Reduced tillage [ເອສໂຕເນຍ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Endla Reintam
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch
minimeeritud harimine
technologies_3120 - ເອສໂຕເນຍ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ()
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Aruksaar Ahti
+37253448354
aruksaar@hot.ee
Viljameister OÜ
Tartumaa, Konguta vald, Kobilu küla, 61201
ເອສໂຕເນຍ
researcher:
researcher:
Lauringson Enn
+37253402207
enn.lauringson@emu.ee
Estonian University of Life Sciences
Kreutzwaldi 1, 51014 Tartu
ເອສໂຕເນຍ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences (IAES/EMÜ) - ເອສໂຕເນຍ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
18/05/2017
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
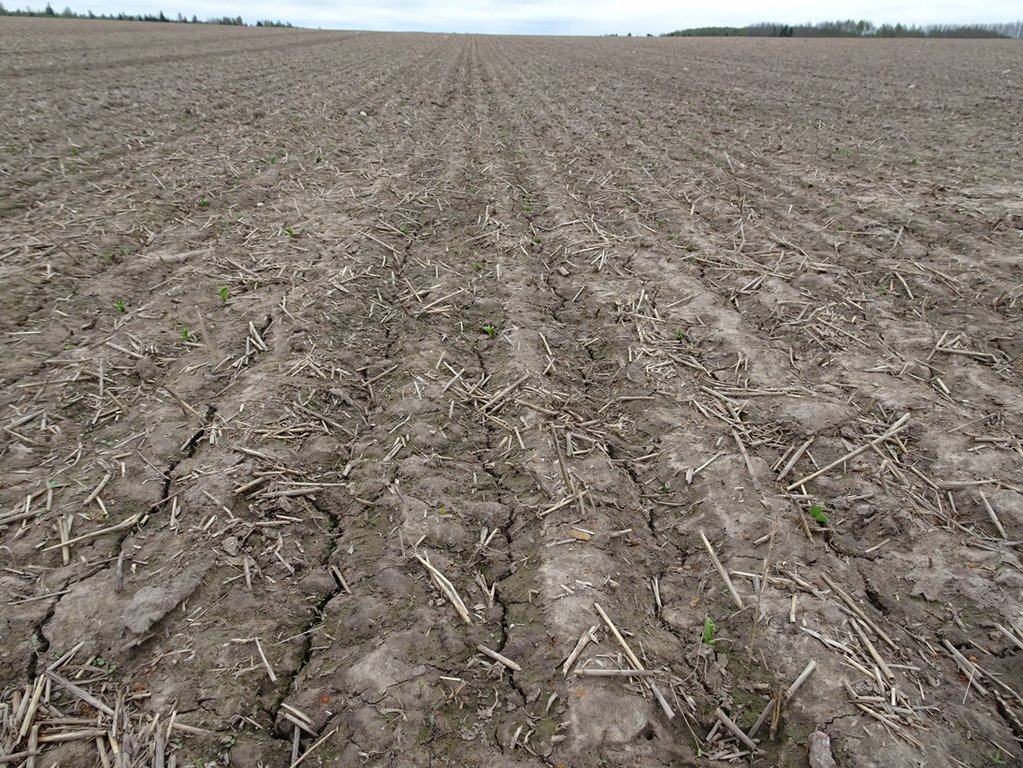
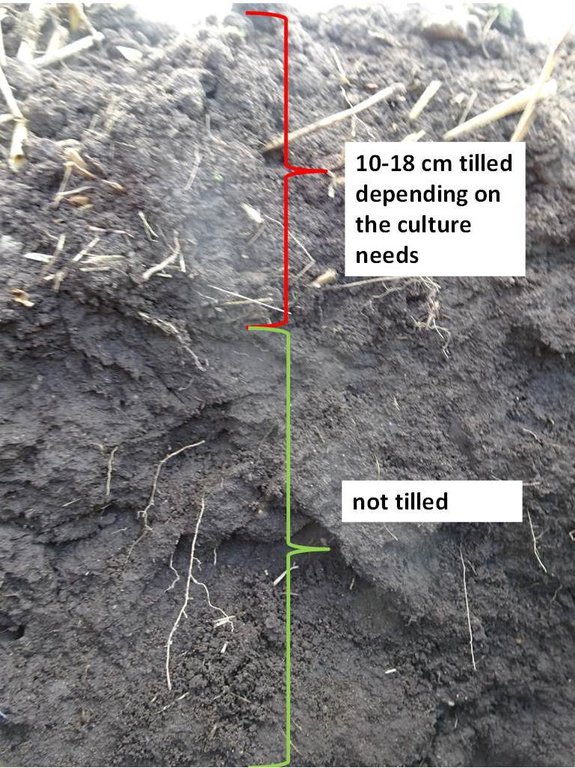
Reduced (minimum) tillage is a tillage method that does not turn the soil over. Usually only the upper 10-18 cm of the soil surface is tilled.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
The technology is applied in sub-humid climate with an average of 696 mm of precipitations per year, from which more comes from July to October and less in March and April. Average annual temperature is +4 C, length of the growing period is 180-195 days. The territory is mostly flat, the southern part is hilly with slopes of 6-10%. Average altitude from the sea level is 50 m. About half of the Estonian territory is above 50 m and half is below it. Soils are from very shallow (less than 0.1 m) in the north to very deep (> 120m ) in the south. Soil cover is very variable. In the agricultural area the soils are medium textured with low (< 1%) to high (>5%) organic matter in topsoil. Groundwater is near the surface in wet soils and deep in hilly areas. Biodiversity varies from high to low depending on soil and landscape. Market orientation of production system is mixed and off-farm income is less than 10%. Relative level of wealth is average from individual households to cooperatives. Soil management is mechanized. Land belongs to land users, but is leased also in case of bigger farms (over 100 ha).
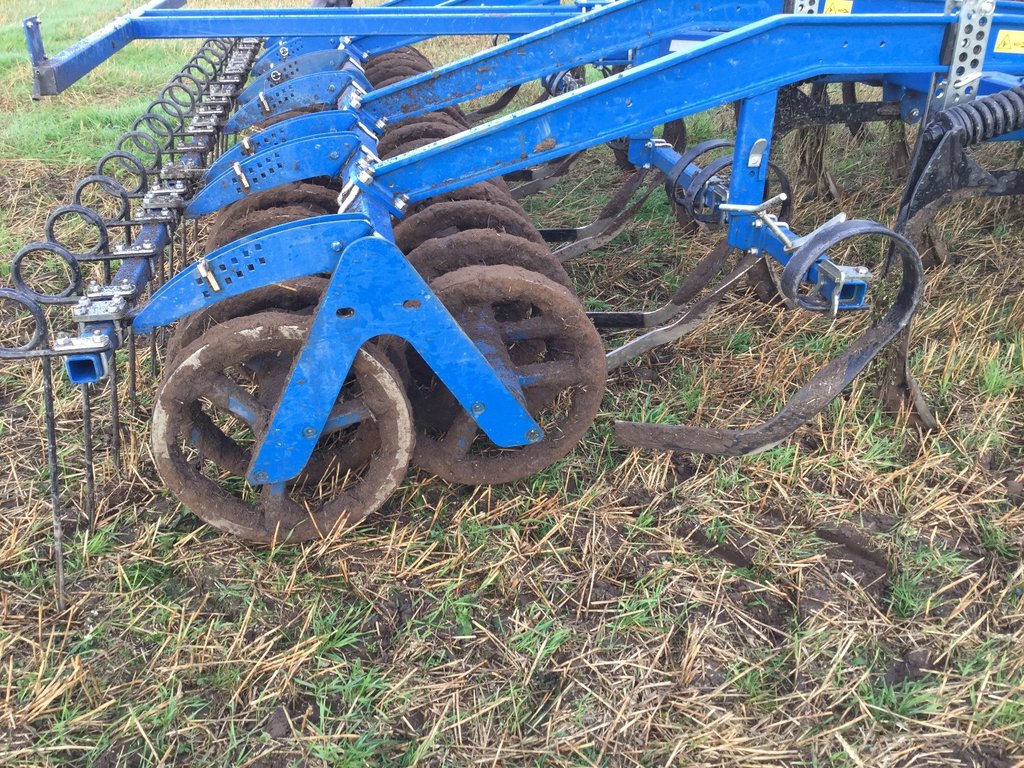
Reduced tillage is the tillage method used in agriculture to prepare the seedbed. Usually only the upper 10-18 cm of the soil surface is tilled. There is no use of ploughing and thus it is the method that does not turn the soil over. This may involve the use of a chisel plough, field cultivators, or other implements. Depth of the soil preparation depends on the culture in the rotation - before cereals 10-12 cm, before oilseed rape 15-18 cm. The main equipments to prepare the seedbed are the disc cultivator and the tine cultivator or a combined cultivator. The work can be ordered from contractors as well. Usually farms own the equipment.
The main goal is to maintain soil structure, to improve water infiltration, to reduce compaction, and to reduce fuel and labour costs. As there will remain 30% more residues on the soil surface it will promote the activity of soil organisms. Less disturbance in deeper layers increases number of earthworms and increases species diversity. The greatest benefits for the land users are the reduced fuel and labour costs. The reduced tillage is more suitable for crop rotations without root crops. For example, rotation can be as follow: winter oilseed rape - winter wheat - pea (or bean) - winter wheat - spring barley undersown with red clover - red clover. However, the soil compaction and weediness can drastically increase during the first years of the implementation without using a proper crop rotation or management plan. The soil conditions (compaction and weediness) can get worser inside the first 4 years and start to improve after that. It is not suitable for fields which are heavily affected by perennial weeds, as noninversional tillage can spread the weed roots and higher doses of herbicides are needed.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ເອສໂຕເນຍ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Tartu county
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Kobilu
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານນະວັດຕະກໍາຄິດຄົ້ນຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
ການປູກພືດຫຼັກ (ທີ່ສາມາດສ້າງລັບຮັບ ເປັນເງິນສົດ ແລະ ເປັນພືດສະບຽງອາຫານ):
winter and spring wheat, winter and spring barley, oat, rye, pea, bean, oilseed rape, corn for silage, buckwheat
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງ ໃນເວລາ ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ແມ່ນໃຫ້ລະບຸວ່າ ດິນພື້ນທີ່ດັ່ງກ່າວ ເຄີຍເປັນດິນປະເພດໃດ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Before the use of reduced tillage conventional tillage (with ploughing) has been used.
3.3 ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 1
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
One harvest of cereals per year.
3.4 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການປັບປຸງດິນ / ພືດຄຸມດິນ
- ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ກິດຈະກໍາ ທີ່ລົບກວນດິນ
3.5 ການຂະຫຍາຍເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່ືື ຢ່າງສະໜ່ຳສະເໝີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ ໂດຍການຄາດຄະເນ:
- 1-10 ກມ 2
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
2/3 of cereals is cultivated by minimum tillage technology in Estonia.
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A3: ການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍລົມ
- ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ
- Pc: ການອັດແໜ້ນ
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
4.2 ການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດອະທິບາຍເຕັກນິກ
To till the soil chisel ploughing or disc cultivator is used without turning the soil over. For cereals the suitable depth is 10-12 cm, for oilseed rape 15-18 cm. Ca 30% from straw will remain on the soil surface. To loosen the soil of deeper layers the deep chiseling down to 25 cm is used.
4.3 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ:
hectar
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
EUR
ລະບຸ ອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນ ຈາກໂດລາ ເປັນເງິນຕາທ້ອງຖີ່ນ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ): 1 ໂດລາ =:
1.18
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
36-40 EUR/day + taxes
4.4 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of cultivator (disc or combination cultivator) | ພືດ |
4.5 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸປະກອນ | Disc cultivator | piece | 1.0 | 15000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 15000.0 | |||||
4.6 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seedbed preparation (tillage before drilling) | ພືດ | before drilling (spring crops in spring (April), winter crops in autumn (August)) |
| 2. | Fertilization, drilling | ພືດ | in spring or in autumn, drilling and fertlization at the same time |
| 3. | Plant protection | ພືດ | up to 3 times during growth period depending of weediness, infections and insects |
| 4. | Fertilization during growth period | ພືດ | For winter crops in spring after snowmelt in the beginning of growth, for spring crops in the beginning of intensive growth |
| 5. | Harvest and grain transport | ພືດ | in the end of season (end of July to beginning of September depending of the crop) |
| 6. | Drying of grain and soil tillage | ພືດ | after harvest |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The example is based on the assumption that the yield will be around 6 t/ha and we grow cereals (winter or spring wheat)
4.7 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸປະກອນ | Seedbed preparation, fertilization, sowing | times | 1.0 | 131.9 | 131.9 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Plant protection | times | 3.0 | 11.2 | 33.6 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Fertilization during growth period | times | 1.0 | 16.2 | 16.2 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Harvest and grain transport | times | 1.0 | 118.5 | 118.5 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Drying and after harvest activities | times | 1.0 | 132.1 | 132.1 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | seeds | kg | 200.0 | 0.28 | 56.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Ammonium nitrate (2x per season) 147 kg/ha N (200 kg fertilizer per ha) | kg | 147.0 | 0.84 | 123.48 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Complex fertilizer (27 kg N, 40 kg P and 112 kg K per ha) (450 kg of fertilizer per ha) | kg | 179.0 | 0.74 | 132.46 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Herbicides (1 time) | times | 1.0 | 27.0 | 27.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Fungicides (1 time) | times | 1.0 | 33.2 | 33.2 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Insecticides (1 time) | times | 1.0 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Retartants | times | 1.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 822.04 | |||||
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
Agricultural producers can have governmental support per unit 83.71 EUR/ha and the greening support 38.81 EUR/ha.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The labour costs are included to the machinery work costs. An average the labour cost for a driver is 15-18 EUR/ha. The average machinery work costs to produce 4.5 t of winter wheat were 388 EUR/ha, 355 EUR/ha and 322 EUR/ha in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively in 2016. Cost of production in this case was 159 EUR/t, 152 EUR/t and 147 EUR/t in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively.
To produce the same amount of spring barley, the cost of machinery was 365 EUR/ha, 345 EUR/ha and 300 EUR/ha in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively. Cost of production in this case was 142 EUR/t, 139 EUR/t and 129 EUR/t in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively.
The machinery cost for minimum tillage is 33 EUR and 20 EUR less than for conventional plough based tillage for winter wheat and spring barley, respectively.
By minimum tillage the use of fuel is ca 38% less than by ploughing.
4.8 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Fuel costs, labour cost
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
696.00
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
Average 696 mm, almost equally spread over the year, more from July to October, less in March and April.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
Tartu Tõravere
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
LGP 180-195 days
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ລັກສະນະສວດ
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
On the main investigated area it is sandy loan Stagnic Luvisol, in some parts Calcaric Luvisol. pH in water 6.9-7.3
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
5-50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ດີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ປານກາງ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ປານກາງ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ການຄ້າ / ຕະຫຼາດ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
- ການຮ່ວມມື
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຊາວໜຸ່ມ
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
5.7 ພື້ນທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ເຊົ່າໂດຍຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດກາງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The total area of one investigated farm is 1036 ha (all covered by minimum tillage), another farm size is 2320 ha and under minimum tillage it is 1231.5 ha.
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ລັດ
- ບໍລິສັດ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ເຊົ່າ
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
- ບຸກຄົນ
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
6.3
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
6.75
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The example is based on winter wheat. For spring barley 4.56 and 4.52, for spring oilseed rape 2.24 and 2.15 t/ha with ploughing and with minimum tillage, respectively.
Different studies have shown that the yield can be higher and also lower compared to the conventional tillage. It depends also on the weather conditions and intensity of mangement (fertilization, pesticides).
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງພືດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
37.7
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
38.1
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The weight of thousand grain of winter wheat can be higher under minimum tillage than under conventional tillage in some years. As an average of different years, there is no differences and under conventional tillage the weight of 1000 grains can be slightly higher.
ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
As there is no conventional ploughing, the management is simplified. However, bigger attention should be paid on weed management and crop rotation, which may hinders the land management. There is need to include weed suppressing species, such red clover (or similar) into the rotation.
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
10.1
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
5.2
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Fuel cost by ploughing and with minimum tillage as EUR/ha. The fuel demand for tillage will decrease from ca 14 l/ha to 7.2 l/ha
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Production costs for producing 1 ton of winter wheat are 5 EUR less by minimum tillage than by ploughing at high yield level (6 t/ha). In some calculations they show 1.7-1.8 times less costs for tillage by minimum tillage compared to ploughing.
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Field operations takes less time, decreasing labour costs.
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Decreasing production costs allows to sell the food with lower price.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Farmers turning to the minimum tillage have to clarify for themselves the behaviour of their soils, crop rotations etc. to prevent excess compaction, weed infestation.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ການຂຸດຄົ້ນ / ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
30% remaining residues on the soil surface helps to catch more snow during the winter.
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Higher amount of residues on the soil surface allows water to infiltrate quicker into the soil, as raindrops can not damaging the soil structure as much as after ploughing.
ການລະບາຍນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Better soil structure allows water to infiltrate quicker into the soil. Without ploughpan and with intact pore system water drains quicker to the deeper soil.
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
30% plant residues do not allow water to evaporate in the same speed as by ploughing.
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Slight differences in deeper soil (20-25 cm) ca. 4% more moisture in minimum than conventional tillage.
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
0
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
30%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
30% more plant residues remain on the soil surface after minimum tillage compared to the ploughing.
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Extra residues on the soil surface and better soil structure compared to ploughing reduces soil loss by wind and water.
ການທັບຖົມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Increase of soil organic carbon by 0.1-0.2% compared to ploughing.
ດິນເປັນຜົງ / ການຈັບໂຕຂອງດິນ ທີ່ມີຂະໜາດນ້ອຍຫຼາຍ ທີ່ມີການຈັບໂຕກັນເປັນກ້ອນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Stronger soil structure because the increasing organic carbon level improves the resistance to raindrop impact and by this it reduces soil crusting.
ການອັດແໜ້ນຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
In the layer 10-20 cm the increase can be over 0.2 g/cm3 compared to ploughed soils. However, after 4-5 years the conditions starts to improve and there will be less compaction in mentioned layer and deeper (plough pan starts to disappear).
ວົງຈອນ ຂອງສານອາຫານໃນດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Less intensive decomposition of organic matter leaves more nutrients in the soil.
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Slight increase of organic carbon by 0.1-0.2%. Depends more on crop rotation than tillage method.
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Due to the need to suppress weeds more winter crops or cover crops are included into the rotation. However, this effect can only be stated if the rotation and management plan will be changed.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Due to the need of changes in crop rotation, more diverse rotations instead of monoculture to suppress weeds. Weeds diversity might increase due to the reduced tillage intensity.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
More spiders, beetles, ants compared to ploughed soils.
ຊະນິດທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
2 species of earthworms
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
3-4 species of earthworms
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
More earthworm species and higher abundance compared to ploughed soils.
ການຄວບຄຸມສັດຕູພືດ / ພະຍາດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Due to the decreased tillage intensity more attention should be paid on weed, pests and disease control by crop rotation and pesticies. As the residues remain on the soil surface there are also better conditions for pests and disease spreading.
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Due to the decreased decomposition intensity, less CO2 emission from soil organic matter (increase of soil organic matter 0.1-0.2% compared to ploughing). As the fuel consumption is ca 40% less than by ploughing, less emission is coming from agriculture.
ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄຟໄໝ້
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
As there will remain 30% of residues on the soil surface, there is an increased risk of fires in spring.
ການປ່ຽນແປງ ອາກາດ ໃນວົງແຄບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Residues regulate soil evapotranspiration and temperature. The fluctuations are not so high as by ploughing.
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການປ້ອງກັນ / ຄວາມອາດສາມາດ ການກັ່ນຕອງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
As the soil organic carbon content increases, also the water holding and the nutrient holding capacity increase.
ລົມ ທີ່ພັດເອົາຕະກອນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Less sediments due to the lower tillge intensity and more residues on the soil surface
ພື້ນທີ່ທໍາການຜະລິດ ຂອງເພື່ອນບ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນກະທົບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Less sediments from the field to the neighbours fields. Effect on water erosion depends on the slope.
ຄວາມເສຍຫາຍ ກ່ຽວກັບພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ ສາທາລະນະ / ເອກກະຊົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Due to the reduced water erosion, less soil will be transported to the diches and roads (depends on slope).
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Due to the decreased decomposition intensity, less CO2 emission from soil organic matter (increase of soil organic matter 0.1-0.2% compared to ploughing). As the fuel consumption is ca 40% less than by ploughing, less emission comes from agriculture.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ຮູບແບບ ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ | |
| ອຸນຫະພູມລະດູການ | ລະດູໜາວ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
| ອຸນຫະພູມລະດູການ | ລະດູໃບໄມ້ປົ່ງ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ | |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕາມລະດູການ | ລະດູໜາວ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕາມລະດູການ | ລະດູໃບໄມ້ລົ່ນ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
| ພາຍຸເມກທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
| ພາຍຸລູກເຫັບທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
| ພາຍຸຫິມະໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
| ພາຍຸລົມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ຄື້ນໜາວ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
| ອາກາດໜາວຮຸນແຮງ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
| ໄຟໄໝ້ດິນ | ປານກາງ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 1-10%
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
85 371 ha
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ທີ່ເປັນຜູ້ປັບຕົວ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 90-100%
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Decrease of work load, time and labour costs. |
| Decrease of fuel consumption, increase of income. |
| Increase of soil biological activity, soil organic matter content, better structure and infiltration. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Decrease of soil organic carbon decomposition. |
| Decrease of soil erosion. |
| Increase of soil biological activity. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Increase of weed abundance and soil compaction | Proper crop rotation and timing |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Higher use of pesticides and risk to soil and water pollution. | Changes in crop rotation, use of cover crops |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
5 during the iSQAPER project, more than 20 in total with other projects
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
5, more than 40 in total with other projects
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
7
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Minimeeritud harimine ja otsekülv. 2017. P. Viil. Eesti Taimekasvatuse Instituut. ISBN 978-9949-9742-2-1:
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
ISBN 978-9949-9742-2-1
7.3 ສາມາດເຊື່ອມໂຍງ ຂໍ້ມູນຂ່າວສານ ໄດ້ໂດຍຜ່ານການອອນລາຍ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Kattetulu arvestused taime- ja loomakasvatuses 2016. Koost: Marju Aamisepp, Helle Persitski. Maamajanduse infokeskus. 2017.:
URL:
http://www.maainfo.ee/data/trykis/kattetulu/KATTETULU2016.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Statistics Estonia
URL:
https://www.stat.ee/en
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Erinevate viljelusmeetodite ( sh. otsekülv) rakendusteaduslik kompleksuuring. Riikliku programmi “Põllumajanduslikud rakendusuuringud ja
URL:
http://www.pikk.ee/upload/les/Erinevad_viljelusviisid_pikk_aruanne.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Minimeeritud harimine ja otsekülv. 2017. P. Viil. Eesti Taimekasvatuse Instituut.:
URL:
http://taim.etki.ee/taim/public/pdf/Trukised/Otseklv-minimeeritudmullaharimine.
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Eesti maaelu arengukava 2014-2020 4. ja 5. prioriteedi meetmete ja 3. prioriteedi loomade heaolu meetme püsihindamisaruanne 2015. aasta kohta ja
URL:
http://pmk.agri.ee/mak/avaleht/
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Projekti ”Erinevate mullaharimise ja külvitehnoloogiate mõ-ju uuring tera- ja kaunviljade saagikusele viljavahelduslikus ja monokultuurses külvikorras” lõpparuanne
URL:
http://www.pikk.ee/upload/files/Teadusinfo/Lopparuanne_111_2002_2006.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Eesti tuleviku kliimastsenaariumid aastani 2100
URL:
https://www.envir.ee/sites/default/files/kliimastsenaariumid_kaur_aruanne_ver190815.pdf
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ