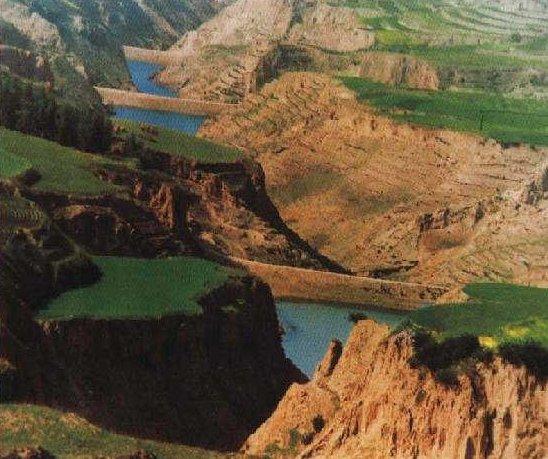
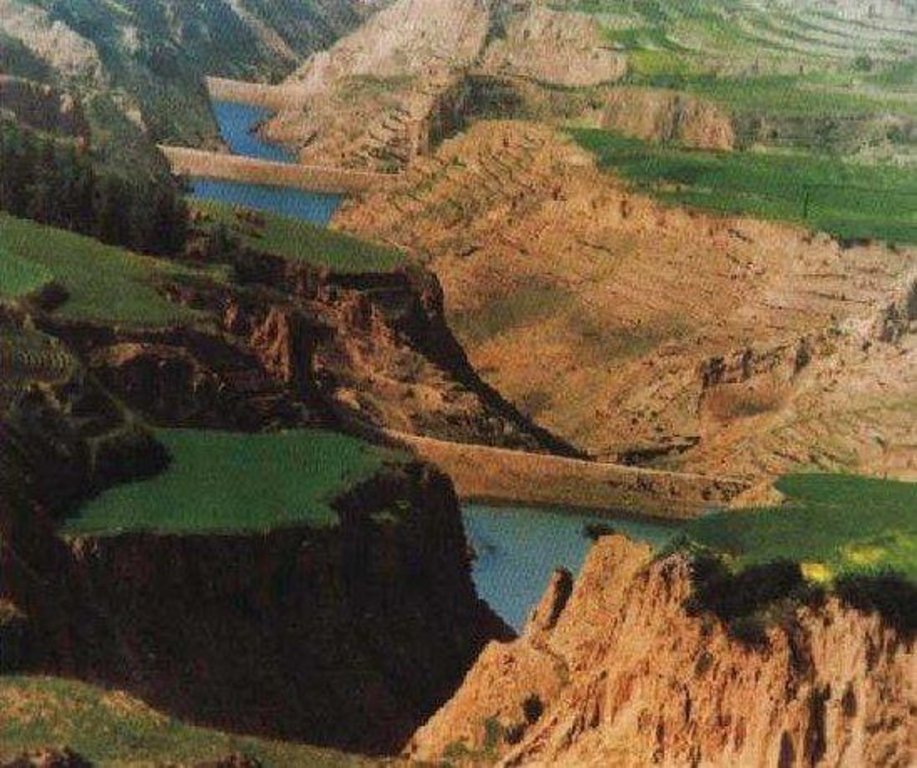
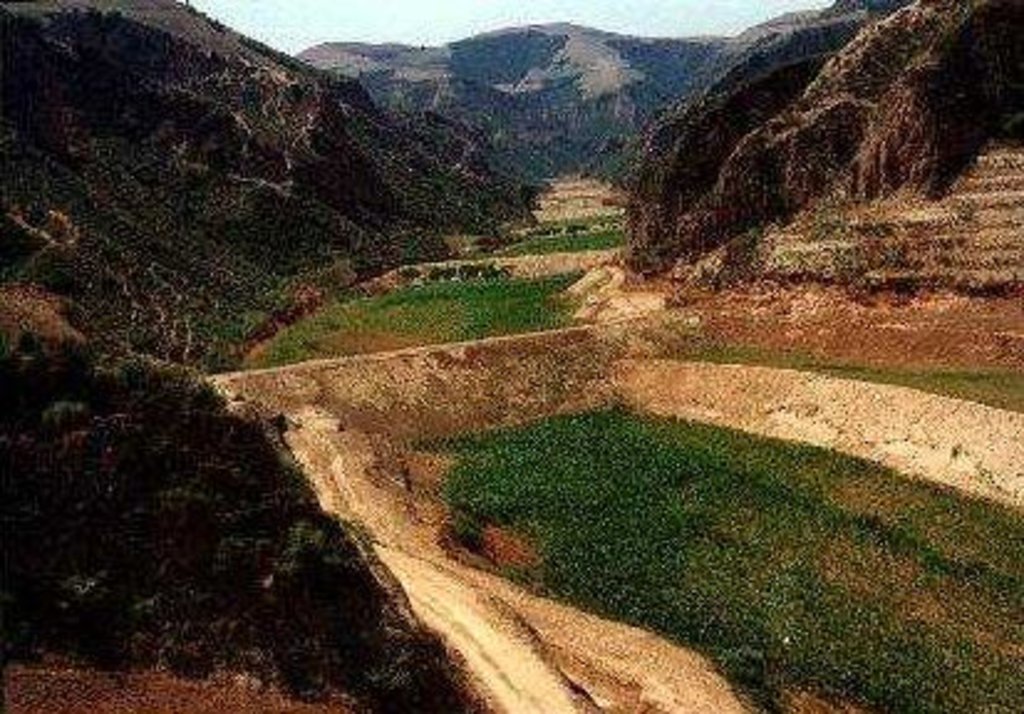
Falling Water Dam [ຈີນ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Yan ZHANG
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Laura Ebneter
approaches_2400 - ຈີນ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University (Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University) - ຈີນ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ (ຫຼາຍ) ກັບແບບສອບຖາມ (ຫຼາຍ) ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
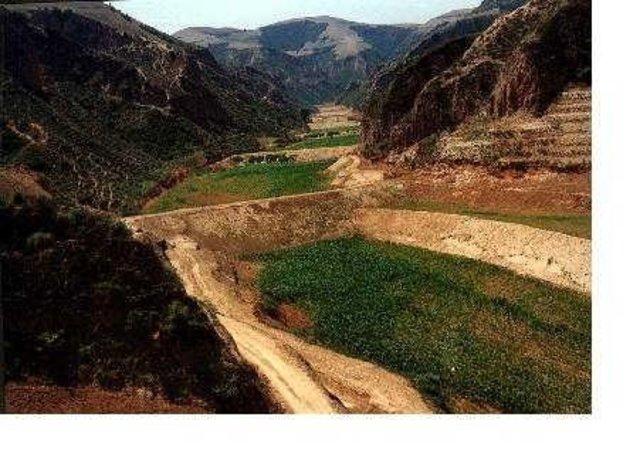

Auto-Flowing Slurry Dam [ຈີນ]
Auto-flowing slurry dams is filled with dense slurry by water flow from upland to maintain eroded soil particles and runoff.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Yan ZHANG
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
The falling water dams are widely built in the middle reach of the Yellow River, the typical dams are filled with dense slurry by water flow from upland. The approach is implemented mainly by government investment.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
Falling water filled dams distribute widely in the middle reaches of the Yellow River. They are used to store water, wrap sediment which results from soil and water loss. On the Loess Plateau, in addition to the conditions of deep gully and steep slope, earth above the top of the dams can be used to build dams. First, soil is loosed with squirt guns, explosion or manually digging. Then, water is pumped up to the loose earth so as to rush the soil down along transporting ditch, turning the soil into dense mud, to dams level surrounded by tamped banks. Under the press of gravity, the mud dehydrates, consolidates and becomes uniformly dense body of the dams. Compared with dams in other areas, the water power filled dams in the Yellow River basin are characterized by much denser mud, uniform particles and body texture, smaller transect of dams body, and wide applicability to soil materials such as sand soil, loess soil and weathering residue. The types of dams have widely applied to build middle and small reservoirs and silt arresters in the middle reaches of the Yellow River, playing an important role in agricultural production and reduction of sediment into the Yellow River.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
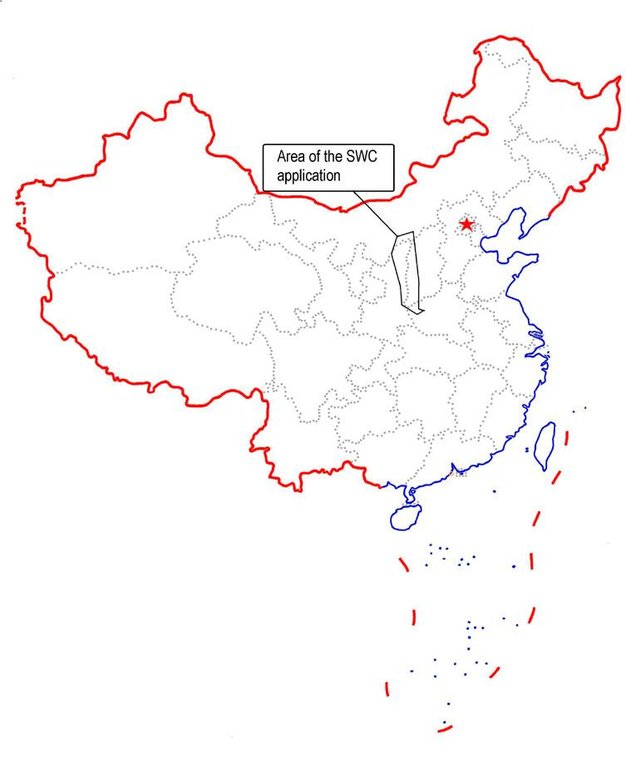
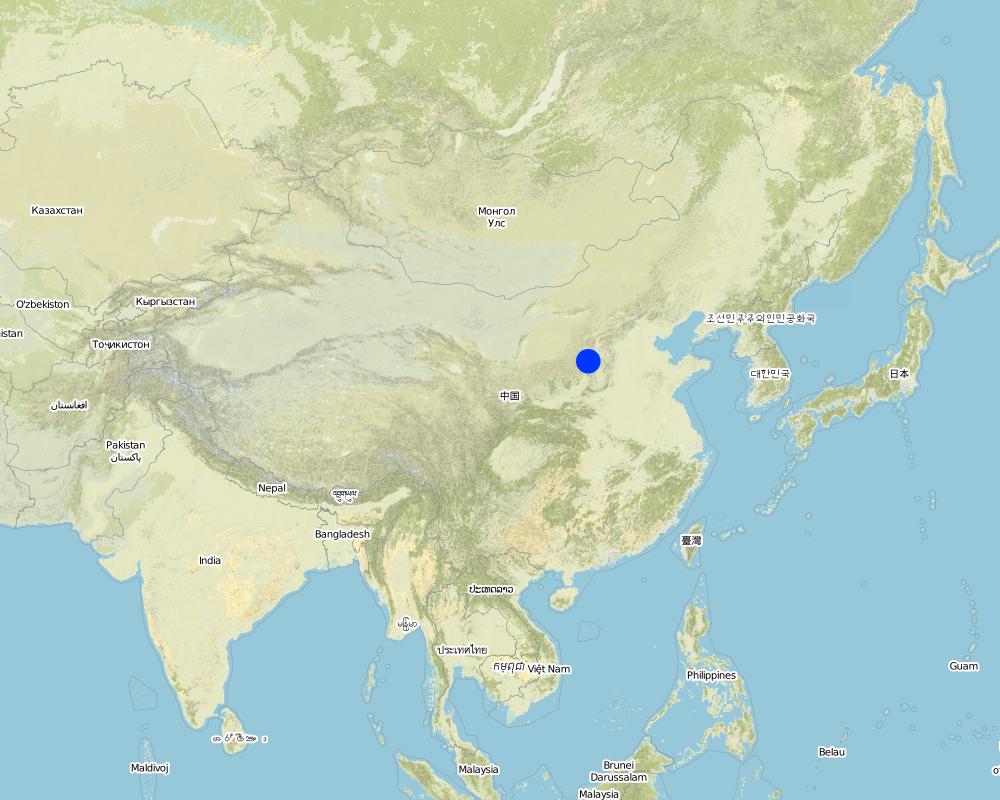
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ຈີນ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Shanxi, Shaanxi, etc.
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
1950
ປີທີ່ສີ້ນສູດ (ຖ້າຢຸດບໍ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ):
2005
2.7 ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
- ພື້ນເມືອງ / ທ້ອງຖີ່ນ
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
The objectives of the approach are to control soil & water loss so as to reduce flood; to make more crop land.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The main existing issues are unreasonable land use planning and low use rate; Lower standard of SWC design and poor quality in construction which would lead to flood danger; low administrative level and economic benefits.
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ມີຄວາມສາມາດ / ເຂັ້າເຖິງຊັບພະຍາກອນດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Only when government invests, the technology can be implemented
Treatment through the SLM Approach: investment
ກ່ຽວກັບກົດໝາຍ (ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ, ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ)
- ອໍານວຍ
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights helped a little the approach implementation: Because land resources belongs to state and land user can lease the land.
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ)
- ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ສາກົນ
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ການນໍາໃໍຊ້ເອງ | rapid/participatory rural appraisal; The approach is a traditional way to harvest water and wrap soils, SWC applied land users easy to understand and accept it if some subsidy being obtained. |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | workshops/seminars; After a program granted, implementing agency and local communities working together. |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ | responsibility for major steps; In practice, local communities are the major part to manager and carry out. |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການບໍ່ປະຕິບັດ | interviews/questionnaires; When monitoring procedures are clear, the local communities could do this and evaluate. |
| Research | ການຮ່ວມມື | Only can give some suggestions or questionnaire. |
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ນັກການເມືອງ / ຜູ້ນໍາ
ອະທິບາຍ:
Decisions on the choice of SLM Technology were made directive (top-down).
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by politicians / leaders (directive, top-down).
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
ຮູບແບບຂອງການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຕົວຕໍ່ຕົວ
- ເນື້ອທີ່ສວນທົດລອງ
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
How to maintain and reinforce the dams
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸວ່າການສະໜອງ ການບໍລິການ ໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ:
- ສູນຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ອະທິບາຍ / ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Name of method used for advisory service: Falling water dam show; Key elements: Selection of site for dam building, size of dam, materials and methods; 1) Mainly: projects own extension structure and agents, Partly: government's existing extension system 2) Mainly: projects own extension structure and agents, Partly: government's existing extension system; Extension staff: mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: demonstration
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; At each government level, there is a SWC office which is in charge of SWC activities including extension.
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
ລະບຸ ທາງສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃນລະດັບໃດ (ຫຼາຍ):
- ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
ລະບຸ ປະເພດ ຂອງສະໜັບສະໜູນ:
- ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ
- ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
- ອຸປະກອນ
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ນີ້້ແມ່ນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ ຂອງວິທີທາງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຫົວຂໍ້:
- ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ແລະ ກໍານົດ ຜູ້ໃດເຮັດການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ:
Pattern and standards for the dam design.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັດງົບປະມານທີ່ແນ່ນອນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານເອົາ:
- > 1,000,000
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national - The central government): 85.0%; local community / land user(s) (Village committee): 5.0%; other (World Bank): 10.0%
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
- ອຸປະກອນ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ | ງົບປະມານເຕັມສ່ວນ | subsidy |
- ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| community infrastructure | ງົບປະມານເຕັມສ່ວນ | financed by government |
ຖ້າແຮງງານ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ, ແມ່ນບໍ່:
- ການອາສາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
If managed by administrative way, land users' input are mainly voluntary, if through a project, usually paid in cash.
5.4 ສິນເຊື່ອ
ໄດ້ປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ພາຍໃຕ້ ວິທີການສໍາລັບກິດຈະກໍາ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນນຍົງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ເງື່ອນໄຂກໍານົດ (ອັດຕາດອກເບ້ຍ, ຈ່າຍຄືນ, ແລະ ອື່ນໆ) :
Interest rate charged: 4.0%; repayment conditions: After 4 or 5 years when SWC produces benefits, loaner should return.
Interest was lower than market rate.
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
They can harvest water and irrigate crops in dry seasons. Meanwhile, more crop land area is made.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ປະເດັນການຖືຄອງທີ່ດິນ / ສິດທິໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The policies of land contract distribute land to individuals so that land users who involved in SWC activities need to be organized together for implementation of the SWC. The organization need much time and hard work. The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. Administrative management can adjust and assort with this issue.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ແມ່ນ
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Raising crop production and return (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: applying fertilizers as possible as can) |
| water can be irrigated in dry seasons and drinks both for cattle and man (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: maintaining and repairing if needed.) |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Storing water (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: reducing vapour and leak as possible as can) |
| Enlarge cropland and raising yield (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: shifting food crops to cash crops) |
| reducing flooding (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: reinforce the dams timely) |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມູມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Costly and frenquently reinforce |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| The dams' quality are not high | standardization for design and construction |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Special Planning Of Soil And Water Conservation in Xinzhou Region , Shanxi Province, 1986-1990
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department, Beijing Normal University.
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
How to design the dry masonry dam in the Hanjiachuan watershed. Tianyuzhu, Wangzuliang. Beijing. Water conservation in Beijing, 2000
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department, Beijing Normal University.
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່

Auto-Flowing Slurry Dam [ຈີນ]
Auto-flowing slurry dams is filled with dense slurry by water flow from upland to maintain eroded soil particles and runoff.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Yan ZHANG
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ