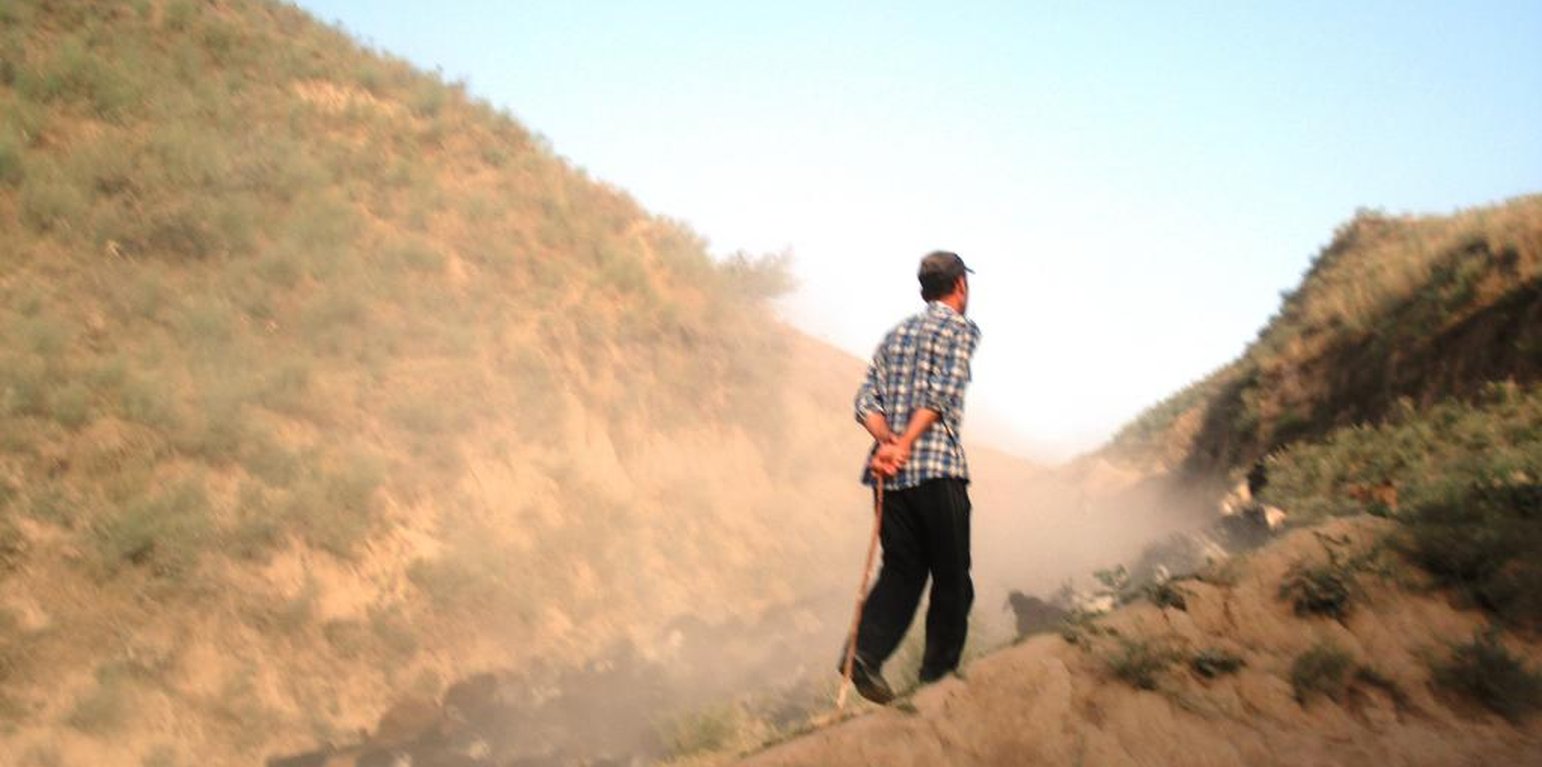
Common village herding
(Тажикистан)
Navbati Poda (succession of herders)
Тодорхойлолт
Village herding system with daily alternation of the herders including each household in a monthly turnus.
Aims / objectives: The herding system has to be easy and little labour-intensive, because children are the main workforce. It is a collective system and thus requires the participation of all households with families: For instance in the village Karsang with 141 households (not all having livestock) and two village herds, each family has to send monthly one child for herding or pay if it does not have workforce. In addition, always at least one adult has to accompany the herd. This means that children of big families only rarely miss school whereas those from small families miss more frequently. The final objective is to nourish animals maximally so they need a minimum of costly hay and concentrated feed (in terms of labour respectively in financial terms).
Methods: Children and adults are taught by the elders, the parents and the village land use committee how the rotation works: They should not stay at one place longer than three days, they should not chase the animals which otherwise lose energy unnecessarily and they shall not lose animals. Children not obeying are punished. In case of lost animals different approaches exist: Mostly the family of the herder who was responsible for the herd on the respective day reaches an agreement with the tenant's family.The village committee or elders can also arbitrate.
Stages of implementation: It is difficult to say when this system first emerged. A land user says that during Soviet Union there were village herds with a fix herder or an alternation like nowadays and, parallely, wealthy people had their own herd with a paid herder. During civil war only a few rich villagers kept animals and only at the beginning of the 2000s collective herding reemerged.
Role of stakeholders: The implementation of herding is a matter of each family's participation. The collaboration of the villagers with institutions is especially important in questions of taxes. In most villages the households pay per capita animal taxes. In order to improve SLM the land use committee on district level and the forest administration (as far as the village has such pastures) together with the local representants of the ecology commission advise the land use committees of each village to take the appropriate measures. And these talk with the herders to influence their comportment. A teacher from the local land use committee says that a lot is said about SLM, but little is effectively done.
Байршил
Байршил: Faizabad, Region of Republican Subordination, Тажикистан
Сонгосон байршлуудын газарзүйн холболт
Эхлэх огноо: 1920
Төгсөх жил: тодорхойгүй
Арга барилын төрөл
-
уламжлалт / уугуул
-
Сүүлийн үеийн орон нутгийн санаачлага / шинэчлэл
-
төсөл / хөтөлбөр дээр үндэслэсэн
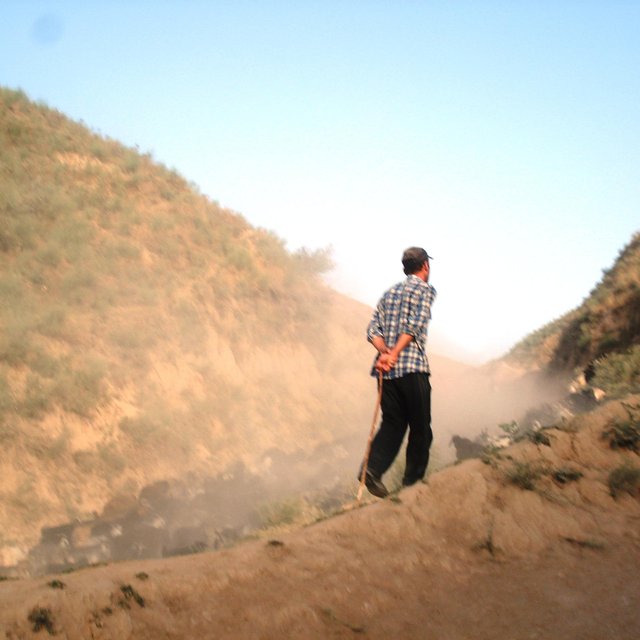

Herder of a large village-herd, with a dust cloud. (Christian Wirz, Switzerland (Switzerland))
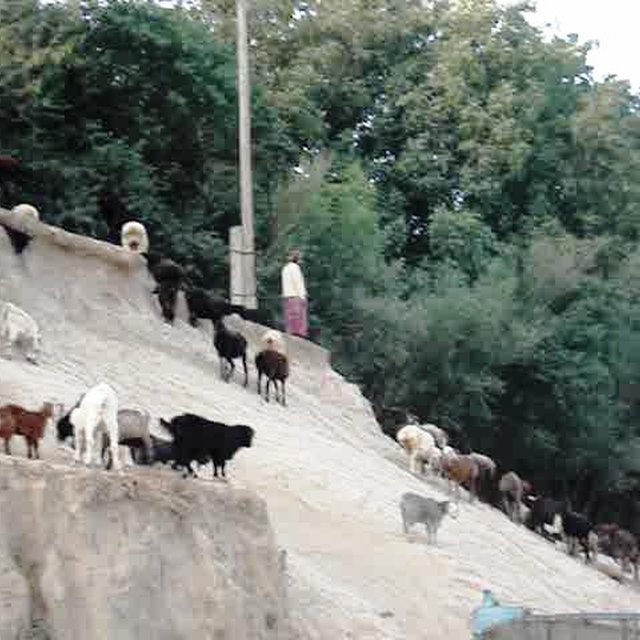

Children of the village bring their animals to the gathering place. (Christian Wirz, (Switzerland))
Арга барилын зорилго ба эерэг нөлөө
Арга барилын үндсэн зорилго, зорилт
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (Maximal nutrition of livestock with child labour.)
In animal husbandry the semi-monetary value of livestock is important. Therefore, 'everyone would like to have more animals', says a land user. At the same time agricultural population has other activities such as the cultivation of kitchen-gardens and of cropland. And labour shortage is omnipresent, with many young men staying in Russia for work. In these multistrategies efforts for herding must be minimised which is best possible if children are sent as herders.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The approach needed and needs to be compatible with the traditionally sedentary culture and with the new employment and income sources in local economy: be it the work as a taxi-driver or selling vegetables on the local market. Today herding has to be especially cheap (finance, labour) because there is a multitude of preferences how to invest resources: building a (better) house, buying a mobile phone and a car or enabling (higher) education of children.
Тухайн Арга барилын хүрээнд нэвтрүүлсэн Технологийг хэрэгжүүлэхэд дэмжлэг болох нөхцлүүд
-
Хууль, эрхзүйн хүрээ (газар эзэмшил, газар, ус ашиглах эрх): The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: The fact that a great part of grassland of former collective farms has not yet been attributed to farmers' associations makes it possible for everyone to use them. The only disadvantage in the eyes of land users is that they have to pay rent fees for this land.
Тухайн Арга барилын хүрээнд нэвтрүүлсэн Технологийг хэрэгжүүлэхэд хүндрэл учруулах нөхцлүүд
-
Санхүүгийн нөөц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж / боломж: Keeping animals is expensive because you have to nourish them (see costs of technology).
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The use of comparatively cheap grazing land of the former collective farms that is under village administration and contracts with forest administration for cheaper land are the solution.
-
Бүтэц зохион байгуулалт: If the defined herding system is not respected, cover is damaged, especially trees. And institutions have little authority in implementation, partly because of their own corruption.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Implementation is based on the households: They do not only send their children for herding, but they also punish them if they treat animals badly.
-
Ажлын багтаамж, хүн хүчний нөөц бололцоо: It is difficult to find labour force that is able to walk to the pastures with the animals, because many young men are in Russia.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Children are cheap and mobile.
Талуудын оролцоо ба үүрэг
Арга барилд оролцогч талууд болон тэдгээрийн үүрэг
| Ямар оролцогч талууд / хэрэгжүүлэгч байгууллагууд арга барилд оролцож байсан бэ? |
Оролцогч талуудыг тодорхойлно уу |
Оролцогч талуудын үүргийг тайлбарлана уу |
| Орон нутгийн газар ашиглагч / орон нутгийн иргэд |
ny people with animals participate in collective herding. Especially poor families cannot afford professional herding. |
There are both boys and girls working as herders. Among adults, men more often working as herders than women.
The role of women is traditionally associated with domestic work and kitchen gardens. |
| ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн/ хөдөө аж ахуйн зөвлөх |
Different institutions: land use committees, forest administration, committee for ecology. |
|
| Багш/ сурагч/ оюутан |
|
|
Тэргүүлэх байгууллага
Mainly land users supported by SLM specialists
Арга барилын янз бүрийн үе шатанд орон нутгийн газар ашиглагчид / бүлгүүдийг татан оролцуулах
үгүй
идэвхигүй
Гадаад дэмжлэг
интерактив
өөрийн хүчийг нэгтгэсэн
санаачлага/идэвхжүүлэлт
Initiatation and planning was organised among villagers. They based themselves on experiences from Soviet times and from before.
Хэрэгжилт
Recently the institutions mentioned have become more important.
Арга барил хэрэгжүүлэх бүдүүвч
ГТМ-ийн технологи сонгох шийдвэр гаргах явц
Шийдвэр гаргасан этгээд
-
Газар ашиглагч дангаараа (өөрийн санаачлага)
-
ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтнүүдийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр, голчлон газар ашиглагчид
-
оролцооны зарчмын хэсэг болох бүх холбогдох талууд
-
голдуу ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтнүүд, газар ашиглагчидтай зөвлөлдсөний үндсэн дээр
-
ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн дангаараа
-
улс төрчид / удирдагчид
Шийдвэр гаргах үндэслэл нь
-
ГТМ-ийн мэдлэгийг баримтжуулалтын үнэлгээ (нотолгоонд суурилсан шийдвэр гаргах)
-
Судалгааны үр дүн, ололтууд
-
Хувь хүний туршлага ба санал бодол (баримтжуулаагүй)
Техникийн туслалцаа, чадавхи бий болгох болон мэдлэгийн менежмент
Дараах үйл ажиллагаа эсвэл үйлчилгээ нь арга барилын нэг хэсэг болсон
-
Чадавхи бэхжүүлэх/сургалт
-
Зөвлөх үйлчилгээ
-
Институцийг бэхжүүлэх (байгууллагын хөгжил)
-
Мониторинг ба үнэлгээ
-
Судалгаа
Мониторинг ба үнэлгээ
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by other through observations; indicators: Local land use committees go to the pastures in spring to decide whether soils are dry enough and gr
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations; indicators: Land users control if their animals are fat and if they give milk. Otherwise they might not send the
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
Санхүүжилт болон хөндлөнгийн материаллаг дэмжлэг
ГТМ-ийн бүрэлдэхүүн хэсгийн жилийн төсөв ам.доллараар
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
100,000-1,000,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: тодорхойгүй
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local government (district, county, municipality, village etc) (Meetings of administration with leaders.): 20.0%; local community / land user(s) (Organising herding: low costs.): 80.0%
Газар ашиглагч нарт дараах урамшуулал, үйлчилгээг үзүүлсэн
-
Газар ашиглагчдад санхүүгийн / материаллаг дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн
-
Тодорхой хөрөнгө оруулалтанд нөхөн олговор олгох
-
Кредит
-
Бусад урамшуулал, хэрэгсэл
Нөлөөллийн дүн шинжилгээ ба дүгнэлт
Арга барилын үр нөлөө
Үгүй
Тийм, бага зэрэг
Тийм, зарим
Тийм, их
Арга барил нь ГТМ-ийн технологийг хэрэгжүүлж, хадгалахад газар ашиглагчдад тусласан уу?
Арга барил нь эмзэг бүлгийнхнийг нийгэм, эдийн засгийн хувьд чадавхижуулсан уу?
Especially poor population could profit from cheap communal pastures and thus afford keeping livestock.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
It can be assumed that this somehow logical solution of herding for settled people (not like in other Central Asian countries) emerged as a part of self-sufficient strategies during USSR. Similar herding patterns might though have existed already before USSR, according to local experts.
Газар ашиглагчид ГТМ хэрэгжүүлэх болсон үндсэн шалтгаан
-
үйлдвэрлэл нэмэгдсэн
-
Ашиг нэмэгдсэн (боломж), зардал-үр ашгийн харьцаа сайжирсан
-
Газрын доройтол буурсан
-
Гамшигийн эрсдэл буурсан
-
Ажлын ачаалал бууруулсан
-
төлбөр / татаас
-
дүрэм журам (торгууль) / сахиулах
-
нэр хүнд, нийгмийн дарамт / нийгмийн холбоо
-
Сүлжээ/ бүлэг төсөл/ хөдөлгөөнд гишүүнээр элсүүлэх
-
Байгаль орчны ухамсар
-
зан заншил, ёс суртахуун
-
ГТМ-ийн мэдлэг, туршлага дээшилсэн
-
гоо зүйн сайжруулалт
-
зөрчилдөөнийг бууруулах
-
well-being and livelihoods improvement
Арга барилын хүрээнд хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагааны тогтвортой байдал
Газар ашиглагчид арга барилаар дамжуулан хэрэгжүүлсэн арга хэмжээг тогтвортой үргэлжлүүлж чадах уу (гадны дэмжлэггүйгээр)?
Дүгнэлт, сургамж
Давуу тал: газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор
-
This form of herding is not conflictive: all people can afford it and everyone contributes to it by sending an own family member for herding. And, if a herder loses a villager's animal, the villager knows that he will also be a herder and might lose an animal, too. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The institutions - be it elders or the land committee - must implement the technology.)
Давуу тал: эмхэтгэгч эсвэл бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн бодлоор
-
Common herding has a strong social component as it makes herders cooperate in order to maintain reputation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Projects in Muminabad proposed by the village with a professional herder elected in a village meeting )
Сул тал/ дутагдал / эрсдэл: газар ашиглагчийн бодлоордаван туулах боломжууд
-
The dependance upon children rather hinders the implementation of SLM, according to some land users. Children prefer to play rather than to respect rules about herding, says for example a teacher. And he adds that also adults do not always respect the established rules and that nobody controls effective implementation of the technology.
It is difficult to find adult herders. One village - Chujamar - decided to engage a professional herder, who would lead the cows to the pastures separately. Because cows cannot be lead only by children like little animals, according to the chief of that village. The villagers pay around 2$ per cow and season for herding.
Сул тал/ дутагдал / эрсдэл: эмхэтгэгч эсвэл бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн бодлоордаван туулах боломжууд
-
Land users mention that implementation is difficult with herders (often children) that lack the necessary knowledge to implement SLM.
It is difficult to abolish child labour. But, by completing the herders' team with at least one professional, paid herder, progress in SLM would be possible perhaps. And making pastures a subject in school might help to araise awareness about SLM.
Суурь мэдээлэлүүд
Баримтжуулсан огноо: 23 2-р сар 2010
Сүүлийн шинэчлэл: 05 7-р сар 2017
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн
-
Christian Wirz (christian.wirz@students.unibe.ch) - ГТМ мэргэжилтэн
WOCAT мэдээллийн сан дахь бүрэн тодорхойлолт
Баримтжуулалтыг зохион байгуулсан
Байгууллага
- CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Швейцар
Төсөл






