Facilitation of micro-watershed management for farmers [ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
Фасилитасияи амалиётхои дехкон барои идораи микрохавза
approaches_2443 - ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Bronkal Daniel
daniel.bronkal@welthungerhilfe.de
ເຢຍລະມັນ
ຊື່ຂອງໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນດ້ານແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)ຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe - ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ (ຫຼາຍ) ກັບແບບສອບຖາມ (ຫຼາຍ) ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
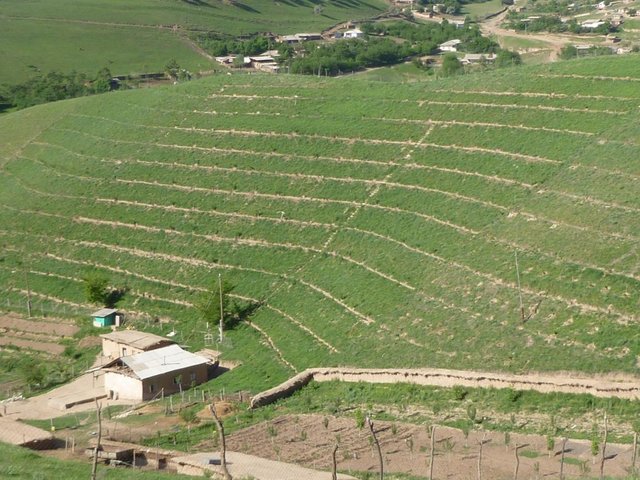

Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches [ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ]
Use of the SLM technology facilitates the development of bench terraces from contour channels by gradually removing soil material up the slope for an estimated 5 years until the terraces on the slope reach a desired width of 1.2 m.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
Relying on integrated watershed management principles, farmers were assisted by the project to implement soil and water conservation measures in a microwatershed.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
Aims / objectives: To strengthen the capacity of the community to plan and implement integrated natural resource management approaches, at micro watershed level in sustainable ways. These include; conserving soil by introducing actions to rehabilitate the eroded land, stop gully formation resulting from water run-off; enable water retention to secure soil moisture for a longer time period; mitigate effects of overstocking resulting in overgrazing; hoof erosion and soil compaction; reverse inappropriate agriculture practices towards more efficient and environmentally friendly management types; enable better employment and higher income generation to improve the livelihood standards and food security.
Methods: The project facilitated the following activities: Farmer participation, and using their initiative, community involvement in the planning, fundraising and implementation. Farmers increased their own contribution for material inputs, and a greater than 50% rate of adoption of the innovation was seen. The project also funded 'on the job' training, technical support, consultancy, and mediation of communication between parties.
Stages of implementation: 1. Awareness raising, 2. On the job training, 3. Watershed management activity planning, 4. Implementation, 5. Monitoring, 6. Evaluation, 7. Readjustment based on results, 8. Further replication in new area
Role of stakeholders: The DWHH Project had a leading role in initiation, orientation, awareness raising, mobilisation, training, consultancy, input provision and mediation of communication to land committee. Farmers have been actively participating, have provided labour input / financial contribution, provided indigenous knowledge and skills. Local authorities - providing land titles, participation in planning and decision making process Village Development Committee (VDC) - community mobilisation, information dissemination, input / finance documentation, fund raising.
Other important information: There are 5 households in the microwatershed. Almost 40 people live in all HH, all are Tajiks. Members of all households took part in discussion rounds and training. Non of HHs were strong enough to implement measures on own funds. One HH has rejected implementation of measures, due lack of capacity and lack of trust of the project's success. Women: farmers came to the discussions together with their wives, women took part in training, in implementing almost all of the adoption measures, and equally benefited from the project. However, they were not involved in decision making.
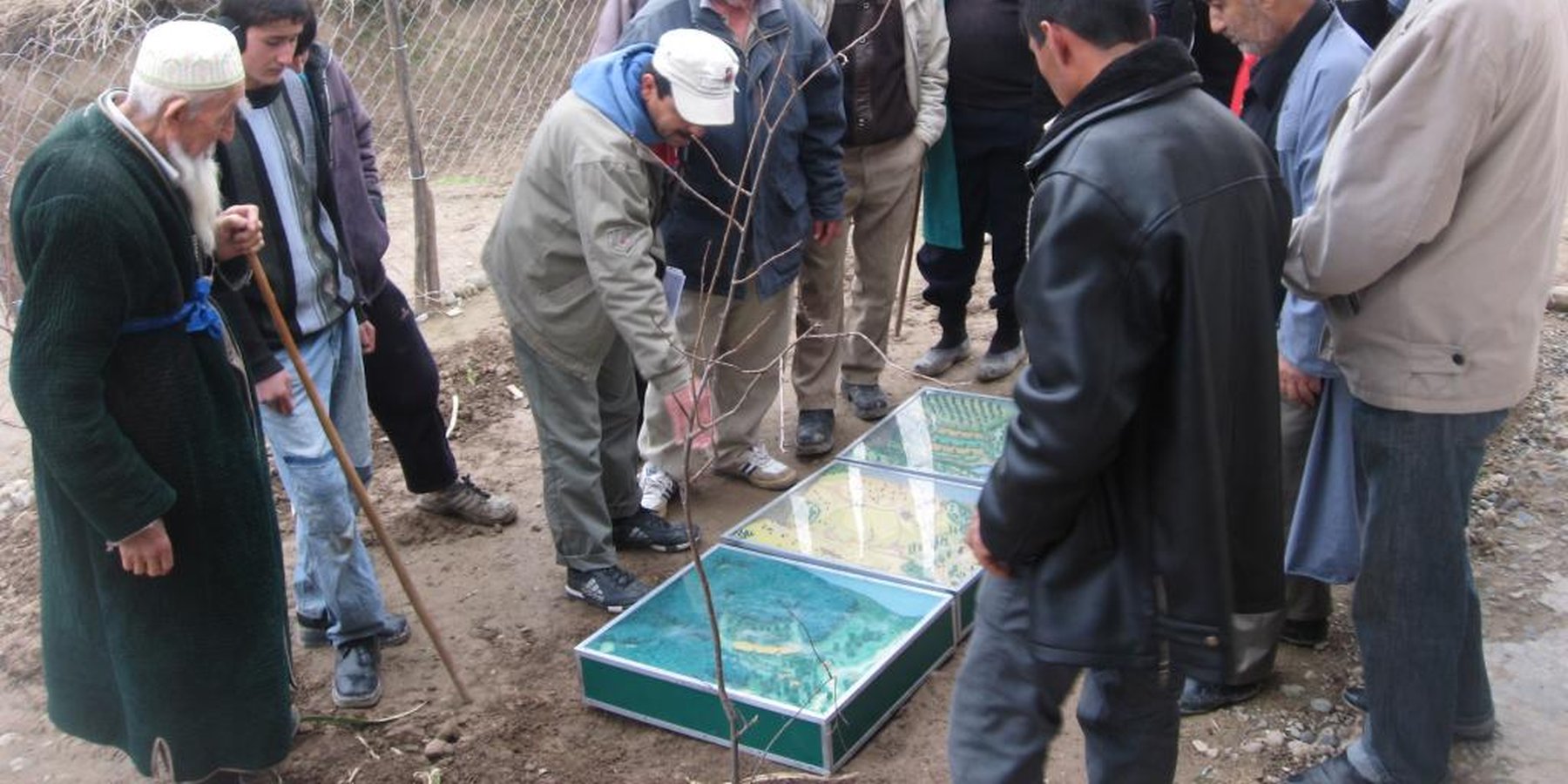
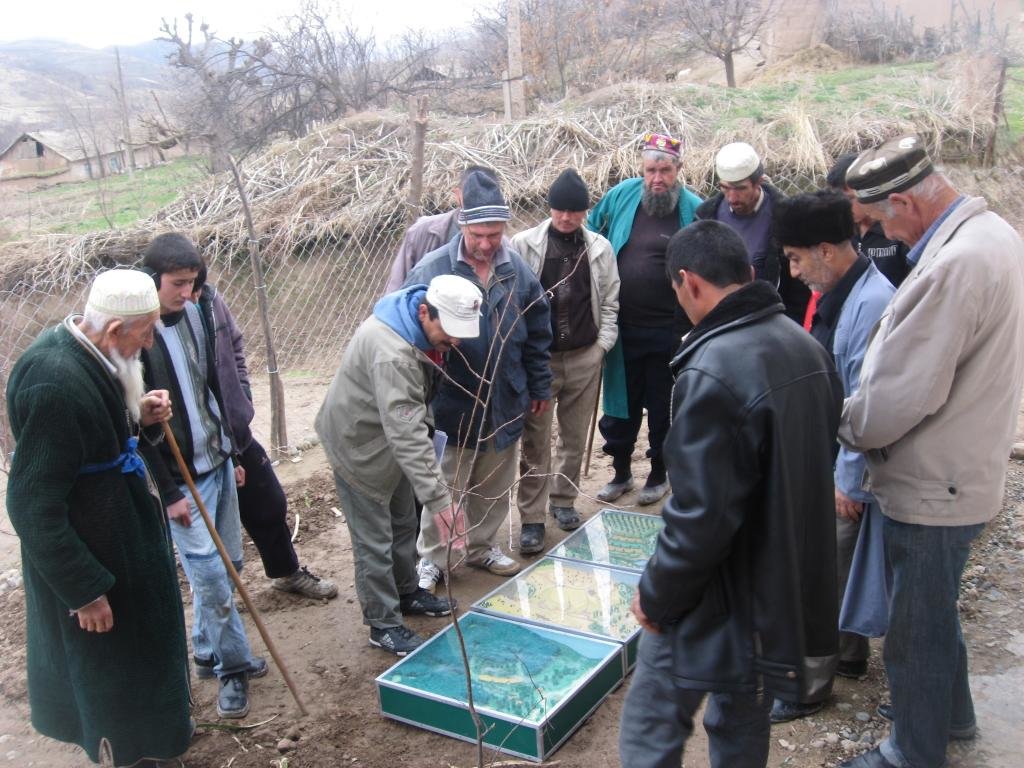
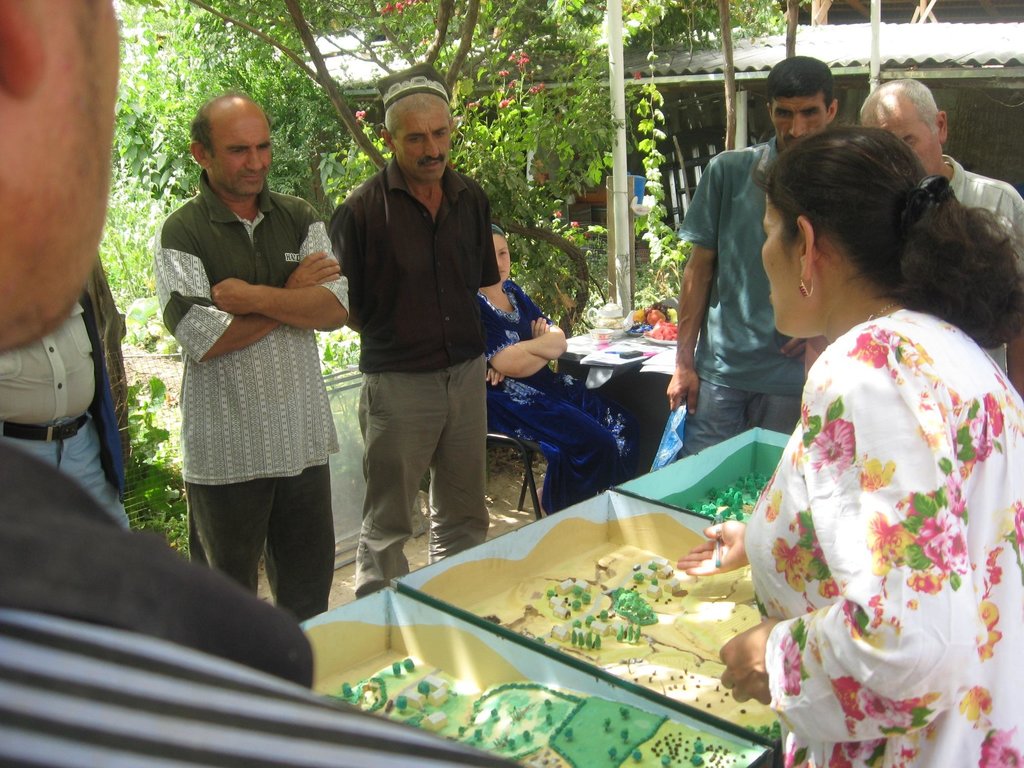
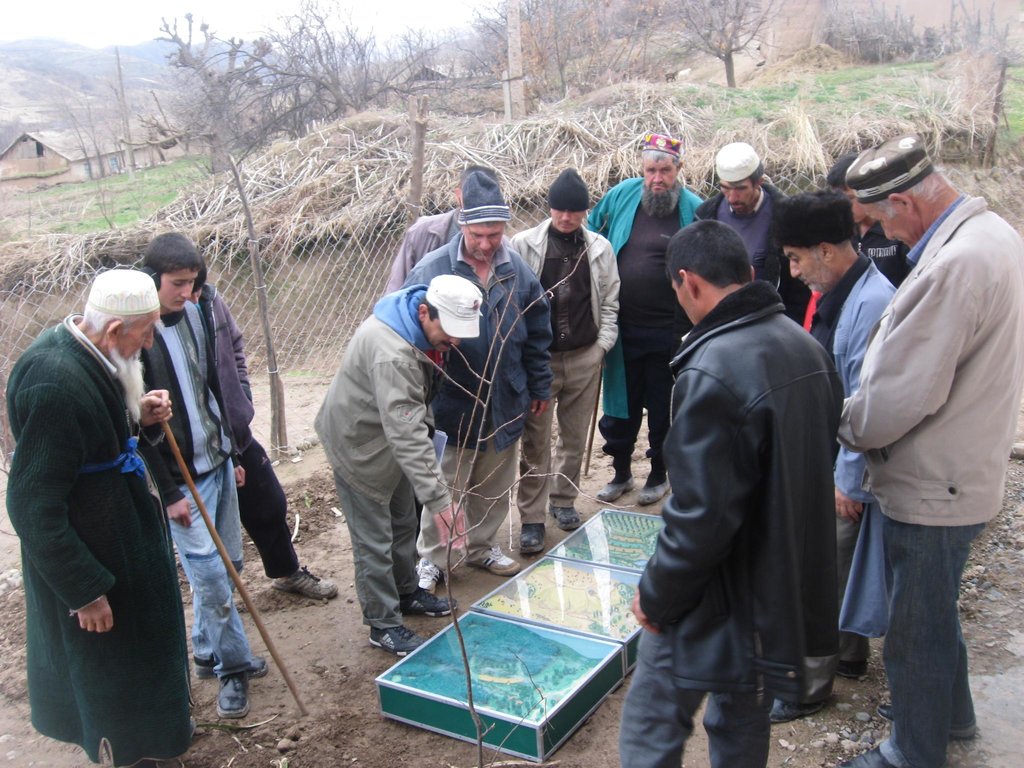
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Tajikistan, Khatlon
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Baljuvon / Khirob
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
2009
ປີທີ່ສີ້ນສູດ (ຖ້າຢຸດບໍ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ):
2011
2.7 ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
- ການລິເລີ່ມ ພາຍໃນປະເທດ ທີ່ຜ່ານມາ / ນະວັດຕະກໍາ
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities ( land use change, resource conservation, capacity building, focus on low cost local material, income generation, on the job training)
To assist farmers in the planning and implementation of activities for the conservation and improvement of the local land, to enable conditions for replication of the approach/technology, and to improve food production, and in the long run provide income generation.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Lack of land tenure rights implementation. Nominal state farm reorganisation. Low agricultural production - lands depleted of nutrients, very low yields, no crop rotation, overgrazing. Soil degradation, progressing land mass transport, gully formation. Lack of technical knowledge and awareness of soil & water conservation measures. Lack of cash to invest in development of land - just limited capacity to invest but need external financial input. Conflict over land use - livestock owners are against land enclosures. Poverty - underlying cause of general lack of potential to invest in development.
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ມີຄວາມສາມາດ / ເຂັ້າເຖິງຊັບພະຍາກອນດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Technology implementation has required a major investment for imported materials, like a metal net for fencing or fuel. Most farmers could not afford themselves to buy costly inputs. Moreover such inputs were rarely available on the local market.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The INGO covered the costs of 50% of each action, here mainly higher price inputs were paid off. The low-cost approach fits the financial capacity of the target group.
ການກໍ່ຕັ້ງສະຖາບັນ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Capacities of communities and local authorities to jointly plan and implement SLM activities at micro-watershed level was weak.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Knowledge improved on the complex interrelations in natural ecosystems (farmers and staff of local authorities). Project cooperation was not limited to those interested, there was inclusion of gov. structures (agriculture, land committee, ecology) committ
ກ່ຽວກັບກົດໝາຍ (ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ, ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ)
- ອໍານວຍ
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: On going legislative development in land tenure and farming provides good opportunities for implementation of the approach. But, ongoing nominal farm reorganisation and corruption at the local level, together with farmers reduced awareness of their land use rights requires more effort, time and funds in the application of SLM approaches. In this situation, DWHH has a good reputation in the district administration and with locals and so this helped overcome many barriers more easily.
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Implementing the land tenure law and the privatisation of state farms is still a difficult process with many inconsistencies for people claiming a land title in the area.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: There are a few instances where the project was able to support farmers in getting land-titles to degraded land plots which they then had to rehabilitate using SLM technologies.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Village Development Committee, farmers
Men have played bigger role in the organisation of activities, in the implementation of more manual work, whereas, women took part in the lighter work and in routine maintenance.
Most of the participating households live below the poverty line.
Farmers joined under one microwatershed approach, male (wife assisted), middle age, Tajiks, rural middle class.
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ທີ່ປຶກສາດ້ານກະສິກໍາ
Project TAJ1068 staff, and an international consultant
- ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ບໍ່ຂື້ນກັບລັດຖະບານ
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe
- ອໍານາດ ການປົກຄອງທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Subdistrict, District Heads, Agriculture, Land committees, Forestry department
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ການຮ່ວມມື | farmers meeting through VDC, orientation explaining goals, objectives, advertising in the local news paper, information boards in 6 watersheds |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | on site planning with farmers |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຮ່ວມມື | training on the job, material input and labour provision, cross visits |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | data input, open to monitoring, communication on ongoing activities, collaboration while monitoring and evaluation |
| Research | ການຮ່ວມມື | collaboration in the test for Acacia seed germination on the plot |
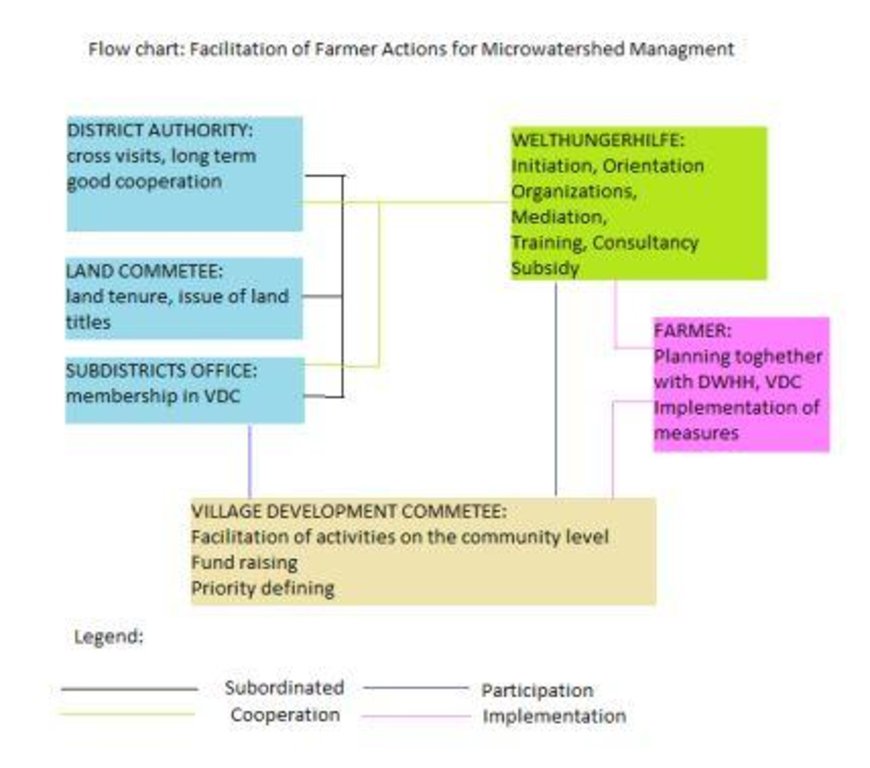
3.3 ແຜນວາດ (ຖ້າມີ)
ການອະທິບາຍ:
Flow chart depicts the major actors involved during implementation of the approach. The relationship between stakeholders and primary functions is described as well.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov (16, Firdavsi Street 734003, Dushanbe)
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ຫຼັກດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ມີການຕິດຕາມປຶກສາຫາລືກັບຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ອະທິບາຍ:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. Focused on principles of farmer participation, self motivation and self help.
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
- ພະນັກງານພາກສະໜາມ / ທີ່ປຶກສາ
- local land and agriculture departments, village development committee
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້, ໃຫ້ລະບຸເພດ, ອາຍຸ, ສະຖານະພາບ, ຊົນເຜົ່າ, ແລະ ອື່ນໆ:
Land users: 5 men, 5 women, 30 to 50 years old, all Tajiks, all families.
ຮູບແບບຂອງການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ການເຮັດຕົວຈິງ
- ເນື້ອທີ່ສວນທົດລອງ
- ກອງປະຊຸມ
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
Use of the A-frame, watershed model, tree planting in contour ditches, intercropping
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸວ່າການສະໜອງ ການບໍລິການ ໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ:
- ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
ອະທິບາຍ / ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
A chain of meetings with international consultants from India and Nepal: Key elements: consultation on watershed concepts and watershed choice, capacity building in strategy design , draft development plan for watershed management
The consultants were : Yashvant Tkhakur, India; Jaganat Joschi, Nepal
Advisory service is inadequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; the govenment branches need more development and organisation to become able to manage land conservation activities; an independent advisory service is not in place, the only potential still exists within the DWHH Project
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
ລະບຸ ທາງສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃນລະດັບໃດ (ຫຼາຍ):
- ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
ລະບຸ ປະເພດ ຂອງສະໜັບສະໜູນ:
- ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ໃຫ້ລາຍລະອຽດເພີ່ມເຕີມ:
Village development committee (VDC), use of locally available resources, focus on low cost
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations; indicators: space used for technology
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: fodder produced cent/ha, vegetables
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: labour availability, health status
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: tree planting
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: soil degradation, gully formation
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: monthly trends, how hardworking they were, gender
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations; indicators: technology adaptation based on own experience
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Change of the design - adjustment of the contour boundary based on experience on the plot; Adjusting of tree planting in contour ditches according to the topography
4.5 ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ນີ້້ແມ່ນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ ຂອງວິທີທາງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຫົວຂໍ້:
- ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ແລະ ກໍານົດ ຜູ້ໃດເຮັດການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ:
Tests were completed on the germination of Acacia seeds in two different setups: on the demo plot of the project and on the farmers plot.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັດງົບປະມານທີ່ແນ່ນອນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານເອົາ:
- 2,000-10,000
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international non-government (material input: tools, fencing, planting material, diesel. etc.): 50.0%; local community / land user(s) (the rest of material input, labour, time (mainly low cost inputs)): 50.0%; other
5.2 ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານ ການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ, ເງື່ອນໄຂ ແລະ ຜູູ້ສະໜອງ (ຫຼາຍ):
50% of activities were subsidised by the DWHH Project TAJ1068
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
- ອຸປະກອນ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ເຄື່ອງມື | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | hand tools |
- ກະສິກໍາ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ແນວພັນ, ແກ່ນພັນ | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | |
| manure | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | |
- ການກໍ່ສ້າງ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| metal net | ງົບປະມານເຕັມສ່ວນ | |
- ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ໂຮງຮຽນ | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | school, 2 rooms thermo insulated |
- ອື່ນໆ
| ອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ) | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel, diesel, oil | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | 1/4 of the need |
ຖ້າແຮງງານ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ, ແມ່ນບໍ່:
- ການອາສາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Rennovation of the chool for the children was a strong and vital argument demanding considerable investment. This was competed with the implementation of the SLM technology, where farmers had to make a choice; either spend the available funds for the school or continue with the SLM. The project has provided partial financial and technology support to farmers which made it easy to overcome the school situation and concentrate again on SLM activities.
5.4 ສິນເຊື່ອ
ໄດ້ປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ພາຍໃຕ້ ວິທີການສໍາລັບກິດຈະກໍາ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນນຍົງບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.5 ສິ່ງຈູງໃຈ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອງມືອື່ນໆ
ການສົ່ງເສີມ ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ໄດ້ສະໜອງສິ່ງກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ:
Village development committee (VDC), use of locally available resources, focus on low cost
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Most of the previous types of damage caused by water runoff were prevented. Trees grew in a landscape where they didn't before, due to long dry periods and high livestock pressure from grazing. There was a change in the farmer's attitudes, who prior to witnessing the technology were highly sceptical
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ທາງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ເສດຖະກິດບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Only four families out of five in the microwatershed were able to receive the opportunity to improve their socio-economic status in the long term as a result of the project.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ປະເດັນການຖືຄອງທີ່ດິນ / ສິດທິໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The approach has added to the farmers self belief, ensured that they will effectively use existing land resources, and following the sustainable improvement of soil conditions, should add good potential for their own economic growth.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Farmers from the neighbouring watershed, came repeatedly to observe the plot. Three of these farmers adopted the technology themselves in the following year.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Vegetables could be grown to supply more food to the family, a good amount of hay could be prepared for winter time, more benefits could be seen in the long run with extra fruits and fire wood
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
This was a pilot project, and only looked at poverty alleviation on a small scale. This technology has the potential to reduce poverty in the long term on a bigger scale.
6.2 ແຮງຈູງໃຈຫຼັກຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນການປະຕິບັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຜະລິດເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ
- ກໍາໄລເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ (ຄວາມສາມາດ), ການປັບປຸງຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ, ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ, ອັດຕາສ່ວນ
- ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນພາລະວຽກ
- ການຊໍາລະເງິນ / ເງິນອຸດໜູນ
- ຄວາມຮັບຮູ້ ທາງສີ່ງແວດລ້ອມ
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າ ໄດ້, ອະທິບາຍເຫດຜົນ:
Yes, but only those who would have enough funds to implement costliest part of technology: the perimeter fencing (metal net). Overall, most farmers will happily continue with the implementation of the technology, if the initial costs are subsidised. There are also a few new farmers who were able to replicate the technology completely by themselves.
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| The approach to share the implementation costs, consideration of general social needs, good project communication. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: More donor funding would be required to support more local farmers in the future. ) |
| The approach has enabled a range of innovations that were never used before: contour lines, mulching etc. |
| The approach has helped to reveal the local problems related to technology implementation. It has helped participants to learn about the strength and potential of local land users in the implementation of the SLM approach and technology. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Lessons learned must be applied in the future implementation of SLM actions and replication. ) |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| The approach enabled the use of both international and local knowledge. Attention was given to capacity building and sustaining the organisation, as well as the mobilisation structure (VDC) at the grass roots level. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: All the knowledge experience gained from the project has to be documented and disseminated for replication.) |
| The reputation of DWHH, and long term collaboration with the Baljuvon district administration played a very positive role in the successful implementation of the conservation approach. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Members of the local authority should be continuously involved in training, capacity building and planning measures. ) |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມູມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Sometimes the approach enabled unproductive discussions during the planning and designing phases. | Project ambitions and objectives have to be adjusted to the local situation and farmer capacity and needs. |
| Farmers were facing situations where their other social and economic needs were strongly competing with the objectives of the project. | Some additional funds, may need to be provided and more awareness of the farmer's situations need to be taken into account. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| The approach required a lot of funding until the majors actors were trained and had the capacity to implement the conservation measures. |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Grant Application Form to EU Commission: 'Individual incomes & Improving Living Standarts in Khatlon and Sughd Regions', TajikistanSketch map of Khirob MicrowatershedInterim Narrative Report 01.05.2009-30.04.2010 Project TAJ 1068
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
DWHH Regional Office, Dushanbe
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Sketch map of Khirob Microwatershed
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
DWHH, Baljuvon
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Interim Narrative Report 01.05.2009-30.04.2010 Project TAJ 1068
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
DWHH, Baljuvon
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່

Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches [ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ]
Use of the SLM technology facilitates the development of bench terraces from contour channels by gradually removing soil material up the slope for an estimated 5 years until the terraces on the slope reach a desired width of 1.2 m.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ