which take censuses of flora and fauna. Community activity reports are written regularly. The major economic activity of livestock trade is monitored by a data collection team that visits the major livestock markets.
ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ການວິໄຈໄດ້ຮັບການຮັກສາຫົວຂໍ້ຕໍ່ໄປນີ້
-
ສັງຄົມ
-
ເສດຖະສາດ / ການຕະຫຼາດ
-
ລະບົບນິເວດ
-
ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
Research questions are often answered by visiting students and local scientists at the Lale'enok Resource Centre. These questions cover a diverse range of issues related to the socioeconomic and ecological factors affecting local livelihoods.
African Conservation Centre. Southern Rift Association of Land Owners. Graduate students hosted by these organizations.
ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
ງົບປະມານປະຈຳປີ ໃນກິດຈະກຳ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ທີ່ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນໂດລາ
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
100,000-1,000,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: n.a.
The primary resource used for implementation of the approach is the time of community members. Inputs from supporting organizations ACC and SORALO, while relevant, have been secondary to the approach and hence are not included in the budget here.
ການບໍລິການ ຫຼື ສິ່ງກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ ດັ່ງລຸ່ມນີ້ ແມ່ນໄດ້ສະໜອງໂດຍຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນເອງ
-
ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
-
ຫຼຸດປັດໃຈນໍາເຂົ້າ
-
ສິນເຊື່ອ
-
ສິ່ງຈູງໃຈ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອງມືອື່ນໆ
ສີ່ງກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ອື່ນໆ
Ecotourism revenue provides some incentive to carry out and continue with rangeland management activities.
ການວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສະຫຼຸບລວມ
ຜົນກະທົບຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ແນວທາງ
ບໍ່
ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
ວິທີທາງ ຊ່ວຍຊຸກຍູ້ ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນທ້ອງຖີ່ນ, ໃນການປັບປຸງ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ຂອງຜູ້ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ບໍ່?
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ດັ່ງກ່າວນີ້ ສາມາດເປັນຫຼັກຖານ ທີ່ສະໜັບສະໜູນ ໃຫ້ການຕັດສິນໃຈໄດ້ບໍ່?
Ecological monitoring and research are prominent aspects of the interventions and community-decision-making.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
It facilitated the implementation of seasonal planned grazing.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ການປະສານງານ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ທີ່ມີປະສິດທິພາບ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືດຍົງໄດ້ບໍ່?
Coordination with neighbouring group ranches has been a key aspect of the interventions.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງຄວາມຮູ້ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືດຍົງໄດ້ບໍ່?
Improved knowledge of rangeland and wildlife ecology.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງໄດ້ບໍ່?
Involvement of customary institutions has contributed to mitigation and resolution of conflicts.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ປະເດັນການຖືຄອງທີ່ດິນ / ສິດທິໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
In theory, tenure rights were already secure. However the weakness of the community institution--the group ranch--could have resulted in land fragmentation or alienation as it had done so in many other group ranches. Strengthening the group ranch's governance has strengthened tenure security.
ສິ່ງກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ໃຫ້ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການປະຕິບັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
ການຜະລິດເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ
-
ກໍາໄລເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ (ຄວາມສາມາດ), ການປັບປຸງຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ, ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ, ອັດຕາສ່ວນ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ
-
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງຂອງໄພພິບັດ
-
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນພາລະວຽກ
-
ການຊໍາລະເງິນ / ເງິນອຸດໜູນ
-
ກົດລະບຽບແລະລະບຽບການ (ລະອຽດ) / ການບັງຄັບໃຊ້
-
ກຽດສັກສີ, ຄວາມກົດດັນທາງສັງຄົມ / ການຕິດຕໍ່ກັນທາງສັງຄົມ
-
ລວມເຂົ້ານໍາກັນກັບການເຄື່ອນໄຫວ / ໂຄງການ / ກຸ່ມ / ເຄືອຂ່າຍ
-
ຄວາມຮັບຮູ້ ທາງສີ່ງແວດລ້ອມ
-
ພາສີ ແລະ ຄວາມເຊື່ອຖື, ສົມບັດສິນທໍາ
-
ການປັບປຸງ ຄວາມຮູ້ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
ການປັບປຸງຄວາມງົດງາມ
-
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ
ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດກິດຈະກໍາຂອງແນວທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຕາມແນວທາງໄດ້ເອງບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກການສະໜັບສະໜູນຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
The approach is based on ensuring strong, community-led governance. This has been achieved and is likely to be sustained.
ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ແລະ ບົດຮຽນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບ
ຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ: ທັດສະນະມູມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
-
The approaches emanates from a strong community with a working customary rangeland management structure. Communal ownership of land and the community's sense of belonging and customary (tribal) right of access and use of natural resources all make it easier for the approach to be successful.
ຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ: ທັດສະນະມຸມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນເອງ
-
The approach is a bottom-up one that builds on traditional resource management practices, adapting them to evolving social, economic and biophysical conditions. This contributes to strong sense of community ownership.
-
As a community driven and implemented the approach, the cost is minimal. With the incorporation of the conservation/wildlife tourism component, a secondary source of income for the community structures and some individuals in the community is realized.
-
The climatic conditions that allow extensive livestock production and wildlife is also another advantage for the approach. The landscape lies between Nguruman escarpment on one side, Lake Magadi on the northwestern part and the Amboseli/Mt. Kilimanjaro on the southern part. These contribute to some degree of isolation and protection of influxes of herders from other locations.
-
The demonstrated success of the grazing management practices put in place has led to changed decisions and management practices reinforcing the community's willingness to continue with the system.
ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ: ທັດສະນະມູມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນວິທີການແກ້ໄຂແນວໃດ
-
There is concern among some community members about the incorporation of conservation activities potentially leading to restrictions on mobility and access to pastures.
Continued awareness raising about the benefits and pre-empting misunderstandings about the conservation activities.
-
The community success in rangeland management is sometimes viewed as a source of failure. This is because the community holds some customary beliefs and norms that allow for practices like reciprocal grazing by other pastoralists on their land. In the case that Olkiramatian is the best quality grass bank during extended droughts, livestock from other communities flock there and mostly cause overgrazing, degradation, and social conflict.
The idea of SORALO networking all the landowners in the southern rangelands and are helping them establish similar approaches means the whole rangeland in southern Kenya will become a continuous, homogenously managed landscape.
ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ: ທັດສະນະມຸມມອງ ຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນເອງວິທີການແກ້ໄຂແນວໃດ
-
The capacity of the group ranch committee to raise and attract appropriate human and financial resources is low.
Continued training on effective governance and help in putting in place working systems.
-
The stocking rates of livestock per household are not corresponding to the holding capacity of the rangeland.
Continued action research and training of the locals on the need to reduce livestock numbers.
ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ
Editors
-
Enoch Mobisa
-
Peter Tyrrell
ການທົບທວນຄືນ
-
Alexandra Gavilano
-
Rima Mekdaschi Studer
-
Hanspeter Liniger
-
Donia Mühlematter
-
Simone Verzandvoort
-
Joana Eichenberger
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: Dec. 14, 2017
ປັບປຸງລ່າສຸດ: Nov. 2, 2021
ບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ
-
Enoch Mobisa (e.ontiri@cgiar.org) - ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
-
Peter Tyrrell (peterdavidtyrrell@gmail.com) - None
ການບັນຍາຍລາຍລະອຽດ ໃນຖານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງຂໍ້ມູນການຄຸ້ມຄອງການນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ເອກກະສານ ແມ່ນໄດ້ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກໂດຍ
ສະຖາບັນ
- ILRI International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) - ເຄັນຢາ
ໂຄງການ
- Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)
- Restoration of degraded land for food security and poverty reduction in East Africa and the Sahel: taking successes in land restoration to scale (ILRI)
ການອ້າງອີງທີ່ສໍາຄັນ
-
Community-based Rangeland Management in Shompole and Olkiramatian Group Ranches. Ontiri, Enoch M. and Lance W. Robinson. 2018.: cgspace.cgiar.org -- open access
ເຊື່ອມໂຍງກັບ ຂໍ້ມູນຕ່າງໆ ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ມີ







