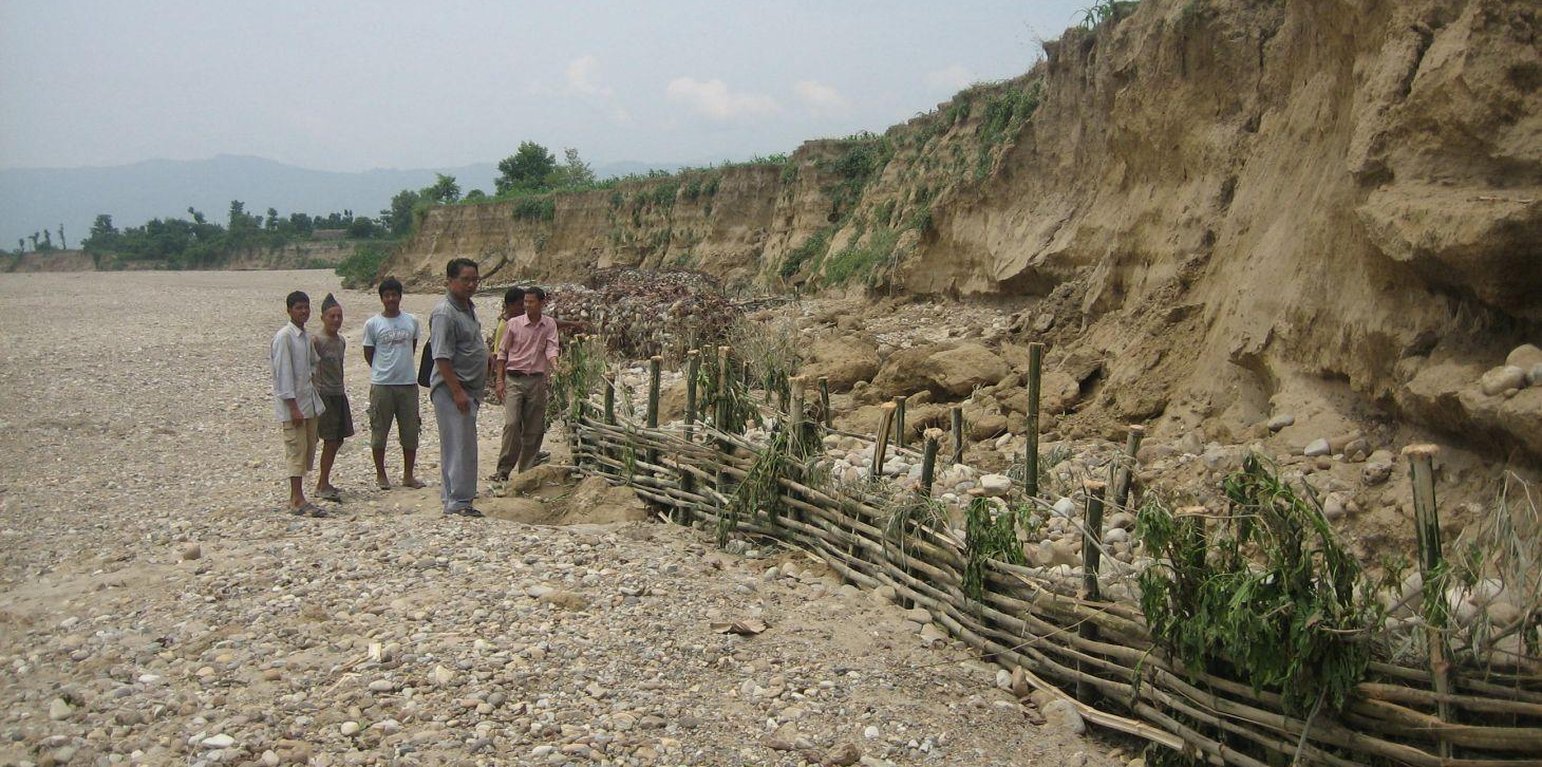




Riverbank cutting occurs naturally along the rivers that run along the foothills of the Chure (Siwalik) range in Nepal when the stream collides with the river bank or the bank is eroded by water coming from agricultural land above the affected area. When riverbank cutting occurs, it leaves behind an eroded area shaped like a small cliff. This erosion takes place naturally and is difficult to stop because the site is devoid of natural vegetation. It is important to undertake conservation measures because when the riverbank is eroded it damages agricultural land and decreases soil fertility. When the productivity of the land is decreased it affects the lives and livelihoods of nearby communities most of whom are subsistence farmers.
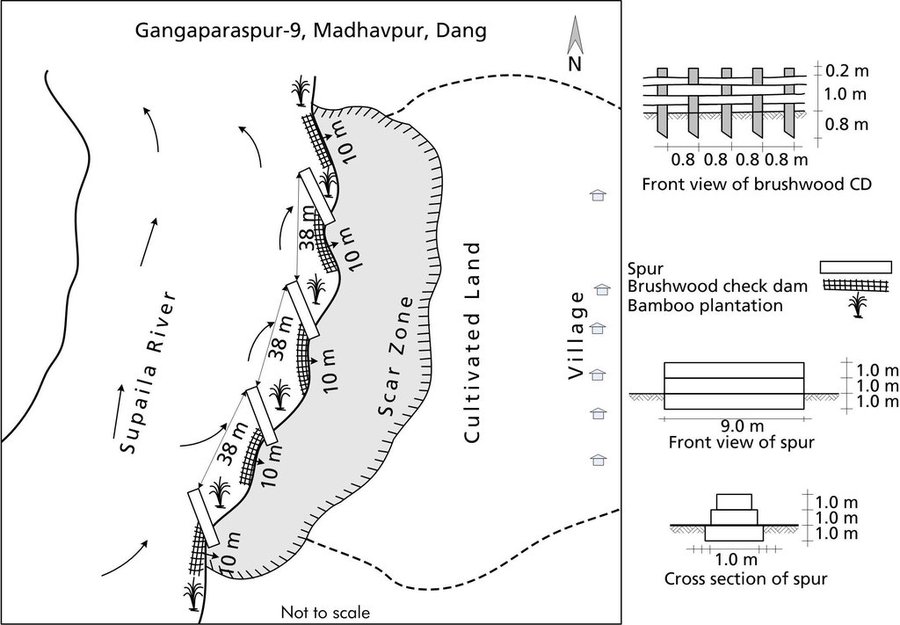
Purpose of the Technology: Communities have developed local measures to help protect the riverbanks and to prevent further erosion and cutting. This technology uses both structural and vegetative measures to help control the erosion and protect both agricultural land and settlement areas from flooding. Check dams are placed at intervals to divert water, additional support is provided by spurs. Bamboo rhizomes are planted between them and Napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum) is planted at the back of the structures so that as the plants grow their roots help to anchor the structure. The washed out areas can be used to generate some income by planting them with greenery and fruit trees. The site needs to be monitored annually and where necessary the structures either need to be repaired or supplemented by building additional structures.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: This technology is a blend of local skills and expertise with some external technical input. The key features of the technology are as follow:
• It uses locally available construction materials, tools, equipment, and vegetation.
• It is easy to replicate.
• It is affordable for local people.
• It is environmentally friendly.
A demonstration plot was established by the District Soil Conservation Office (DSCO) in Dang, but the technology needs to be replicated in other areas with action research and experience
Байршил: Gobardiha-9, Madhabpur, Dang District,, Непал
Дүн шинжилгээнд хамрагдсан технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын тоо:
Технологийн тархалт: тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт?:
Хэрэгжилтийн огноо:
Нутагшууллын төрөл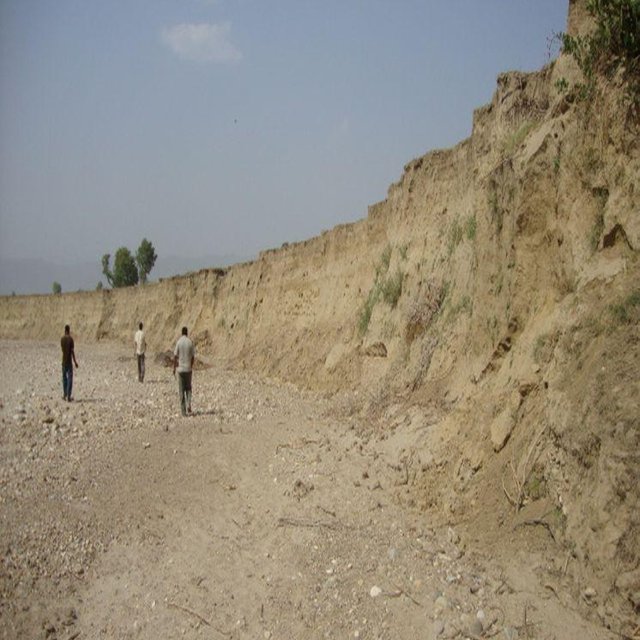





| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ (Ам.доллар) | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг (Ам.доллар) | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | |||||
| Construction of rivervbank protection | ha | 1.0 | 892.0 | 892.0 | 51.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 21.0 | 21.0 | 51.0 |
| таримал материал | |||||
| Napier grass, bamboo seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | |||||
| Stone | ha | 1.0 | 1281.0 | 1281.0 | 51.0 |
| Bamboo poles | ha | 1.0 | 274.0 | 274.0 | 51.0 |
| Wire for gabion box | ha | 1.0 | 1644.0 | 1644.0 | 51.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 4'126.0 | ||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 4'126.0 | ||||
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ (Ам.доллар) | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг (Ам.доллар) | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | |||||
| Fortify and reapir check dams | ha | 1.0 | 52.0 | 52.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | |||||
| Napier grass, bamboo seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | |||||
| Bamboo poles for replacing | ha | 1.0 | 123.0 | 123.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 182.0 | ||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 182.0 | ||||
Agricultural land is conserved and production is increased