Index Based Livestock Insurance
(Кени)
IBLI
Тодорхойлолт
Index-Based Livestock Insurance (IBLI) is a product that was designed to help protect pastoralists and their livestock against the effects of prolonged forage scarcity. IBLI triggers payment to pastoralists when the forage situation deteriorates to levels considered to be severe, as compared to historical conditions over time.
In the event of severe seasonal drought, forage and grazing resources are depleted and livestock may die because of starvation. Index Based Livestock Insurance (IBLI) is the technology applied in the provision of forage based livestock (asset) protection insurance. IBLI uses Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), a satellite-derived indicator of the amount and vigor of vegetation, based on the observed level of photosynthetic activity (Tucker et al., 2005). NDVI is derived from 10-day composites of 250m filtered eMODIS processed by the United States’ National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and transformed by The Earth Resources Observation Systems (EROS) Data Center (EDC) of the US Geological Survey (USGS). NDVI data from the AQUA satellite platform are available from July 2002 to present at https://lta.cr.usgs.gov/emodis.
In the case of IBLI, the index is a deviation of cumulative forage availability (ZCumNDVI) in the insured season. It measures forage conditions over a defined time period and compares the observed NDVI over a particular season, with the observed NDVI over a given historical period (e.g. 15 years). A set threshold below which payouts must be made is called the trigger level. Therefore, when the forage situation in a given season is worse than the 20th worst season in the last 15 years, a payout is triggered. In other words, IBLI will compensate if the forage conditions fall below the worst 20th percentile of seasonal pasture levels cumulated over the historical drought seasons in the past 15 years. IBLI therefore uses the satellite-based vegetation index to measure forage availability and to trigger timely payouts to pastoralists based on the costs of providing supplementary feeds to the animals for the specific season that a drought is triggered.
For precision and proper administration each insured county is broken down into smaller units of insurance which are referred to as Unit Areas of Insurance (UAIs). Each UAI represents a geographical area whose forage availability index data are aggregated as one unit for insurance purposes. The identification of the geographic areas that constitute UAIs is a key step in IBLI contract design because the use of average NDVI over insurable units is based on the premise that drought is a covariate shock and that pastoral communities affected in a particular area are deemed to suffer in equal measure.Thus, for accuracy and acceptability, the index should be tightly correlated with forage scarcity and reflect relative conditions on the ground. Also forage access should be relatively homogeneous for herders residing in the same insurable unit. The process of demarcating UAIs is known as clustering. It is done through a combination of active participatory community engagement and scientific methods .
Insured pastoralists are not always paid when there is drought. They are only paid when drought is so severe that the amount of forage falls below the strike level. Insured pastoralists will not receive payments if the forage availability is more than the strike level. This is an annual policy which covers forage availability as measured by satellite Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) in up to 2 rainy seasons as per the bimodal rain patterns in Kenya. Pastoralists who do not hold insurance contracts are not covered by under, and therefore do not receive payments, even if they live in the same UAIs as the ones who have insured their livestock.
Байршил
Байршил: Кени
Дүн шинжилгээнд хамрагдсан технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын тоо: 2-10 байршилд
Сонгосон байршлуудын газарзүйн холболт
-
35.63652, 3.05989
-
37.96562, 2.31365
-
40.08598, 1.72076
-
39.00932, 3.47669
-
41.72294, 3.80562
-
39.67949, -0.49822
-
37.59508, 0.33855
Технологийн тархалт: газар дээр жигд тархсан (approx. 100-1,000 км2)
Тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт?:
Хэрэгжилтийн огноо: <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
Нутагшууллын төрөл
-
Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
-
Уламжлалт системийн хэсэг (> 50 жил)
-
Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
-
Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр

-

-
Үндсэн зорилго
-
үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
-
газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
-
экосистемийг хамгаалах
-
сав газрыг хамгаалах (усны эх/ голын адаг) - бусад технологитой хослуулах
-
биологийн төрөл зүйлийг хамгаалах / сайжруулах
-
гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
-
уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим байдал болон түүний нөлөөлөлд дасан зохицох
-
уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, түүний үр нөлөөг багасгах
-
үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
-
нийгэмд үзүүлэх үр нөлөөг бий болгох
Газар ашиглалт
-
Бэлчээрийн газар
- Нүүдлийн мал аж ахуй
- Хагас нүүдлийн бэлчээрийн аж ахуй
Амьтдын төрөл зүйл: ямаа, тэмээ, хонь, cattle
Усан хангамж
-
Байгалийн усалгаатай
-
Байгалийн/усалгаатай арга хосолсон
-
бүрэн усалгаатай
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотой зорилго
-
газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
-
Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
-
Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
-
газрын доройтолд дасан зохицох
-
холбогдолгүй
ГТМ бүлэг
-
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй ба бэлчээрийн газрын менежмент
Техникийн зураг
Техникийн үзүүлэлтүүд
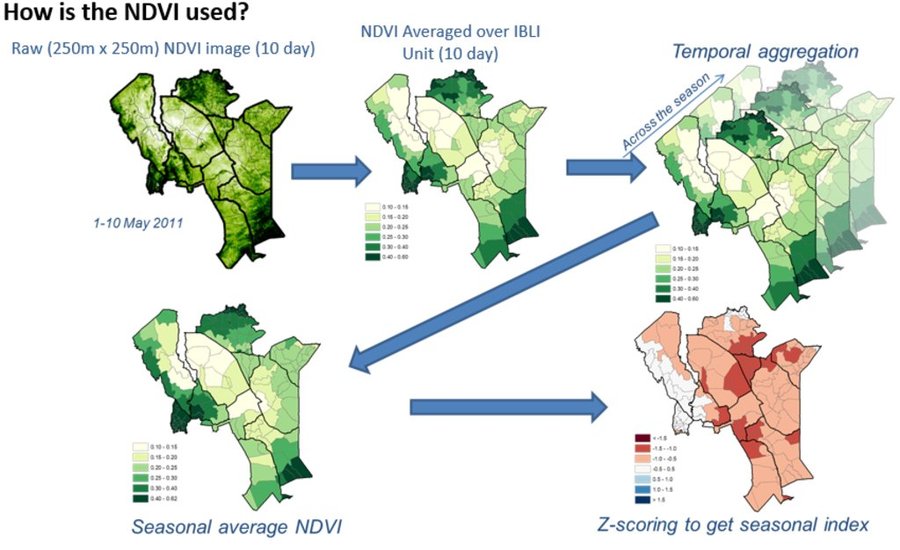
Picture 1 &2: Monthly NDVI for each insured unit in a month is derived by averaging the 10-day NDVI values for each Insured Unit over the three 10-days periods in each month, where the 10-day NDVI value for each Insured Unit is derived by averaging the pixel-level NDVI of all the pixels that fall within the insured unit boundary.
Picture 3: An accumulation of monthly NDVI over the critical months of each season starting from the beginning of the season (March for LRLD and October for SRSD).
Picture 4: There is a representation of a cumulation of monthly NDVI (CumNDVI) which represents the evolution of green vegetation and can be used as a proxy of the green biomass that has developed, and as such a proxy of the available forage across the season.
Picture 5: Deviation of Cumulative NDVI from normal conditions of the particular season and insured unit (ZCumNDVI) - is derived by
subtracting CumNDVI derived for each season and each insured unit by the long-term historical average value and dividing by long-term historical standard deviation of the particular season (SRSD or LRLD) in each
insured unit. ZCumNDVI thus measures the deviation from the historical mean,
expressed as a standard deviation. A positive ZCumNDVI value therefore indicates above normal vegetation cover while negative ZNDVI value indicates below normal vegetation. The purpose of this transformation is to provide an indicator that expresses current forage conditions in comparison to average forage conditions for each specific insurance unit
at the prescribed period within the season.
NOTE: The delineations used in this figure are just for purposes of illustration, assuming Kenya as an entire unit. However, IBLI used smaller delineated units which can be seen in the lines with lighter shade within the map.
Бий болгох ба арчилах: үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
Материал, зардлын тооцоо
- Тооцоолсон зардлууд:
- Зардал тооцоход ашигласан валют: тодорхойгүй
- Валютын ханш (ам.дол): 1 ам.дол = тодорхойгүй
- Нэг өдрийн ажилчны хөдөлмөр хөлсний дундаж: тодорхойгүй
Зардалд нөлөөлөх хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйлс
тодорхойгүй
Хэрэгжүүлж эхлэхэд шаардлагатай үйл ажиллагаа
n.a.
Арчилгаа, урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
n.a.
Байгалийн нөхцөл
Жилийн дундаж хур тундас
-
< 250 мм
-
251-500 мм
-
501-750 мм
-
751-1,000 мм
-
1,001-1,500 мм
-
1,501-2,000 мм
-
2,001-3,000 мм
-
3,001-4,000 мм
-
> 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
-
чийглэг
-
чийглэг
-
хагас хуурай
-
хуурай
Уур амьсгалын үзүүлэлтүүд
Цаг уурын станцын нэр: Kenya Meteorological Department
Налуу
-
хавтгай (0-2 %)
-
бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
-
дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
-
хэвгий (11-15 %)
-
налуу (16-30 %)
-
их налуу (31-60 % )
-
эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр
-
тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
-
нуруу
-
уулын энгэр
-
дов толгод
-
бэл
-
хөндий
Далайн түвшнөөс дээшхи өндөр
-
0-100 д.т.д. м.
-
101-500 д.т.д. м.
-
501-1,000 д.т.д м.
-
1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
-
1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
-
2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
-
2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
-
3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
-
> 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологийг нэвтрүүлсэн
-
гүдгэр нөхцөл
-
хотгор нөхцөл
-
хамааралгүй
Хөрсний зузаан
-
маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
-
нимгэн (21-50 см)
-
дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
-
зузаан (81-120 cм)
-
маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс)
-
бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
-
дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
-
нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Хөрсний бүтэц (гадаргаас доош > 20 см)
-
бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
-
дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
-
нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсний ялзмагийн хэмжээ
-
их (>3 %)
-
дунд (1-3 % )
-
бага (<1 % )
Гүний усны түвшин
-
гадаргаас
-
< 5 м
-
5-50 м
-
> 50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж
-
хангалттай
-
сайн
-
дунд зэрэг
-
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (боловсруулаагүй)
-
сайн чанарын ундны ус
-
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
-
зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
-
ашиглах боломжгүй
Усны чанар гэж:
Усны давсжилтын түвшинийг орчны асуудал гэж тооцдог уу?
Үерийн давтамж
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлолт
Зах зээлийн чиг хандлага
-
амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
-
холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
-
худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Орлогын бусад эх үүсвэр
-
Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
-
Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
-
Нийт орлогын 50 %-иас дээш
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин
-
нэн ядуу
-
ядуу
-
дундаж
-
чинээлэг
-
маш чинээлэг
Механикжуулалтын түвшин
-
гар ажил
-
ердийн хөсөг
-
механикжсан / мотортой
Суурин эсвэл нүүдлийн
-
Суурьшмал
-
Хагас-нүүдэлийн
-
Нүүдэлийн
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлгүүд
-
Хувь хүн / өрх
-
бүлэг / олон нийтийн
-
хоршоо
-
ажилтан (компани, засгийн газар)
Нас
-
хүүхэд
-
залуус
-
дунд нас
-
ахимаг нас
Өрхийн зориулалтаар ашиглах газрын талбай
-
< 0.5 га
-
0.5-1 га
-
1-2 га
-
2-5 га
-
5-15 га
-
15-50 га
-
50-100 га
-
100-500 га
-
500-1,000 га
-
1,000-10,000 га
-
> 10,000 га
Хэмжээ
-
бага-хэмжээний
-
дунд-хэмжээний
-
том-хэмжээний
Газар өмчлөл
-
төрийн
-
компани
-
нэгдлийн/ тосгон
-
бүлэг
-
хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
-
хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх
-
нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
-
нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
-
түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
-
хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх
-
нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
-
нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
-
түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
-
хувь хүн
Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр)
Нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
нийгэм, эдийн засгийн эмзэг бүлгүүдийн нөхцөл байдал (жендер, нас, төлөв, яс үндэс г.м.)
Зэргэлдээ талбайд илрэх нөлөө
Reduction of livestock mortality as a result of forage scarcity due to drought.
Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад олсон ашиг
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал
Урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад олсон ашиг
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал
Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
жилийн дундаж хур тундас Бууралт
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Нутагшуулах ба дасан зохицох
Тухайн нутаг дэвсгэрт Технологийг нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын хувь
-
жишээ/ туршилт
-
1-10 %
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
Технологийг нэвтрүүлсэн бүх хүмүүсийн хэд нь материаллаг урамшуулал авалгүйгээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
Хамрагдсан өрх ба/эсвэл газар нутгийн хэмжээ
over 25,000 households
Технологи нь өөрчлөгдөж буй нөхцөл байдалд дасан зохицохын тулд өөрчлөгдсөн үү?
Ямар өөрчлөлтөнд эмзэг вэ?
-
уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим үзэгдэл
-
зах зээлийн өөрчлөлт
-
ажил хөдөлмөр эрхлэх боломж (ж.нь шилжих хөдөлгөөний улмаас)
Дүгнэлт, сургамж
Давуу тал: газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор
-
The use NDVI for forage monitoring in provision of IBLI eliminates the high costs of loss verification which would otherwise be expensive and consuming in the case of vast and remote ASALs of Kenya.
Давуу тал: эмхэтгэгч эсвэл бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн бодлоор
-
IBLI contract design is based on robust scientific design which is easily verifiable hence boosting trust in the product.
Сул тал/ дутагдал / эрсдэл: газар ашиглагчийн бодлоордаван туулах боломжууд
-
A key concern of index-insurance products is that there might occur variances in perceived loss versus the actual payouts (basis risk)
Proper contract design should be backed with ground truthing efforts together with awareness creation.
Сул тал/ дутагдал / эрсдэл: эмхэтгэгч эсвэл бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн бодлоордаван туулах боломжууд
-
Basis risk is a weakness with IBLI as they could arise differences in perceived level of forage scarcity by the clients,
vis a vis the index trigger level indicated by the NDVI data. Increased precision in contract design alongside proper capacity and awareness creation to the pastoralists can help mitigate this challenge.
Суурь мэдээлэлүүд
Хянагч
-
Alexandra Gavilano
-
Rima Mekdaschi Studer
-
Donia Mühlematter
-
Hanspeter Liniger
-
Joana Eichenberger
Баримтжуулсан огноо: 24 1-р сар 2018
Сүүлийн шинэчлэл: 02 11-р сар 2021
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн
-
Duncan Collins Khalai - ГТМ мэргэжилтэн
WOCAT мэдээллийн сан дахь бүрэн тодорхойлолт
Баримтжуулалтыг зохион байгуулсан
Байгууллага
- ILRI International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) - Кени
Төсөл
- Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)
- Index Based Livestock Insurance, Kenya (IBLI)
Гол сурвалж баримт сэлт
-
Chelang'a et. al 2017:
-
Tucker et al., 2005:
Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос