



Climate change presents significant challenges for agriculture and crop production. One possible solution to enhance climate resilience is the development and adoption of improved, better adapted crop varieties. These varieties are specifically engineered to withstand specific threats, offering farmers a more reliable means of ensuring successful harvests despite the challenges posed by a changing climate. Improved varieties are thus crucial for achieving food security.
However, a major limitation of this solution is that researching and producing new crop varieties is a complex process that demands considerable time and resources. It involves cross design, segregating generation advancement and rigorous field testing to identify traits. The development of new varieties often spans several years, if not decades, before they are ready for widespread adoption by farmers. Sustained investment and collaboration across scientific organizations are thus crucial.
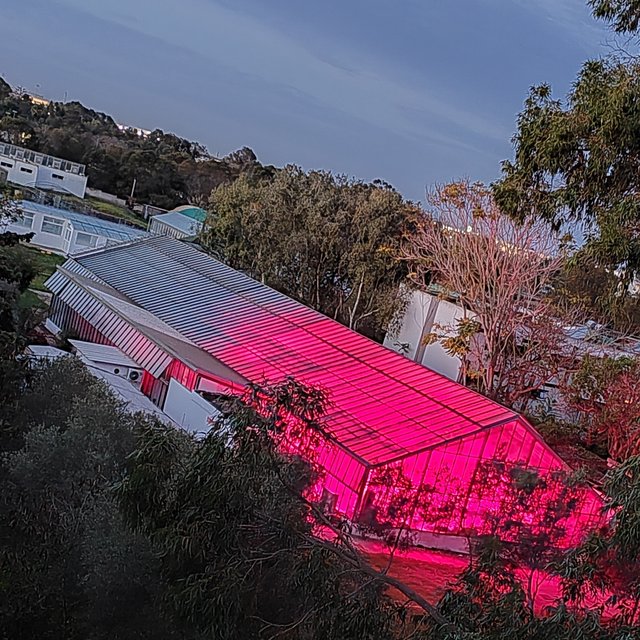
To accelerate the development of improved crop varieties, the International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA), together with partners is implementing Speed Breeding as its main generation advancement method. Through the support of the Arab Fund for Economic and Social development (AFESD), the Templeton World Charity Foundation, Inc and the Crop Trust, protocols to accelerate the generation advancement of the main crops (wheat, barley, faba bean, lentil, grasspea and chickpea) have been developed and are available to NARES. ICARDA has also established the Speed Breeding Platform in Rabat, Morocco. Covering approximately 500 square meters, this facility comprises four buildings, including two greenhouses of 175 m2 and 185 m2 respectively, each housing five independently controlled growth chamber.i
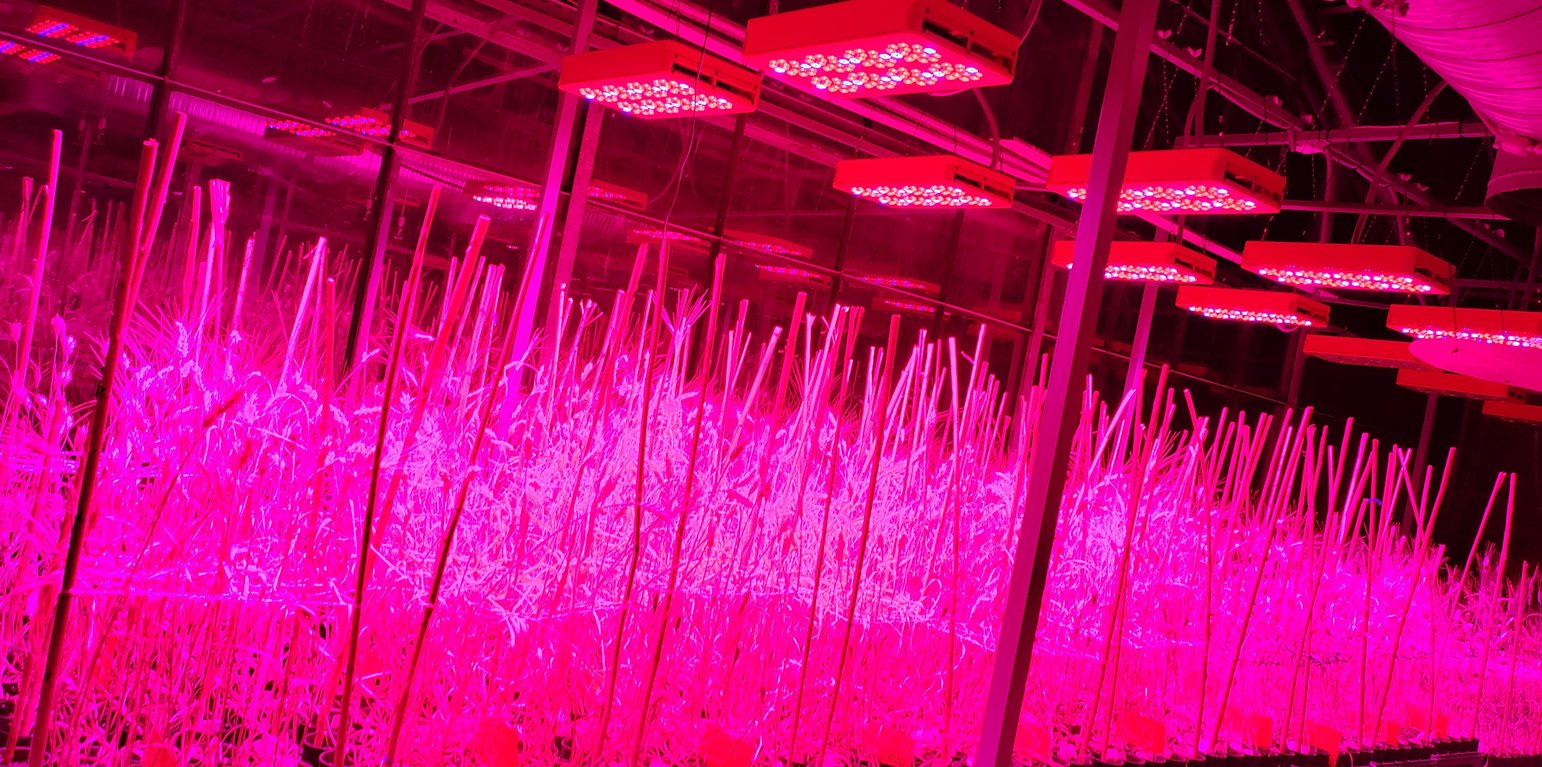
The Speed Breeding method utilises LED lighting - originally invented by NASA to sustain astronauts during prolonged space missions to compensate for the absence of sunlight in space. By providing plants with approximately 22 hours of light per day, this accelerates their growth significantly. Cultivating crops in a controlled environment shields them from the unpredictable impacts of adverse weather conditions. The major advantage is thus its ability to accelerate the breeding process for improved crop varieties. For instance, while traditional methods may take between 6 and 12 years to breed a new grass pea (Lathyrus sativus) variety, utilizing the Speed Breeding Platform reduces this timeframe to approximately 5 years. The Speed Breeding Platform thus enhances efficiency and responsiveness in addressing agricultural challenges.
The Speed Breeding Platform has a capacity for advancing over 50,000 cereal and legume plants. This is done in close collaborations with fellow scientists from other CGIAR centers and National Agricultural Research and Extensions Services (NARES) centers. NARES centers play an indispensable role in determining the traits and varieties to prioritize for advancement, using their direct engagement with farmers in field settings to assess their specific needs and challenges. The main advantages are:
- Varieties reach farmers faster by reducing the time from crossing to field testing;
- Testing during advancement increases the resilience of new varieties to pests and diseases i.e., higher quality of improved varieties;
- It can help coordinating breeding action between CGIAR and NARES by co-designing crosses and centralizing advancement i.e., higher resource efficiency.
The main disadvantage is the high costs associated with building and operating the facilities of the Platform. In addition, it requires expertise to operate. However, NARES personnel are currently being trained and educated in breeding and using the Speed Breeding Platform.
In conclusion, while improved crop varieties hold immense potential for climate resilience in agriculture and ensuring food security, their development remains a complex, time-consuming and resource-intensive process. The approach of the Speed Breeding Platform represents a promising step forward, by faster and more efficient crop breeding, facilitating a prompter solution.
Acknowledgement: the pilot facilities used to set up the ICARDA Speed Breeding Platform were funded by a project from the Third Call for Proposals under the Benefit-sharing Fund of the International Plant Treat for Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture entitled “Addressing the challenges of climate change for sustainable food security in Turkey, Iran and Morocco, through the creation and dissemination of an international database to promote the use of wheat genetic resources and increase genetic gains.” CFP 2014/2015-W3B-PR-18-Turkey. The final facilities were funded by a project from the Arab Fund for Economic and Social Development (AFESD) entitled “Modernization of ICARDA Breeding Programs".
ສະຖານທີ່: Rabat, ມໍລອກໂກ
ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ: 2021
ປີຂອງການສິ້ນສຸດ: n.a.
ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ

| ແມ່ນໃຜ / ພາກສ່ວນໃດ ທີ່ເປັນເຈົ້າການ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີການ? | ລະບຸ ພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ | ພັນລະນາ ບົດບາດ ໜ້າທີ່ ຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ |
| ນັກຄົ້ນຄວ້າ | CGIAR, ICARDA, and NARES breeders | They decide the plant populations to be advanced and the type of testing involved. |
| ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ສາກົນ | AFESD and FAO | The Benefit Sharing fund of the ITPGR (FAO) funded the growth chamber that was later used as pilot chamber to adapt and test the technology. Then, AFESD through the Breeding Modernization of ICARDA Breeding Programs provided the funds to build the new facilities. |
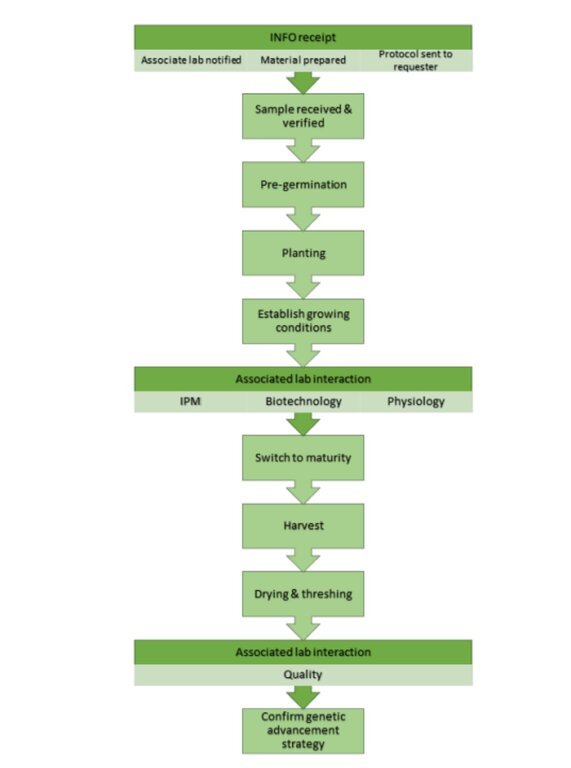
1: Receive information from requester (including material description, advancing strategy, traits, germplasm)
2: Receive and check samples: ICARDA Speed Breeding Platform staff inspect the samples prior to placing them in ICARDA Speed Breeding Platform Store 1 to identify and
address potential pests and other problems. Then, the samples are kept at -20°C for 24h to eliminate potential insect pests in the seeds.
3: Pre-germination: seeds are placed on the trays with systematic labeling. The results of pre-germination process are reported to the requester.
4: Growing conditions: The establishment of the growing conditions will depend on the crop and type of selection strategy applied.
5: Planting and transfer to growth room: Once the scientist confirms the planting list, the staff start planting on cones following the agreed protocol.
6: Trait collection: the facility manager will notify one week in advance the concerned labs when the plants are reaching the key growing stage set in the Project Protocol for trait recording or leaf sampling. Before maturity, the relevant disciplines are IPM, physiology and biotechnology. For traceability and data safety, data are recorded via Fieldbook Android Application, to be imported to BMS via BrApi.
7: Switch to maturity mode : After flowering the plants will enter the accelerated maturity process as per the protocols. Thus, the irrigation is stopped to force plant maturity. The requester will be notified of the entries with missing spikes or pods. At this stage, the FM will inform the quality lab to prepare for the reception of samples if established in the Project Protocol.
8. Harvest: The ICARDA Speed Breeding Platform staff harvest the plants following the requester selection (if any). The harvested spikes/pods are put in labeled bags showing: Crop, trial name, harvesting date, entry code and the barcode.
9. Drying and threshing: The harvested plants are placed in ovens for 2 days at 45°C, then threshed. If the Project Protocol includes it, the seeds are sent to the quality lab for end-use quality analysis. Otherwise, the seeds are kept in Store 1 for short term storage. The facility manager communicates the seed number of each entry to the requester, together with all recorded data.
10. Generation advancement strategy: Based on the data collected during the experiment, the requester confirms the next step of the genetic advancement strategy. In case a selection is made, the requester provides the required information by adding the information to the request form and send it to the RS to generate a new Project Protocol.
ການຕັດສິນໃຈໂດຍ
ການຕັດສິນໃຈບົນພື້ນຖານ
Breeding
Research in breeding is done by ICARDA, CGIAR centers and NARES centers
Through the Speed Breeding Platform, improved varieties are publicly released to farmers and seed cooperation. This allows them to use their land more sustainable.
Building on strong collaboration between international partners and national partners, breeding became more centralized making it more cost-effective. The reduced breeding time also contributes to higher resource efficiency.
Staff of NARES centers are trained in breeding.
Staff of NARES centers are trained in breeding.
Improved varieties are more climate resilient contributing to food security.
Improved varieties are better adapted to the changing climate.