Eligibility Criteria and Environmental Planning Tools for SLM [ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Nandita Jain
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
approaches_2578 - ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
- ສະຫຼຸບສັງລວມຢ່າງທັງໝົດທີ່ເປັນ PDF
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ PDF ເພື່ອສັ່ງພິມ
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ ຢູ່ໃນ browser
- ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ສະບັບເຕັມ (ບໍ່ມີແບບຟອມ)
- Eligibility Criteria and Environmental Planning Tools for SLM: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
- Eligibility Criteria and Environmental Planning Tools for SLM: Aug. 10, 2017 (inactive)
- Eligibility Criteria and Environmental Planning Tools for SLM: July 7, 2017 (inactive)
- Eligibility Criteria and Environmental Planning Tools for SLM: July 7, 2017 (inactive)
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Mott Jessica
World Bank
ສະຫະລັດອາເມລິກາ
ຊື່ຂອງໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນດ້ານແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)ຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
World Bank (World Bank) - ສະຫະລັດອາເມລິກາ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
19/11/2007
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ (ຫຼາຍ) ກັບແບບສອບຖາມ (ຫຼາຍ) ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ

[ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ]
None
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: MIZROBSHO AMIRBEKOV
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
Using eligibility criteria and participatory environmental analyses for selecting and assessing SLM investments.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
Aims / objectives: As part of the Community Agriculture and Watershed Management Project (CAWMP), tools were developed to ensure farmers chose appropriate SLM technologies while preparing Community Action Plans (CAPs) and to improve environmental assessments during CAP preparation and in rural investment activities.
Methods: Eligibility Criteria: CAWMP financed small grants for three types of rural production investments: farm productivity, rural infrastructure, and land resource management (the largest type). The eligibility criteria for these grants included meeting at least one of the following impacts on fragile lands: • Prevent/reduce soil erosion • Increase vegetative cover through perennial crops and pasture • Provide soil and moisture conservation • Improve soil quality • Improve water use efficiency • Increase sustainable fodder/wood supply • Increase sustainable renewable energy supply • Increase integrated pest management These criteria ensured an environmental focus, and kept the grant proposals consistent with a list of eligible activities which is critical for a large-scale, community-driven project such as CAWMP. The criteria helped avoid diversion of grant funds to investments not directly related to land sustainability. Combining income-generating investments with environmental criteria encouraged sustainable land use by addressing vital interests of local people. The criteria were used to monitor local environmental impacts. Project arrangements provided for land use right certificates to beneficiaries with Project-financed investments on sloping lands, giving them a stake in the sustained productivity of their land. Traditionally such land use right certificates were issued only for irrigated and other valley areas. The Project financed a total of almost US$ 5.3 million in grants for land resource management, through almost 2,300 subprojects, benefitting over 43,000 households.
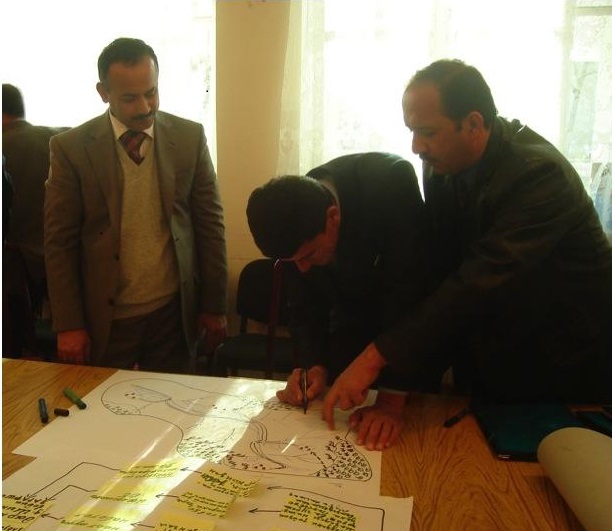
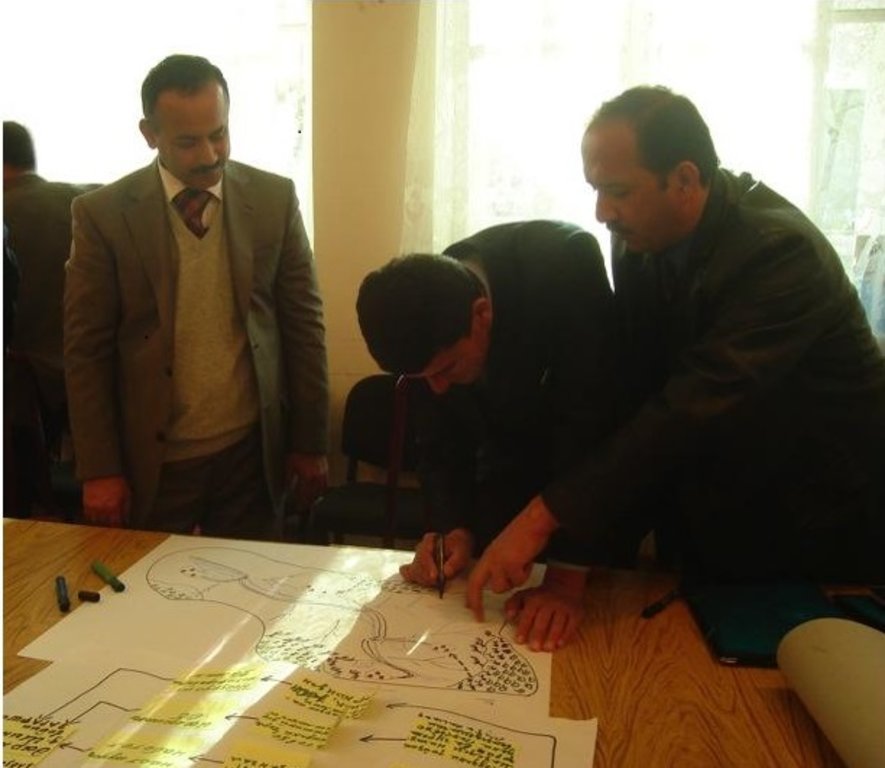
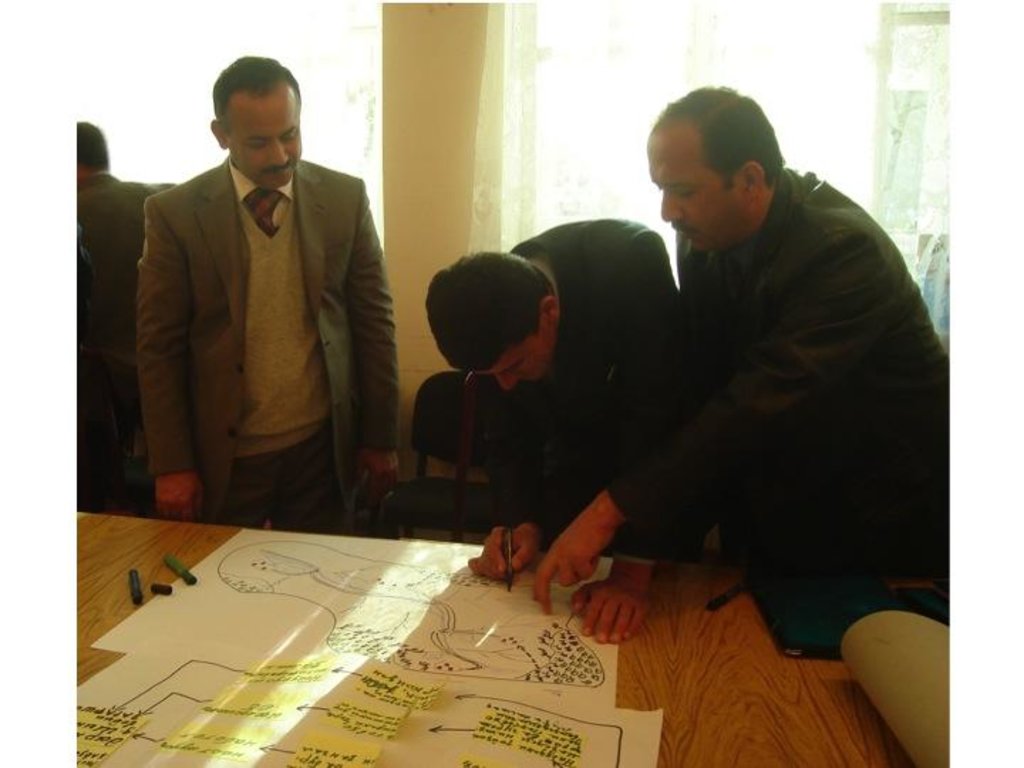
Stages of implementation: Participatory environmental analyses. A review of investment proposals and field activities in 2007 revealed that farmers were not capable of properly assessing their local land management problems, identifying the most environmentally appropriate investments or actions, nor monitoring their effectiveness. Tools were developed for project partners and officials to address these concerns including: 1) Developing Conceptual Models of Local Environments/Watersheds; 2) Mapping Local Environments/Watersheds and Associated Threats; 3) Identifying and Ranking Environmental Threats; and 4) Community Environmental Assessment. More than 50 persons attended the two-day interactive training course on the use of the tools. Detailed guidelines for facilitators and trainers to use the tools were prepared in Tajik and Russian. While the training could not influence many of the SLM-related investments already submitted for funding, participants urged that similar training be conducted at the inception of SLM-related projects and that the tools be requirements of SLM planning.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
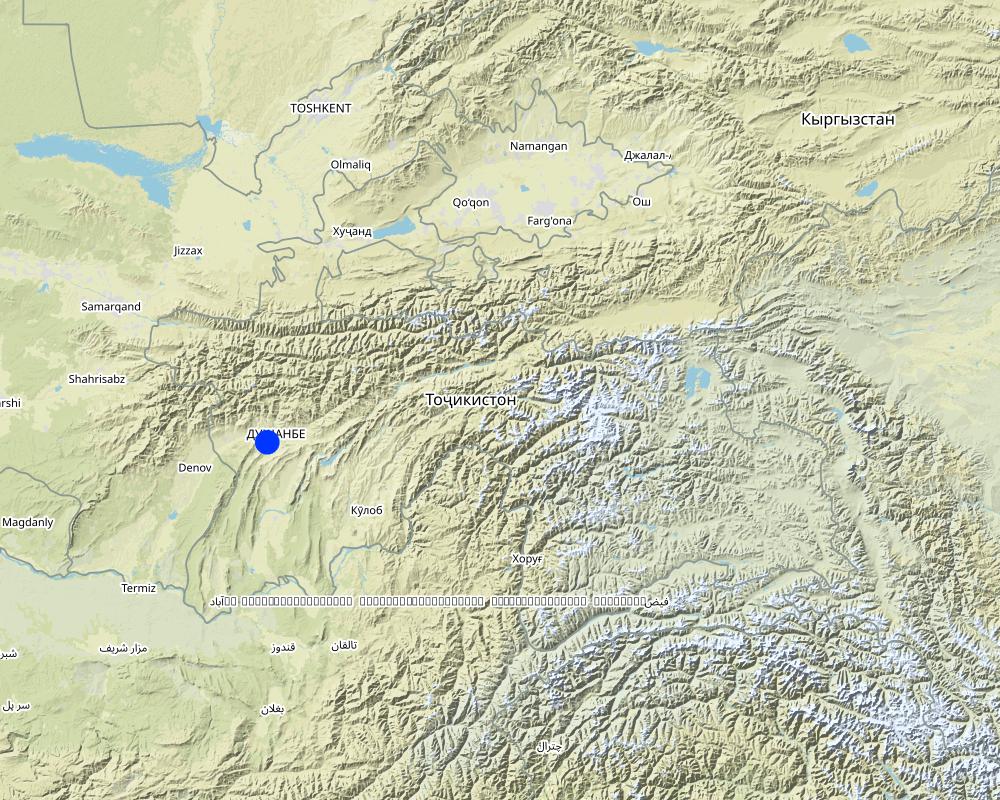
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Sughd, RRS, Khatlon, GBAO
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Jirgital, Tajikibad, Vanj, Aini, Matcha, Penjikent, Danghara
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The Community Agriculture and Watershed Management Project was implemented in four project sites/watersheds - Surkhob, Toirsu, Vanjob and Zarafshan - and included 7 districts/raions and 39 sub-districts/jamoats. The total catchment area was 35,000km2. Total arable, farm and pasture land was approximately 319,500ha
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
2005
ປີທີ່ສີ້ນສູດ (ຖ້າຢຸດບໍ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ):
2012
2.7 ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
- ພາຍໃຕ້ໂຄງການ / ແຜນງານ
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (participatory environmental analyses, eligibility criteria, monitoring, assessment, training, guidelines, )
Application of the criteria and tools to help ensure that proposed rural investments in Community Action Plans kept their environmental management focus.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Inappropriate investments with questionable SLM benefits proposed in CAPs. Uneven, sometimes, missing focus on environmental risks and benefits in small grant proposals for rural production investments. Lack of skills in and knowledge of participatory environmental appraisals.
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ການກໍ່ຕັ້ງສະຖາບັນ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Legacy of command-economy focus on infrastructure investments for improving land management and agriculture
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Tools to analyse a range of environmental aspects of land management and propose alternative technologies and approaches, training for project implementers and stakeholders.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Lack of appropriate analyses of environmental relationships, threats, risks and impacts in choice and design of investment proposals at the village level
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Establishing eligibility criteria, development of participatory learning tools on environmental issues, training for project partners and stakeholders.
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Jamoat (Sub-district) Development Committees
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ທີ່ປຶກສາດ້ານກະສິກໍາ
Facilitating organization staff, local government specialists, project field staff
- ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ)
Project Management Unit (PMU), Project Coordination Units (PCUs)
ຖ້າຫາກມີຫຼາຍພາກສ່ວນທີ່ເຂົ້າຮ່ວມ ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ອົງການທີ່ເປັນຫຼັກ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
PMU
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ບໍ່ມີ | |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ບໍ່ມີ | |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Villagers used criteria for selecting and designing rural investments. JDCs received training in environmental tools |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Local JDCs assisted in assessment of rural production investments using eligibility criteria as well as other factors. |
| Research | ບໍ່ມີ |
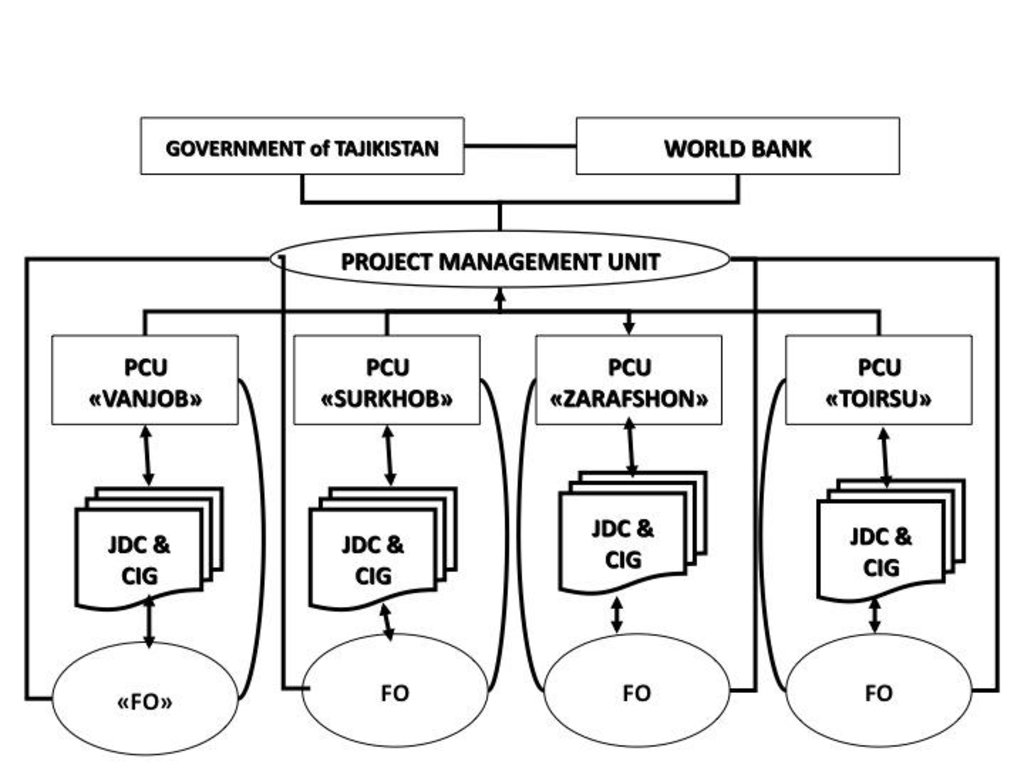
3.3 ແຜນວາດ (ຖ້າມີ)
ການອະທິບາຍ:
CAWMP - Implementation Arrangements and Project Partners
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Project Management Unit (Dushanbe)
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນຫຼັກ, ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ໂດຍຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ອະທິບາຍ:
Common Interest Group members and technical specialists from the respective facilitating organisation and project coordination unit made decisions on the choice of SLM technologies in rural investments proposed in Community Action Plans. A number of SLM technologies could be used in any one proposal.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Common Interest Group members and technical specialists from the respective facilitating organisation and project coordination unit made decisions on the method/s for implementing SLM technologies in any one proposal.
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ພະນັກງານພາກສະໜາມ / ທີ່ປຶກສາ
- Jamoat (sub-district) Development Committees
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
Participatory environmental analyses, assessing rural investments including use of eligibility criteria.
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
ລະບຸ ທາງສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃນລະດັບໃດ (ຫຼາຍ):
- ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
ໃຫ້ລາຍລະອຽດເພີ່ມເຕີມ:
See TAJ047 on the role and activities of Jamoat (sub-district) Development Committees
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Use of tools aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Types of investments proposed, Quality of proposals,
Application of criteria aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Types of proposals, use in assessment of rural investments
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Not directly relevant
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: No directly relevant
4.5 ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ນີ້້ແມ່ນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ ຂອງວິທີທາງບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັດງົບປະມານທີ່ແນ່ນອນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານເອົາ:
- 10,000-100,000
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (World Bank and Global Environment Facility): 95.0%; government (Estimate of co-financing ): 5.0%
5.4 ສິນເຊື່ອ
ໄດ້ປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ພາຍໃຕ້ ວິທີການສໍາລັບກິດຈະກໍາ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນນຍົງບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
More appropriate investments chosen, criteria contributed to environmental monitoring of rural investments.
Not directly relevant
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Interest shown by organisations and projects in participatory tools.
6.2 ແຮງຈູງໃຈຫຼັກຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນການປະຕິບັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຜະລິດເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ
- ລວມເຂົ້ານໍາກັນກັບການເຄື່ອນໄຫວ / ໂຄງການ / ກຸ່ມ / ເຄືອຂ່າຍ
- ຄວາມຮັບຮູ້ ທາງສີ່ງແວດລ້ອມ
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າ ໄດ້, ອະທິບາຍເຫດຜົນ:
Land-users may require facilitation assistance to conduct environmental analyses, but some individuals and groups may be able to do so independently. Some JDC members may be able to assist. Eligibility criteria along with list of activities can used in other projects or independently by beneficiaries.
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| JDCs learned more about environmental relationships, impacts beyond immediate areas, as well as biodiversity aspects of SLM. Also resulted in shifts in thinking about causes of degradation and effects, and so the choice of appropriate activities (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ensure that training in the tools, monitoring and related activities are given at the start of projects and programmes.) |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Criteria were understandable and integrated into monitoring of project rural investments. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Disseminate formats for investment monitoring. Criteria can be also be integrated into appraisal stages for rural investments. ) |
| Tools highlighted environmental issues neglected during initial participatory rural appraisals. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue dissemination of tools, and further refine some tools as needed.) |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Limited impact of tools training due to project implementation schedule. | Provide training in initial stages of projects. |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Environmental Assessment Templates for Rural Production Investments in CAWMP (2009, English, Russian and Tajik)Tools for Participatory Environmental Analyses (2007, Separate Guidelines for Trainers and Facilitators, English, Russian and Tajik)Eligible and Ineligible Activities for Rural Production Investments in CAWMP (2007, English and Russian)Outline and Assessment for Training in Tools for Participatory Environmental Analyses (2007, English)
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Project Management Unit
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Tools for Participatory Environmental Analyses (2007, Separate Guidelines for Trainers and Facilitators, English, Russian and Tajik)
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Project Management Unit
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Eligible and Ineligible Activities for Rural Production Investments in CAWMP (2007, English and Russian)
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Project Management Unit
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Outline and Assessment for Training in Tools for Participatory Environmental Analyses (2007, English)
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Project Management Unit
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່

[ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ]
None
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: MIZROBSHO AMIRBEKOV
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ