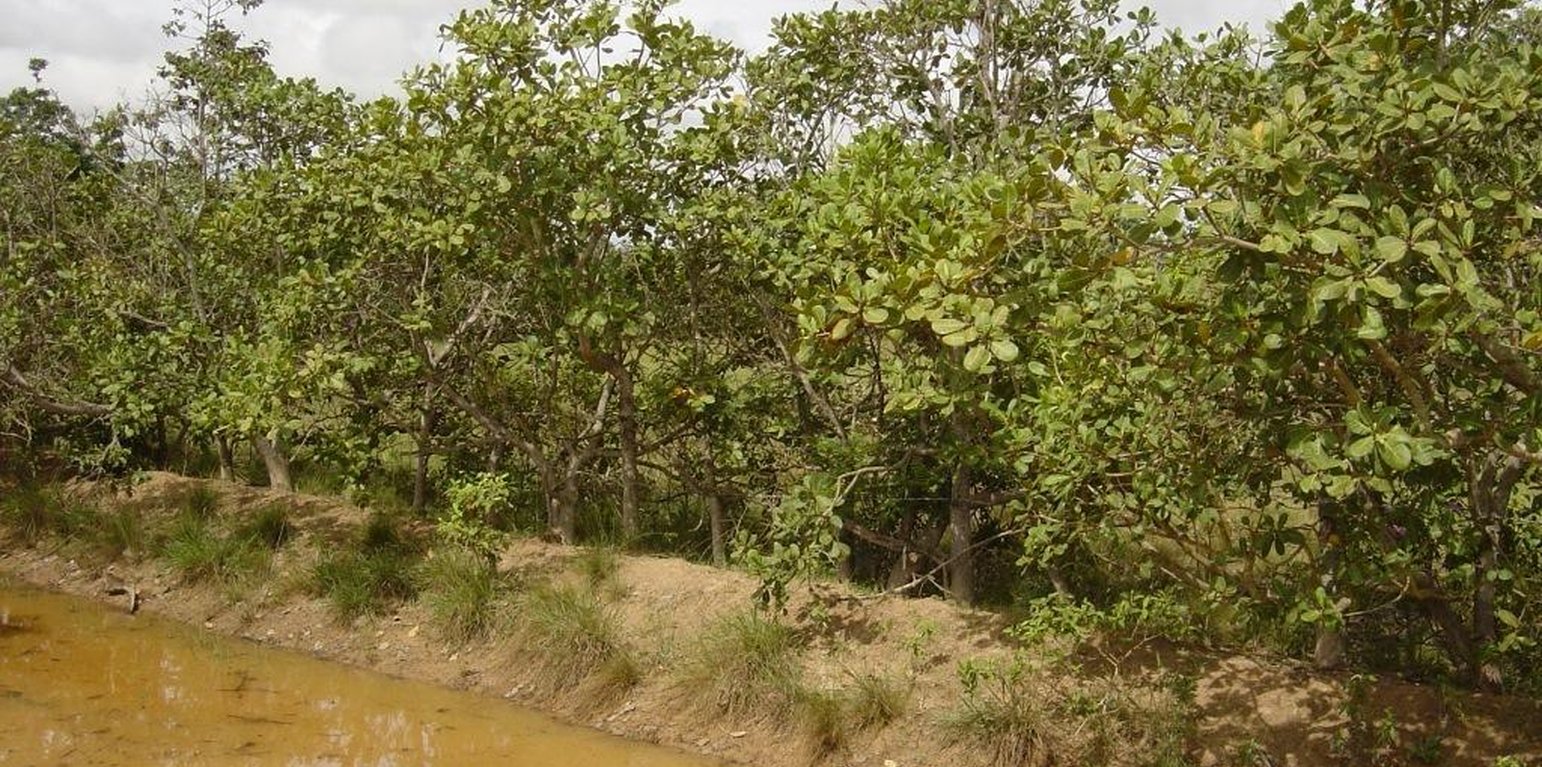




Cashews (Anacardium occidentale) are fast growing, waterlogging tolerant tropical trees that can be used as living fences. The cashews act as fence posts, and are reinforced with bamboo poles and/or barbed wire. The living fences are used to either fence cattle into fields or fence them off, usually around the house. The fenced areas can be planted during the dry season. Without fences, the cattle are free roaming and use to destroy the crops.
Besides fencing the cattle, the purposes of cashew living fences are the production of nuts and fruits, fuel, and soil enhancer. The nuts are sold, but there is no market for the fruits, thus they are fed to cattle or let to rot. The wood is used to cook or to produce charcoal; the ash is added to the compost. The leaves are gathered as well and added to the compost.
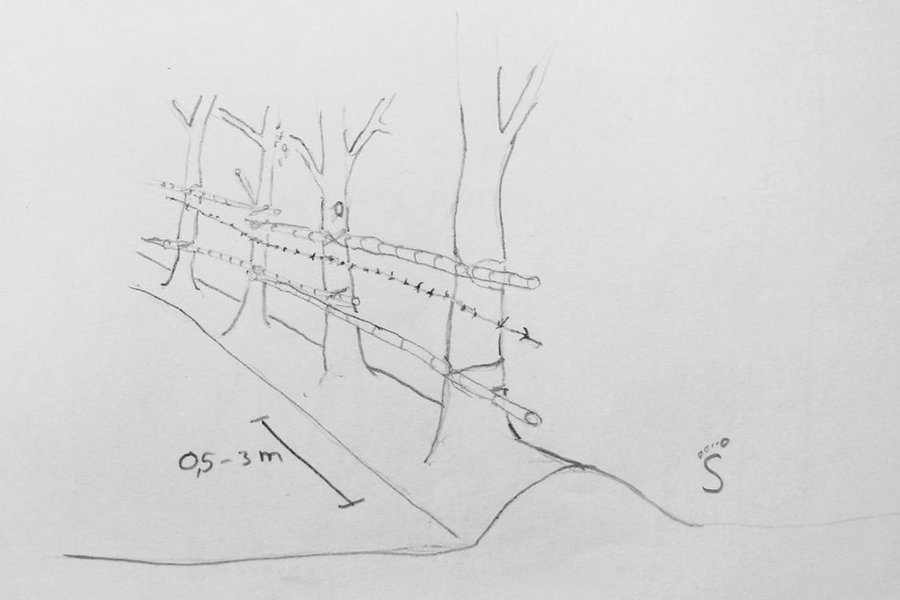
Although cashews can stand waterlogged conditions, they prefer a well-drained soil. Thus a small berm is built up on the emplacement of the fence, and sown with cashew seeds spaced from 0.5 to 3 m. Cashews grow faster when directly sown than when transplanted. The spacing varies according to the farmers’ purpose. If a higher production of nuts is intended, the spacing is wider; if the fence is more important, the plants are grown closer. Cattle do not eat the leaves and branches, thus do not need protection from grazing. One year after sowing the cashews, the trees are tall enough to act as fence posts and support bamboo pole as well as barbed wire. The bamboo is either gathered from the wild or grown in the fields and home gardens. The bamboo is fixed to the living posts with natural fibers/vines or old clothes, and has to be replaced every two to three years to withstand cattle.
The analysed area is flat (slope < 2%), with a tropical climate (dry season from November to May and wet season from June to October), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soil has a low fertility, contains little organic matter, and acidifies. The area has been deforested a long time ago, and the groundwater table is rather high (1-2 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season).
Due to climate change, farmers notice more erratic rainfalls, temperature rises and more recurrent droughts. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Cattle are usually grazing on the fields after the harvest, without much control. Thus the cattle grazes too often and too much on the same spot, leading to degradation.
The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge. Several NGOs are trying to re-establish the knowledge.
Байршил: Krang Liav, Rolea Pha-er, Kampong Chhnang, Камбодж
Дүн шинжилгээнд хамрагдсан технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын тоо:
Технологийн тархалт: газар дээр жигд тархсан (approx. < 0.1 км2 (10 га))
Тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт?:
Хэрэгжилтийн огноо: 10-50 жилийн өмнө
Нутагшууллын төрөл







| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ (тодорхойгүй) | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг (тодорхойгүй) | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | |||||
| labour | 1.0 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 100.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | |||||
| tools | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 | |
| barbed wire | 1.0 | 21.0 | 21.0 | 100.0 | |
| таримал материал | |||||
| seeds | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 51.5 | ||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 51.5 | ||||
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ (тодорхойгүй) | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг (тодорхойгүй) | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | |||||
| labour | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 | |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 3.0 | ||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 3.0 | ||||
Due to shading and root competition.
Used as fuel and charcoal.
Firewood production.
Quality, trough bioremediation of groundwater. Difficult to quantify.
If spaced, production of cashew nuts and apples.
Improved self-sufficiency on firewood.
Every additional income source/diversification increases the human well-being.
But increased evapotranspiration.
Nutrients are picked up from the groundwater, and put back into the cycle.
Leaves used for compost.
Wormcasts could be seen under the trees. Difficult to quantify.
Tree layer.
Bioremediation difficult to quantify.
Slowing down of wind speed.