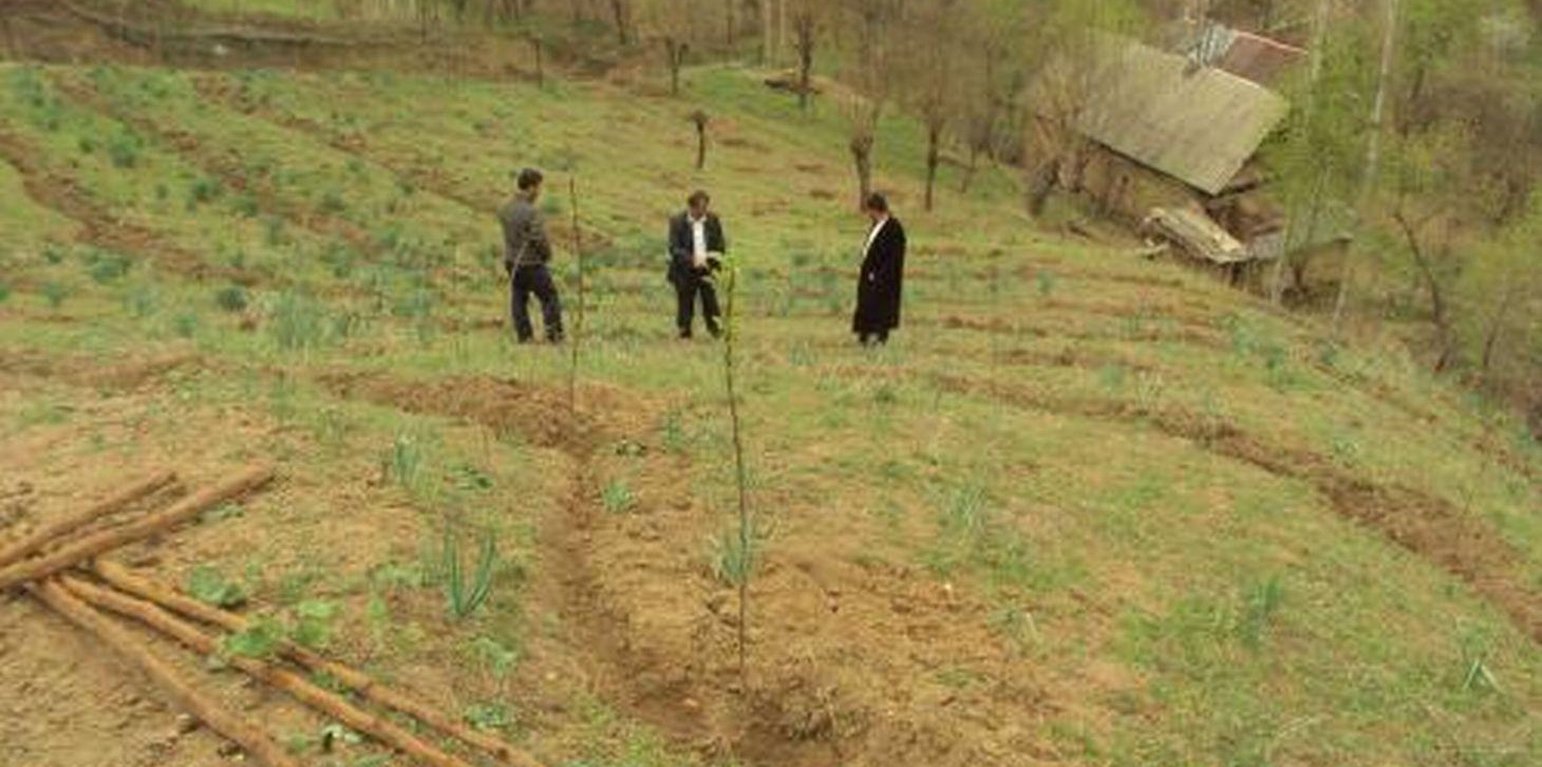




This technology involved the planting of several varieties of native fruit trees to help stabilise steep loess mountain slopes. Seven species of fruit trees were planted in seven different locations, in two watersheds within the district of Nurobod in Tajikistan. The locations were chosen as a result of a natural disaster workshop that identified the areas most susceptible to landslides.
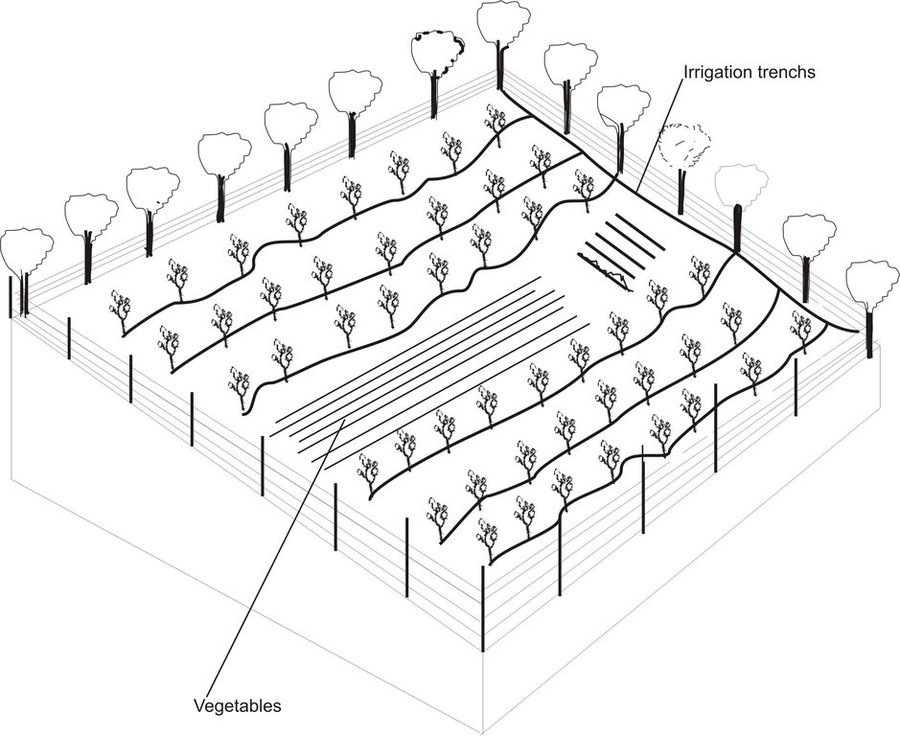
In consultation with the Institute of Horticulture a fruit tree planting scheme was devised and using project money the identified area was enclosed with a wire perimeter fence. The fruit trees were planted along irrigation contours running at shallow angles parallel to the slope.
Purpose of the Technology: The best locations for planting the fruit trees were decided on via a participatory community workshop on natural disaster risk management.
During the workshop the community identified areas around the village that were considered high risk. A fruit tree planting scheme was implemented in these areas to help stabilise the slopes, reduce surface water run off and top soil erosion, and reduce the risk of landslides. As the trees grew they were intercropped with wheat and espercet.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Several 'at risk' areas were identifed within these workshops, therefore the project team had to assess the areas for suitability. Two of the main criteria used included the access to water and if there was sufficient depth of top soil to sustain a fruit orchard.
Once the area was decided upon, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed with the particular land user. It was made clear to the community that the land was chosen based upon the decisions from the workshop and not because of any form of favouritism towards the land user. The MoU stated that the land user was responsible for the planting and maintenance of the orchards.
The Horticultural Institute devised a planting a scheme based upon the loaction and soil type. The implementation activities occurred in early spring. A continuos wire fence was erected around the area, and the fruit trees were planted at five metre intervals along a dug contour irrigation ditch. One kilo of organic fertiliser was applied to each tree and later in the season they were sprayed with pesticides.
Natural / human environment: Nurobod district is a mountainous area, with large tributaries flowing into the Vasht river. There are mass erosion processes at work, causing gullies and washing away the top soil. The previous civil war, compounded by harsh winters resulted in extensive clearance of the surrounding vegetation for fuel. These areas have became further degraded by over grazing on the remaining grass lands.
The local population suffers from high levels of labour migration of young men to Russia and resulting in a drain of knowledge and able bodied workers. This leaves the remaining families particulary vulnerable in this specific climate.
ສະຖານທີ່: Nurobod, Tajikistan, ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ:
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່ (approx. < 0.1 ກິໂລແມັດ2 (10 ເຮັກຕາ))
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?:
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ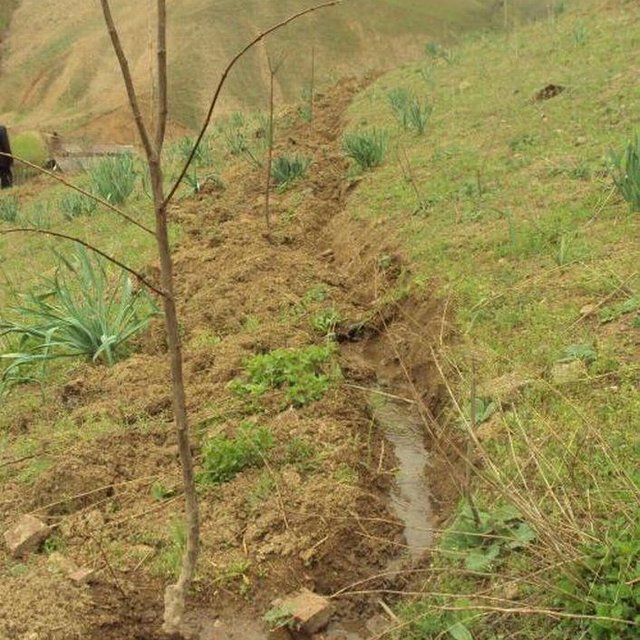





| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (somoni) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (somoni) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ແຮງງານ | |||||
| Building fence | Persons/day | 28.0 | 25.0 | 700.0 | 100.0 |
| Planting fruit trees | Persons/day | 40.0 | 25.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | |||||
| Tools | Pieces | 6.0 | 20.0 | 120.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | |||||
| Seedlimgs | pieces | 400.0 | 8.0 | 3200.0 | |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | |||||
| Compost/manure | tons | 1.0 | 225.0 | 225.0 | 100.0 |
| 1.0 | |||||
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | |||||
| Metal fence and posts | meter | 400.0 | 12.0 | 4800.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 10'045.0 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 2'232.22 | ||||
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (somoni) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (somoni) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ແຮງງານ | |||||
| Prunning and tree care | Persons/day | 15.0 | 16.6666667 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 250.0 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 55.56 | ||||
400 trees planted
new products to sell
seven varieties of fruits
new source of sustainable income
The implementation of the technology is supported with training.
increased fruit production
training provided
Training on fruit tree cultivation was provided for the community in conjunction with the implementation of the planting of the trees, to help improve the fruit yields in the community and the health of the trees.
trees absorb the water
regeneration of the biomass cycle
introduced new species to the area.
main goal of the SLM technology