Hedgerow technology
(Непал)
Ghase har Prabadhi (Main Contributor: Gyanbandhu Sharma, LI-BIRD)
Тодорхойлолт
A technology that uses hedgerows to help establish terraces on sloping land; farmers learn improved methods to manage a cultivation practice that stabilizes the soil, enhances food production, and adds to on-farm cash income.
Hedgerow technology provides options and opportunities for farmers working on sloping land. These hedgerows are a soil conservation measure but they also help to generate additional biomass and fodder and/or income for marginal farmers; in addition, they offer the added benefit of helping to balance the ecosystem and to address climate change by encouraging biodiversity. This improved version of a local technology makes maximum use of indigenous knowledge and adds to it by making available the latest scientific knowledge.
Purpose of the Technology: Farmers have traditionally selected plants for hedgerow cultivation based on practical considerations such as the availability of seeds and seedlings, how well seeds germinate, how well the plants grow and how well they can be coppiced, their branching habit, the amount of biomass they can produce, and how much cash the crop can generate. They made these choices without the benefit of any external input or scientific knowledge, relying solely on what they have been able to observe locally over the years. The participatory technology development process aims to help farmers by providing them with scientific input to augment their traditional knowledge on the selection, plan, and design of hedgerows. Over a very short time, the farmers learn to make good use of the new information and start enjoying the benefits that the improved agriculture yields in terms of social, economic, and environmental benefits.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The following steps outline how hedgerows can be established on sloping land:
• A participatory designing and planning process is used to choose which sloping lands will be cultivated and to select which hedgerow species are to be planted. Trained manpower is recruited with the help of farmers and other related stakeholders.
• The necessary materials such as A-frames, seeds, and seedlings are prepared.
• The technology is implemented in the field by trained manpower.
• The hedgerow seedlings are regularly maintained.
• The land users participate in periodic monitoring and evaluation of the technology. They report on progress and provide feedback.
Байршил
![]()
Байршил: Gorkha, Tanhun, Chitwan, Makwanpur, Nawalparasi, Dhading district, Непал
Дүн шинжилгээнд хамрагдсан технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын тоо:
Сонгосон байршлуудын газарзүйн холболт
Технологийн тархалт: газар дээр жигд тархсан (approx. 1-10 км2)
Тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт?:
Хэрэгжилтийн огноо:
Нутагшууллын төрөл
-
Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
-
Уламжлалт системийн хэсэг (> 50 жил)
-
Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
-
Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр

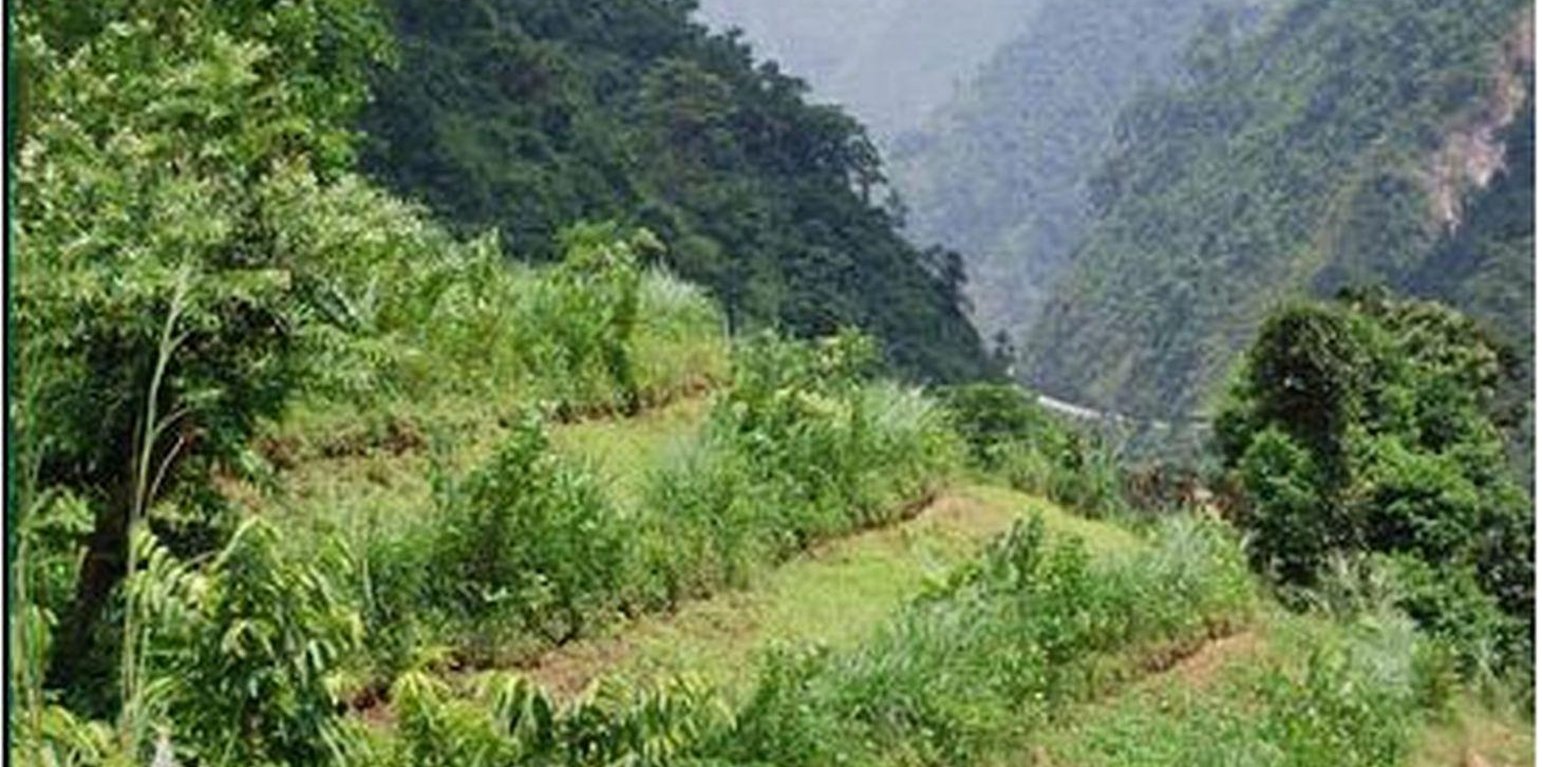
Initial stage of establishing hedgerow technology on sloping land (Gyanbandhu Sharma)
Үндсэн зорилго
-
үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
-
газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
-
экосистемийг хамгаалах
-
сав газрыг хамгаалах (усны эх/ голын адаг) - бусад технологитой хослуулах
-
биологийн төрөл зүйлийг хамгаалах / сайжруулах
-
гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
-
уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим байдал болон түүний нөлөөлөлд дасан зохицох
-
уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, түүний үр нөлөөг багасгах
-
үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
-
нийгэмд үзүүлэх үр нөлөөг бий болгох
Газар ашиглалт
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт: Тийм - ХАА-н ойжуулалт
-
Тариалангийн талбай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо: 2
-
Байгалийн ой / модтой газар
Усан хангамж
-
Байгалийн усалгаатай
-
Байгалийн/усалгаатай арга хосолсон
-
бүрэн усалгаатай
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотой зорилго
-
газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
-
Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
-
Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
-
газрын доройтолд дасан зохицох
-
холбогдолгүй
Доройтолын төрөл
-
хөрс усаар эвдрэх - Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
-
хөрсний химийн доройтол - Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
ГТМ арга хэмжээ
-
Ургамлын арга хэмжээ - V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг
-
Менежментийн арга хэмжээ - М1: Газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг өөрчлөх
Техникийн зураг
Техникийн үзүүлэлтүүд
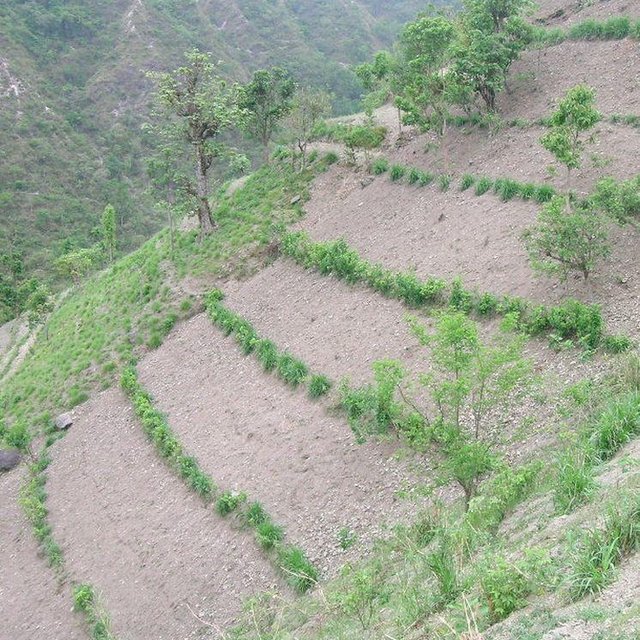
Hedgerow technology on sloping land; note that the hedgerows help to stabilize the land and to control soil erosion and runoff.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, Prevent Soil erosion
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
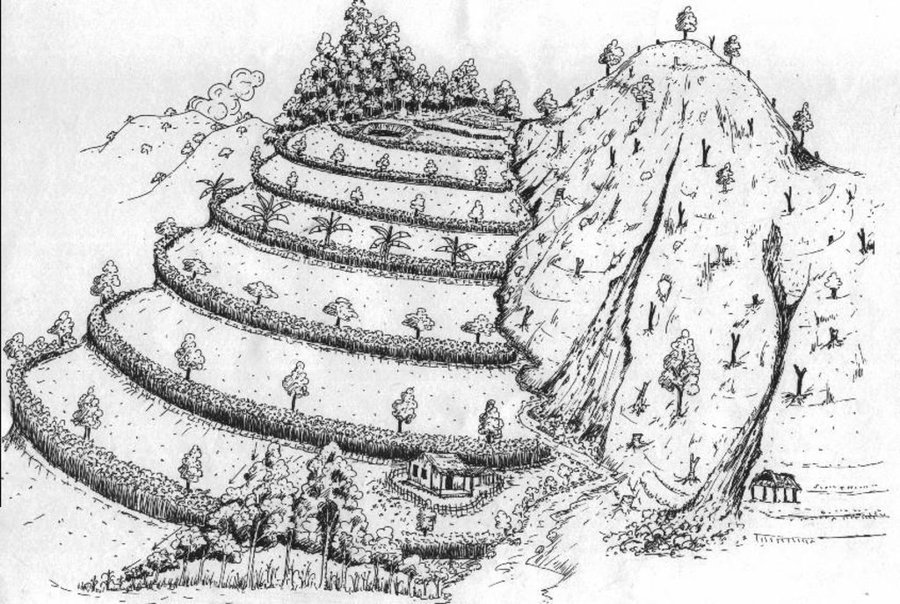
Author: Bir Bahadur Tamang
Бий болгох ба арчилах: үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
Материал, зардлын тооцоо
- Тооцоолсон зардлууд: Технологийн нэгж тус бүр (хэмжээ ба талбайн нэгж: ha)
- Зардал тооцоход ашигласан валют: Ам.доллар
- Валютын ханш (ам.дол): 1 ам.дол = тодорхойгүй
- Нэг өдрийн ажилчны хөдөлмөр хөлсний дундаж: 2.7
Зардалд нөлөөлөх хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйлс
The cost of implementing this technology is dependent on the gradient of the slope (and other geographical features), the local cost of the seeds or seedlings, and the availability of labour.
The technology has a low to average cost for implementation. Locally available seeds and seedlings and locally trained manpower and resources are valuable low-cost inputs for implementation. The technology has a higher likelihood of adoption in some social and physiographic areas, especially where land users can integrate their own expertise with scientific knowledge. Many factors play a role in determining whether the technology is effective and sustainable and whether farmers are willing to adopt it; these include that if the technology is demand driven, it is more likely to be adopted, and if land users can use inexpensive local resources they are more likely to try it.
All costs and amounts are rough estimates by the technicians and authors
Хэрэгжүүлж эхлэхэд шаардлагатай үйл ажиллагаа
-
The equipment that is needed for planting is collected and prepared; this can include such things as A-frames, spades, and sickles.• The hillside where the technology is to be implemented is first cleaned and groomed to make way for the new hedgerows.• Contour lines are demarcated.• The seeds and/or seedlings are planted along the contour lines. (Хугацаа / давтамж: None)
Бий болгоход шаардагдах материал ба зардал (per ha)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл |
Хэмжих нэгж |
Тоо хэмжээ |
Нэгжийн үнэ (Ам.доллар) |
Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг (Ам.доллар) |
Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % |
|
Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт
|
| Prepare and plant along the contour lines |
persons/day/ha |
10.0 |
2.7 |
27.0 |
100.0 |
|
Тоног төхөөрөмж
|
| Tools |
ha |
1.0 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
100.0 |
|
таримал материал
|
| Seedlings |
ha |
1.0 |
68.0 |
68.0 |
100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг |
127.0 |
|
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар |
127.0 |
|
Арчилгаа, урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
-
The hedgerows are weeded and cleaned to discourage unwantedplants and pests.• Enrichment planting• The hedgerows are pruned and the clippings are mulched.• Manuring (Хугацаа / давтамж: None)
Арчилгаа, урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах материал ба зардал (per ha)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл |
Хэмжих нэгж |
Тоо хэмжээ |
Нэгжийн үнэ (Ам.доллар) |
Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг (Ам.доллар) |
Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % |
|
Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт
|
| Maintenance of hedgerows |
persons/day/ha |
26.0 |
2.7 |
70.2 |
100.0 |
|
таримал материал
|
| Seedlings |
ha |
1.0 |
34.0 |
34.0 |
100.0 |
|
Бордоо ба биоцид
|
| Compost / manure |
ha |
1.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг |
124.2 |
|
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар |
124.2 |
|
Байгалийн нөхцөл
Жилийн дундаж хур тундас
-
< 250 мм
-
251-500 мм
-
501-750 мм
-
751-1,000 мм
-
1,001-1,500 мм
-
1,501-2,000 мм
-
2,001-3,000 мм
-
3,001-4,000 мм
-
> 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
-
чийглэг
-
чийглэг
-
хагас хуурай
-
хуурай
Уур амьсгалын үзүүлэлтүүд
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Налуу
-
хавтгай (0-2 %)
-
бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
-
дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
-
хэвгий (11-15 %)
-
налуу (16-30 %)
-
их налуу (31-60 % )
-
эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр
-
тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
-
нуруу
-
уулын энгэр
-
дов толгод
-
бэл
-
хөндий
Далайн түвшнөөс дээшхи өндөр
-
0-100 д.т.д. м.
-
101-500 д.т.д. м.
-
501-1,000 д.т.д м.
-
1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
-
1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
-
2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
-
2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
-
3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
-
> 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологийг нэвтрүүлсэн
-
гүдгэр нөхцөл
-
хотгор нөхцөл
-
хамааралгүй
Хөрсний зузаан
-
маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
-
нимгэн (21-50 см)
-
дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
-
зузаан (81-120 cм)
-
маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс)
-
бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
-
дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
-
нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Хөрсний бүтэц (гадаргаас доош > 20 см)
-
бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
-
дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
-
нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсний ялзмагийн хэмжээ
-
их (>3 %)
-
дунд (1-3 % )
-
бага (<1 % )
Гүний усны түвшин
-
гадаргаас
-
< 5 м
-
5-50 м
-
> 50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж
-
хангалттай
-
сайн
-
дунд зэрэг
-
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (боловсруулаагүй)
-
сайн чанарын ундны ус
-
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
-
зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
-
ашиглах боломжгүй
Усны чанар гэж:
Усны давсжилтын түвшинийг орчны асуудал гэж тооцдог уу?
Үерийн давтамж
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлолт
Зах зээлийн чиг хандлага
-
амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
-
холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
-
худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Орлогын бусад эх үүсвэр
-
Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
-
Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
-
Нийт орлогын 50 %-иас дээш
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин
-
нэн ядуу
-
ядуу
-
дундаж
-
чинээлэг
-
маш чинээлэг
Механикжуулалтын түвшин
-
гар ажил
-
ердийн хөсөг
-
механикжсан / мотортой
Суурин эсвэл нүүдлийн
-
Суурьшмал
-
Хагас-нүүдэлийн
-
Нүүдэлийн
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлгүүд
-
Хувь хүн / өрх
-
бүлэг / олон нийтийн
-
хоршоо
-
ажилтан (компани, засгийн газар)
Нас
-
хүүхэд
-
залуус
-
дунд нас
-
ахимаг нас
Өрхийн зориулалтаар ашиглах газрын талбай
-
< 0.5 га
-
0.5-1 га
-
1-2 га
-
2-5 га
-
5-15 га
-
15-50 га
-
50-100 га
-
100-500 га
-
500-1,000 га
-
1,000-10,000 га
-
> 10,000 га
Хэмжээ
-
бага-хэмжээний
-
дунд-хэмжээний
-
том-хэмжээний
Газар өмчлөл
-
төрийн
-
компани
-
нэгдлийн/ тосгон
-
бүлэг
-
хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
-
хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх
-
нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
-
нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
-
түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
-
хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх
-
нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
-
нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
-
түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
-
хувь хүн
Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр)
Нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
бүтээгдэхүүний олон янз хэлбэр
тариалангийн усалгааны усны хэрэгцээ
Reduce need for external agriculture inputs
орлогын олон янз эх үүсвэр
very steep slope (>30 degree)
time to become well established
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Empowerment of the community
livelihood and human well-being
The hedgerows provide fodder and forage for animals; selling or bartering fodder helps to diversify food sources for humans and can also be a significant source of income.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
газрын дээрхи / доорхи карбон
хортон шавж/өвчний хяналт
competition for water, sunlight and nutrients
Зэргэлдээ талбайд илрэх нөлөө
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
буферлэх/шүүх чадавхи (хөрс, ургамал, ус намгархаг газар)
Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад олсон ашиг
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал
Урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад олсон ашиг
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал
Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Нутагшуулах ба дасан зохицох
Тухайн нутаг дэвсгэрт Технологийг нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын хувь
-
жишээ/ туршилт
-
1-10 %
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
Технологийг нэвтрүүлсэн бүх хүмүүсийн хэд нь материаллаг урамшуулал авалгүйгээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
Хамрагдсан өрх ба/эсвэл газар нутгийн хэмжээ
450 households in an area of 1- 10 sq km (10 - 50 persons per sq km)
Технологи нь өөрчлөгдөж буй нөхцөл байдалд дасан зохицохын тулд өөрчлөгдсөн үү?
Ямар өөрчлөлтөнд эмзэг вэ?
-
уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим үзэгдэл
-
зах зээлийн өөрчлөлт
-
ажил хөдөлмөр эрхлэх боломж (ж.нь шилжих хөдөлгөөний улмаас)
Дүгнэлт, сургамж
Давуу тал: газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор
Давуу тал: эмхэтгэгч эсвэл бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн бодлоор
-
Effective control of soil erosion on sloping land
How can they be sustained / enhanced? This vegetative measure of planting along contour lines can be sustained in the long run by initially selecting species preferred by farmers and by continuing to maintain them
-
Improved soil fertility
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Hedgerows help to increase soil fertility because they trap water and sediment on the terraces; leguminous hedgerow plants fix nitrogen in the soil and when they are mulched their residues increase organic matter in the soil.
-
Quality fodder and forage production
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Hedgerows produce fodder and forage for livestock
-
Bioterracing
How can they be sustained / enhanced? When leguminous plants with deep roots are used in the hedgerows they help to anchor the edges and over time, as the soil accumulates, bioterraces are established.
-
High adoption potential
How can they be sustained / enhanced? This technology is simple to implement using only local resources and is assured of replication since it was demand driven
Сул тал/ дутагдал / эрсдэл: газар ашиглагчийн бодлоордаван туулах боломжууд
Сул тал/ дутагдал / эрсдэл: эмхэтгэгч эсвэл бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн бодлоордаван туулах боломжууд
-
Hedgerows are difficult to establish on steep slopes and in areas where the soil is dry and degraded
Increase moisture in the soil by mulching the hedges
-
Hedgerows take a long time to establish
Increase the amount of manure (compost, crop residue) added to the hedgerows and add more frequently. Increase the frequency of weeding and cleaning.
-
It is difficult to establish bio-terraces on steep land
Reduce the spacing between hedgerows and grow tree species. Remember that that this technology is not recommend for very steep slopes
-
High initial cost
Make maximum use of local resources and local labour
-
Hedgerows threatened by free grazing of animals
Control grazing in the area
Суурь мэдээлэлүүд
Хянагч
-
David Streiff
-
Alexandra Gavilano
Баримтжуулсан огноо: 11 8-р сар 2015
Сүүлийн шинэчлэл: 04 6-р сар 2019
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн
-
Shreedip Sigdel - ГТМ мэргэжилтэн
-
Gyan Bandhu Sharma - ГТМ мэргэжилтэн
WOCAT мэдээллийн сан дахь бүрэн тодорхойлолт
Баримтжуулалтыг зохион байгуулсан
Байгууллага
- ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Непал
- Local Initiatives for Biodiversity, Research, and Development (LI-BIRD) - Непал
Төсөл
Гол сурвалж баримт сэлт
-
Factors responsible for acceptance or rejection of SALT and other technological options suitable for shifting and sloping land cultivation areas, Technical Paper submitted to Hill Agriculture Research Project (HARP), Regmi, BR; et al. (2004),:
-
A resource book: Integrated hedgerow technology (in Nepali), Sharma, G; Regmi, BR; Tamang, BB; Shrestha, PK (2008):
-
Manual on contour hedgerow inter-cropping technology, ICIMOD, 1999:
-
Impact of contour hedgerows: A case study, Focus on Godavari No 3. Kathmandu, Nepal: ICIMOD, Ya, T; Murray, AB (eds) (2004):











