Addressing shallow landslides by using wooden pole structures. [ບອສເນຍ ແລະ ເຣີໂກວີນາ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Milenko Blesić
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Donia Mühlematter, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, THEODORA FETSI
Zaustavljanje plitkih klizišta drvenim šipovima
technologies_4285 - ບອສເນຍ ແລະ ເຣີໂກວີນາ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Čustović Hamid
University of Sarajevo, Faculty of Agriculture and Food Sciences
ບອສເນຍ ແລະ ເຣີໂກວີນາ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Bajrić Muhamed
University of Sarajevo, Faculty of Forestry
ບອສເນຍ ແລະ ເຣີໂກວີນາ
Municipality Kladanj Agronomist:
Hajdarević Hajda
Department of Finance, Entrepreneurship and Local Economic Development, Municipality of Kladanj
ບອສເນຍ ແລະ ເຣີໂກວີນາ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Hotović Huso
Land user, Borak Locality, Kladanj Municipality
ບອສເນຍ ແລະ ເຣີໂກວີນາ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Utilization of wooden pole structures placed in parallel, to reduce shallow landslides (2-3 m) in relatively small surfaces. Possibility to be combined with drainage system for better results.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
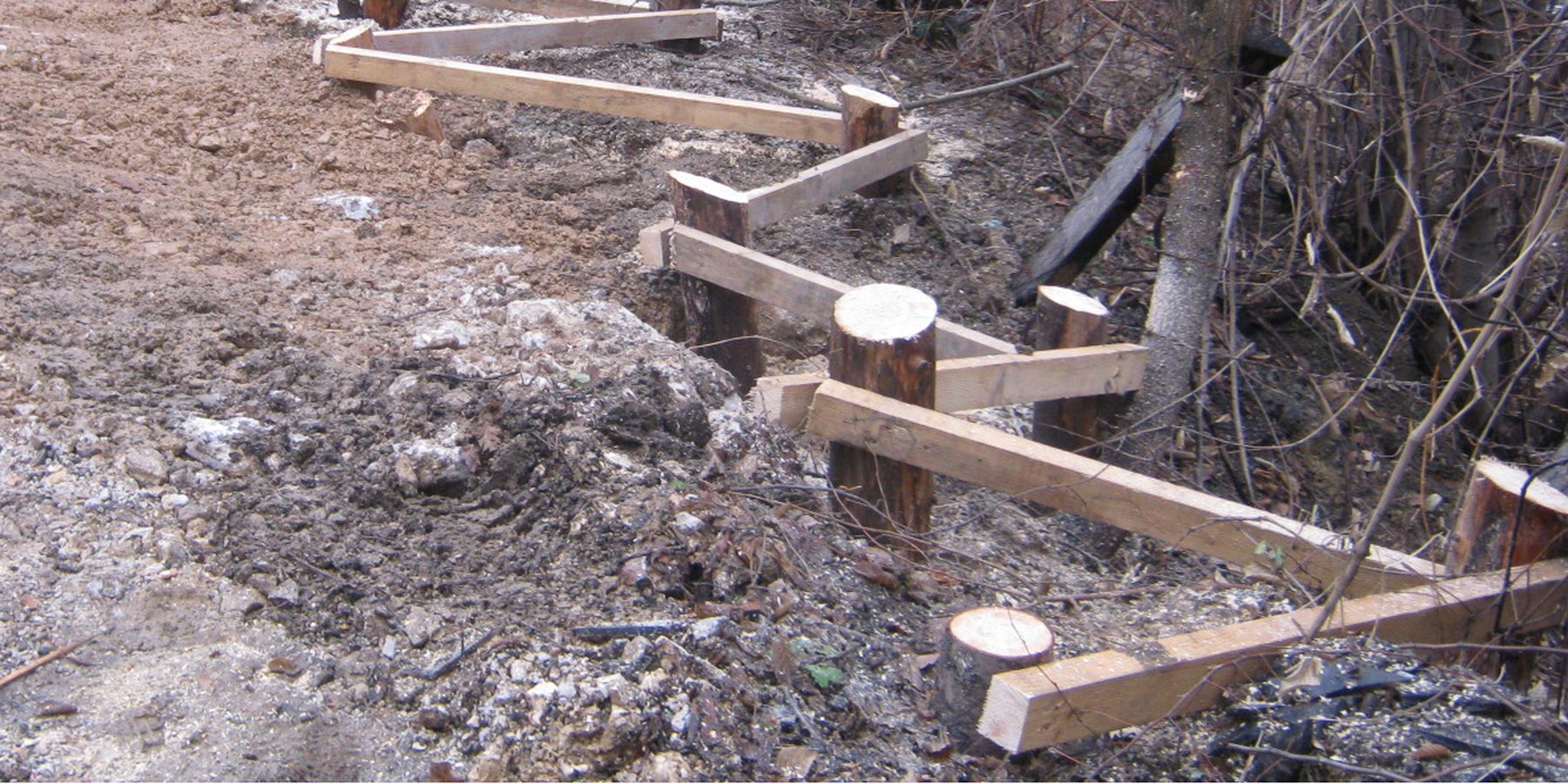
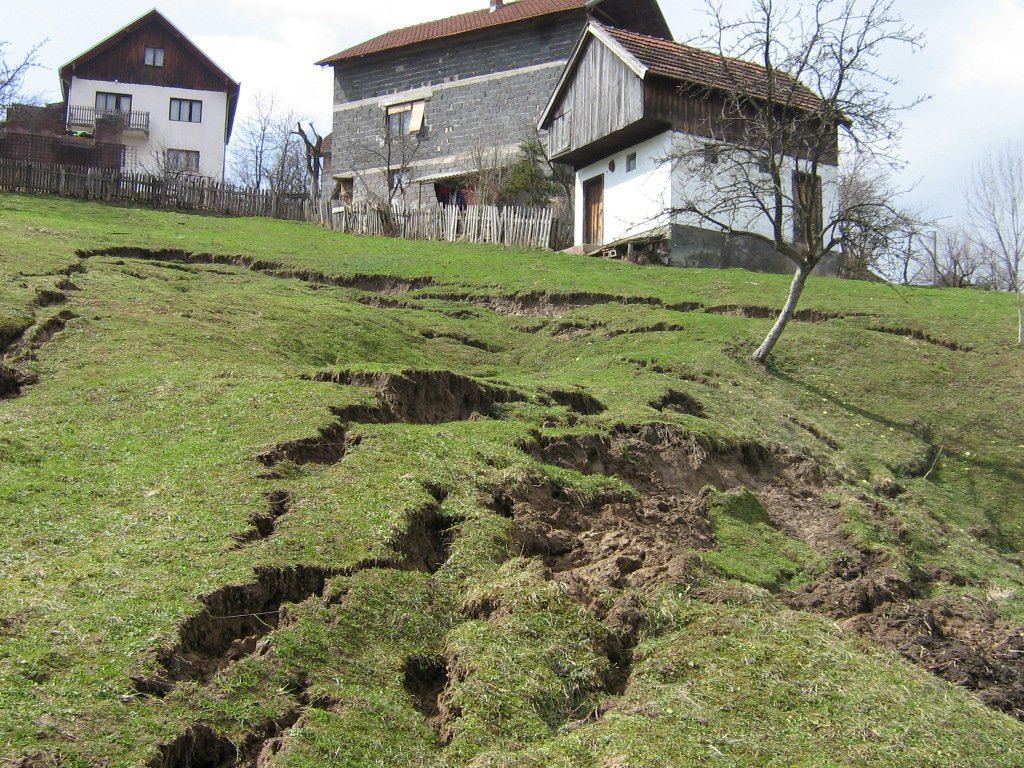
Farmers in northeast parts of Bosnia and Herzegovina traditionally applied the technology to address shallow landslides, surface erosion or loss of top soil due to sheet or interrill erosion. Movements of the upper layers of the soil appears due to unfavorable properties of the soil layers (clays, pseudoclays), set on impermeable geological substrates, all under conditions of intense and long-term rainfall. During the last decades, it has been frequently applied in the area of Kladanj municipality, whose administrative services for agriculture and forestry technically specified and promoted the technology. Landslides are one of the major problems in the hilly areas of Bosnia and Herzegovina, threatening particularly the agricultural lands. The technology is being applied by farmers on their own properties, but it is also part of public interventions, e.g. for the protection of roads or other infrastructure from landslides or in the context of roads recovery programs damaged by landslides. The technology aims to reduce the impact of the shallow (up to 2 - 3 m in depth) landslides of relatively small surface, by preventing further movement of the soil. So far, it is sporadically applied on around 20 – 30 locations in Kladanj Municipality, whose territory is around 355 sq. kilometers.
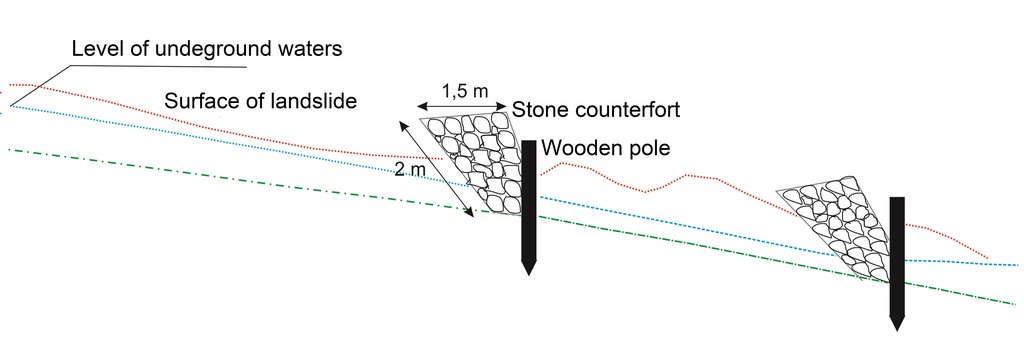
The technology implies pounding wooden poles in front (below) of the frontline of the landslide, along the contour, perpendicular to the slope. Land users recommend oaken pols due to their durability. The poles are usually 3.5 – 4 m long and 20 – 30 cm in diameter. One pole formation consists of two parallel lines of poles, with 1.5 to 2 m distance from line to line. The poles are positioned in a staggered way that a zigzag is formed. The poles are interconnected with wooden laths. One pole formation is usually enough to address smaller landslides, but in case of larger landslides, two formations are recommended. In the latter case, in combination with a drainage system, stone counterforts are formed in front (above) the poles' formation. See technical drawing for more details.
The primary purpose of the technology is to recover shallow and small landslides on slopping terrains. Stopping the movement of agricultural land after reparation of cracks and land gaps caused by landfall enables re-utilization of the land for either agricultural production or agro-forestry. In the municipality of Kladanj walnuts or other wooden fruit species with strong roots are often planted on recovered landslides.
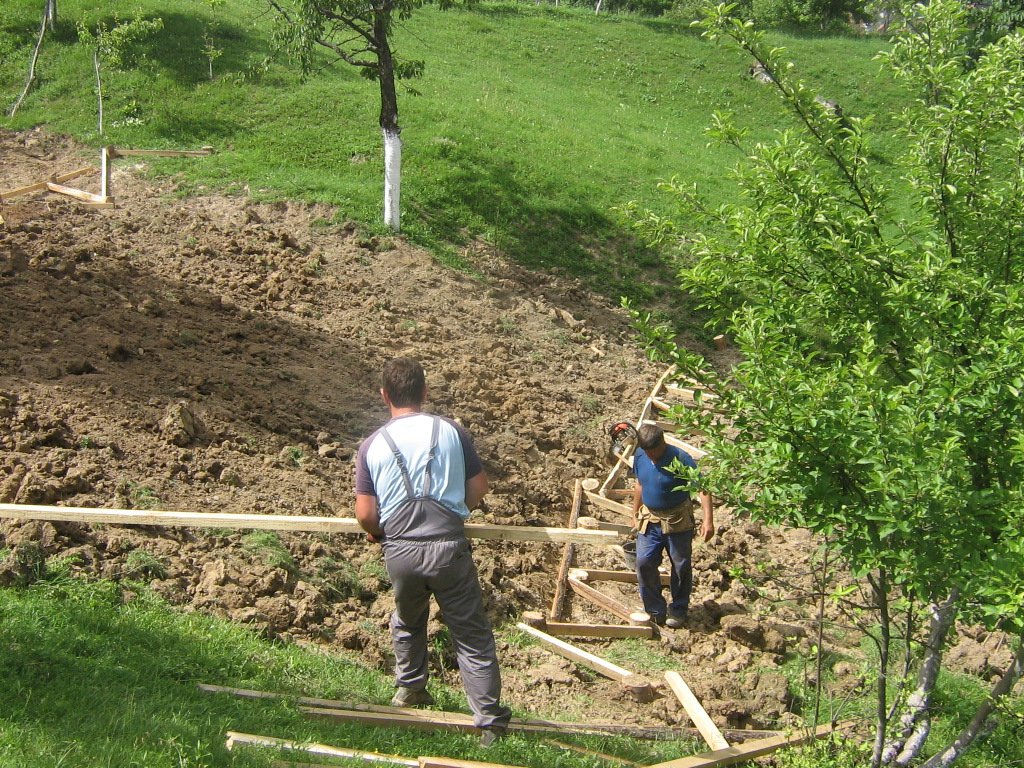
After a prior assessment of the depth and surface of the landslide, an expert or a technician prepares simple project sketches. The sketches define configuration of pole formations and materials needed for the construction (oak poles, laths). The realization of the technology is not particularly demanding. Nowadays machines are used to pound poles in the ground (mainly by a dredge's spoon).
It is a relatively inexpensive technology which could be financed by even small farmers who can protect or recover their, under Bosnia and Herzegovina conditions, usually small agricultural land parcels.
Although not an integral part of the technology, modification with water drainage from the body of bigger landslide ensures additional, long lasting stability of the terrain. If performed, the drainage is carried out by depositing drainage material (perforated pipes, pebbles, tiny stone fractions) in the lower zone of drainage trenches whose configuration and depth depends on the terrain conditions. Another modification of the technology could include construction of a stone counterfort in front (above) the pole formation. These modifications are briefly presented in the technical specification of the technology, but they were not applied on the site (Borak locality) where activities, establishment and maintenance costs of the technology were observed.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ບອສເນຍ ແລະ ເຣີໂກວີນາ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Tuzla canton
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Kladanj municipality
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ສ່ວນຫຼາຍສະຖານທີ່ຕັ້ງຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນ ຢູ່ໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ສະຫງວນບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- 10-50 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງ ທາງໄພພິບັດທໍາມະຊາດ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
- ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ ຈາກການປູກພືດ
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ທັນຍາພືດ-ສາລີ
- ທັນຍາພືດ-ພືດ ອື່ນໆ
- ພືດອາຫານສັດ - ປະເພດຫຍ້າ
- ພືດອາຫານສັດ-ພືດປພະເພດອື່ນໆ
- ຜັກ-ອື່ນໆ
- Apples, Plums, Pears, Berry fruits
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 1
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບສັບຫວ່າງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າມີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸວ່າປູກພືດຊະນິດໃດທີ່ປູກສັບຫວ່າງ:
Vegetables in orchards

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບປ່ອຍ ຕາມທຳມະຊາດ:
- ແບບຂັງຄອກ
ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດແບບສຸມ / ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ:
- ປັບປຸງ ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
ປະເພດສັດ:
- ສັດໃຫ່ຍ-ງົວພັນນົມ
- ສັດໃຫ່ຍ-ງົວພັນຊີ້ນ
- ແກະ
ແມ່ນການເຝືກຄຸ້ມຄອງ ການປູກພືດປະສົມປະສານ ກັບການລ້ຽງສັດບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຜະລິດຕະພັນ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ:
- ຊີ້ນ
- ນ້ຳນົມ

ການຕັ້ງຖິ່ນຖານ, ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
- ການຈາລະຈອນ: ຫົນທາງ, ທາງລົດໄຟ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology could be applied on various types of land use. In the northeast region of Bosnia and Herzegovina it is commonly applied on: grazing land, cropland (annual, perennial, trees and shrubs), and mixed land uses. In Kladanj municipality the technology is frequently applied for protection or reconstruction of roads damaged by landslides.
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
- ບໍ່ (ຕໍ່ເໜືອງກັບ ຄຳຖາມ 3.4)
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ມາດຕະການ ຕັດຂວາງ ກັບຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ
- stopping landslides, recovery of landslides
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S3: ຮ່ອງ, ຄອງນໍ້າ, ທາງໄຫຼນໍ້າ
- S6: ແລວກັນເຈື່ອນ, ຮົ້ວ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wm: ການເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍອິນຊີວັດຖຸ / ດິນເຈື່ອນ
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
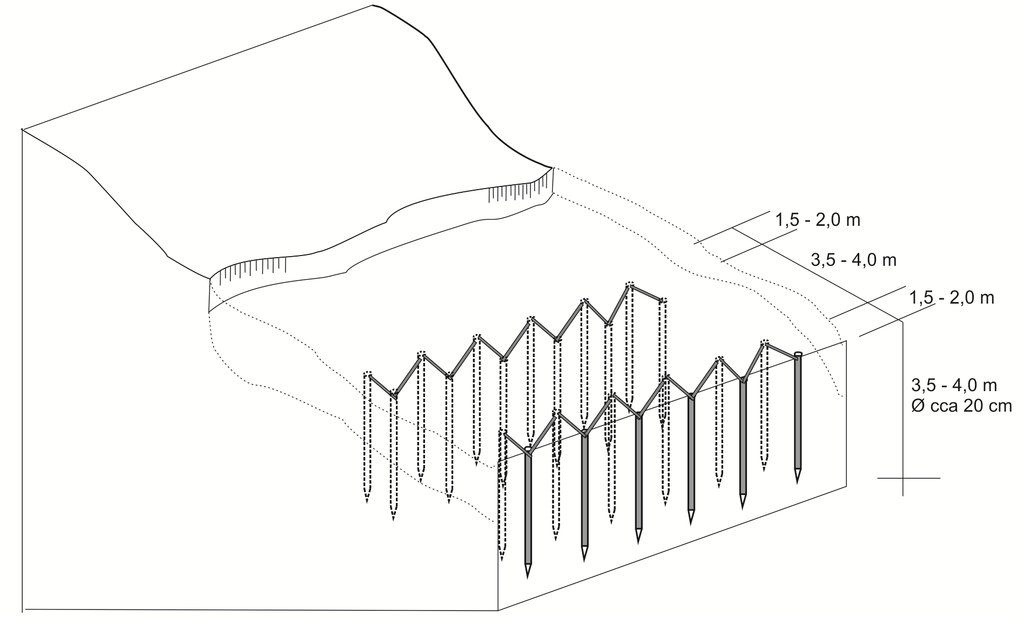
The sketch depicts the cross-section of the terrain, illustrating the wooden poles’ structures and the technical characteristics of the technology. Two wooden structures are being placed in parallel, at a distance of 3.5-4 m. Each structure is consisted by wooden poles positioned in a zigzag form. The poles are pounded in the ground at a depth of 3.5 m and are connected to each other with wooden laths. The distance between the poles is 1.5-2 m. The number of poles to be used, depends on the size of the area where the intervention is needed. The recommended distance between the two parallel structures is 3 – 4 m, depending on the characteristics of the terrain.
The implementation of the technology does not bring any change on the slope and could be applied on various slopes. The technology is mostly applied on agricultural or infrastructural land, i.e. on slopes not above 30%.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Muhamed Bajrić, Milenko Blesić
ວັນທີ:
20/10/2018
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
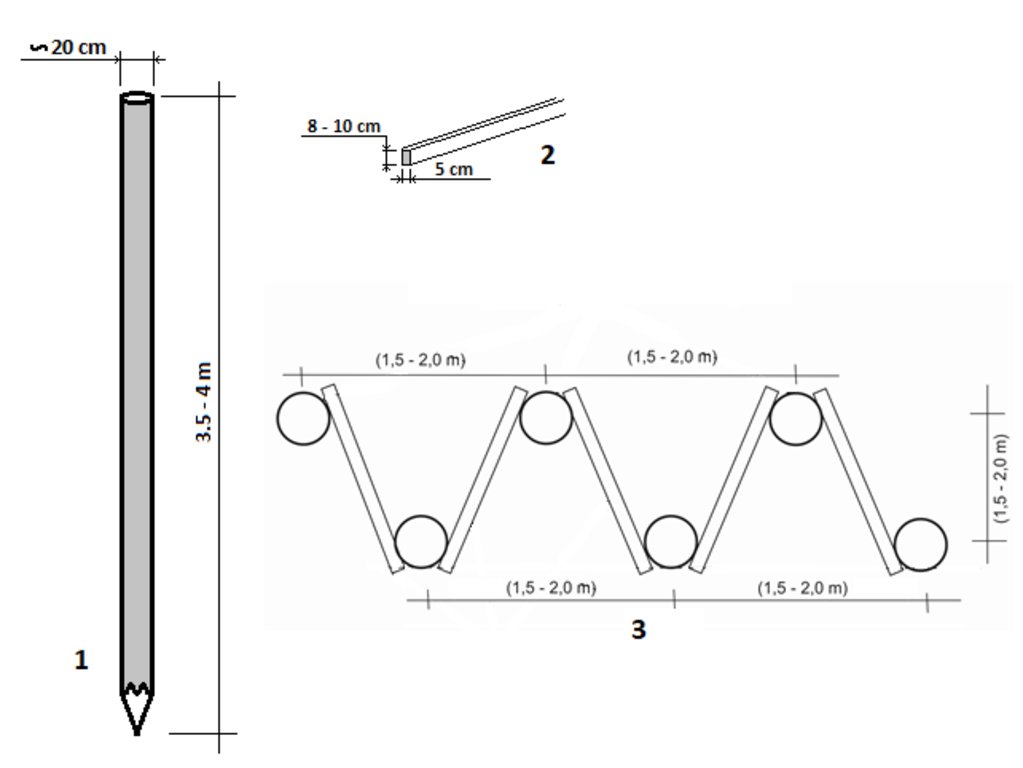
Drawing 1 shows the recommended dimensions of the poles.Drawing 2 illustrates the technical characteristics of the laths (2) which connect the poles. Drawing 3 shows the top view of the overall structure with the required dimensions.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Milenko Blesić, Muhamed Bajrić
ວັນທີ:
20/10/2018
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
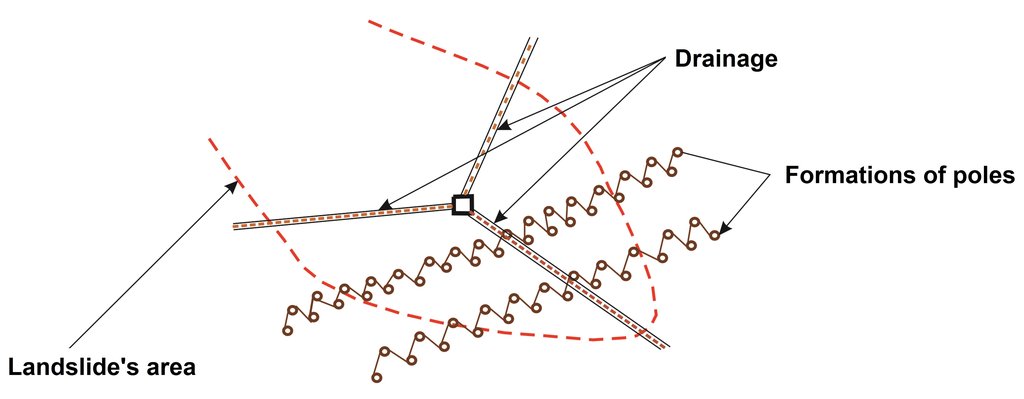
Modification (improvement) of the technology with a drainage system. The modification (drainage) was not applied on the site where the technology was observed.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Muhamed Bajrić
ວັນທີ:
10/11/2018
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Modification (improvement) of the technology by construction of the stone counterforts just above the line of poles. The modification (stone counterforts) was not applied on the site where the technology was observed.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Muhamed Bajrić
ວັນທີ:
10/11/2018
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ:
Landslide on Borak locality - Kladanj municipalitay
ກໍານົດຂະຫນາດຂອງຫົວນ໋ວຍ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ):
0,35 ha
ລະບຸ ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບ ການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- USA
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
29.24 USD
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Expert's characterization of landslide | Any time |
| 2. | Designing the structure and identifying the materials | Any time |
| 3. | Purchase and transport of materials (poles, laths) | Any time |
| 4. | Pounding poles in the ground | Spring - autumn |
| 5. | Connection of poles' heads (above ground parts) with laths | Spring - autumn |
| 6. | Machine leveling of the terrain | Spring - autumn |
| 7. | Planting of walnut seedlings | Autumn |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Establishment activities are presented in accordance withe the activities on one specific (Borak) locality. The surface of landslide on this locality was around 0,35 ha, and after its stopping with the formation of wooden poles, its full recovery was done by leveling of the terrain and planting of 300 walnut seedlings (further walnut orchard). The list of final recovery activities could be different on other localities and it depends of landowners' intentions and financial possibilities.
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Expert's characterization of landslide, designing of construction, specification of materials | Working day | 2.0 | 100.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Pounding the poles into the ground | Working day | 10.0 | 29.24 | 292.4 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Connecting poles with lathes | Working day | 1.0 | 29.24 | 29.24 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Planting of walnut seedlings | Working day | 10.0 | 29.24 | 292.4 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Heavy machinery (dredge) work on pounding poles into the ground (hired) | Hour | 16.0 | 46.78 | 748.48 | 30.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Heavy machinery (dredge) work on leveling of terrain | Hour | 4.0 | 46.78 | 187.12 | 30.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Walnut seedlings | Piece | 300.0 | 2.92 | 876.0 | 30.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Wooden (oak) poles | Piece | 100.0 | 17.5 | 1750.0 | 30.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Wooden connecting laths | m | 200.0 | 0.5 | 100.0 | 30.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Other auxiliary materials (nails, wire, etc.) | Lump sum | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 4487.64 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 4487.64 | |||||
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
So far, introduction of the technology in Kladanj municipality is supported from the municipality's budget (contribution in purchase of materials and hiring of heavy machinery).
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The presented activities and costs are related to the landslide (0,35 ha) on Borak (Kladanj municipality) locality. On this particular site, the technology is applied without drainage system and stone counterforts next to wooden pole lines. Though they are not linearly connected, costs on other sites may be smaller or higher, depending on the size of landslides and concrete conditions on the ground.
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
After establishment, the technology does not need any particular maintenance activities.
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Due to the fact that after establishment the technology does not need any major maintenance activities, there are not any significant costs for maintenance. The maintenance is limited to annual checking of joints between lathes and poles and necessary minor interventions (replacement of possibly damaged lathes, re-connection of laths).
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Prices of the construction materials (poles, laths).
Hiring costs of heavy machinery (dredge).
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
894.00
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
The highest precipitations appear during spring and early summer, (June 111 L/m2; February 55 L/m2). Heavy downpours during summer is one of the climatic features of this area.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
Tuzla
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
ເທິງຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ປານກາງ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາພຽງຢ່າງດຽງ (ຊົນລະປະທານ)
ຄຸນນະພາບນ້ຳ ໝາຍເຖີງ:
ນ້ຳໜ້າດິນ
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ເປັນປົກກະຕິ:
ຕອນ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ປານກາງ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ປານກາງ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- > 50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
- ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດກາງ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສິດນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ແມ່ນ ອີງໃສ່ລະບົບກົດໝາຍແບບດັ້ງເດີມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຂອງດິນ / ຊາກສະລະຫະພັງ
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ການທັບຖົມ ຂອງດິນຕະກອນ ຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ພື້ນທີ່ທໍາການຜະລິດ ຂອງເພື່ອນບ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນກະທົບ
ຄວາມເສຍຫາຍ ກ່ຽວກັບພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ ສາທາລະນະ / ເອກກະຊົນ
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີ | |
| ອຸນຫະພູມລະດູການ | ລະດູຮ້ອນ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີ |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕາມລະດູການ | ລະດູຮ້ອນ | ຫຼຸດລົງ | ດີ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຮູນແຮງ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 1-10%
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
According to information from Kladanj municipality administration, on the municipality territory there are around 30 localities with the applied technology.
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 0-10%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Most of the interventions on private properties were partly supported by specific municipal/cantonal programs for recovery of lands, damaged by heavy rains, flash floods and landslides. All interventions on infrastructure (mainly roads) were fully supported by municipal/cantonal budgets.
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸແຈ້ງ):
Improvemnts of the technology effects and durability
ລະບຸການຮັບຮອງເອົາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ການອອກແບບ, ອຸປະກອນການ / ຊະນິດພັນ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The original technology (wooden poles barriers) has been recently modified by parallel installment of drainage of landslide, and most recently by stone enforcement just above the line of wooden poles.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Relatively affordable way to stop and recover landslides on agricultural land |
| Wide availability of construction material (wood) in the region |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Costly effective way to recover agricultural land on small private parcels (usual in Bosnia and Herzegovina) endangered by landslides |
| The technology keeps land from further degradation or possible loss of soil and allows continuation of its current or different functional use |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| It is not always easy to find/hire heavy mechanization for pounding of poles into the ground | Organization of farmers who want to introduce the technology and request for municipality support in hiring heavy machinery |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Limited durability of the wooden poles. | |
| The technology itself (i.e. without extensive drainage) is not efficient in stopping and recovering larger and deep landslides | Added investment in properly projected and implemented drainage system |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
Field surveys from May to December 2018, valuable information from Ms Hajda Hajdarević, Kladanj municipality's office for agriculture.
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
During filed surveys five land users who applied the technology were interviewed.
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
Besides field surveys, precious information regarding the landslide issues and possible technology effects were provided by professors Hamid Čustović and Muhamed Bajrić (University of Sarajevo).
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Field data compilation was done through six field surveys performed between May and December 2018.
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ